In this example we will create a simple CI system that uses Jenkins to build our example application.
- Operator works by checking a repo for specific directories in it, more info here https://jenkinsci.github.io/kubernetes-operator/docs/getting-started/latest/configuration/, but the main idea is that you have to prepare pipelines and job definition in your GitHub repository using the following structure:
cicd/
├── jobs
│ └── build.jenkins
└── pipelines
└── build.jenkins
- In this repository I am going to set this up. If you are forking, then just update
cicd/jobs/build.jenkinsandcicd/pipelines/build.jenkinswith your own fork names.
Prerequisites:
- Helm
- Webhook Relay account
- Kubernetes
We begin by installing Jenkins operator:
helm repo add jenkins https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator/master/chart
helm repo update
helm install jenkins/jenkins-operator
Official docs can be found here: https://jenkinsci.github.io/kubernetes-operator/docs/installation/.
Forward traffic to Jenkins:
kubectl --namespace jenkins port-forward jenkins-example 8080:8080
Lookup username/password (if you have renamed CR, then your secret name will also have a different name):
kubectl --namespace jenkins get secret jenkins-operator-credentials-example -o 'jsonpath={.data.user}' | base64 -d
jenkins-operator
kubectl --namespace jenkins get secret jenkins-operator-credentials-example -o 'jsonpath={.data.password}' | base64 -d
oHlaSPMslZr3w
And now you can open your browser:
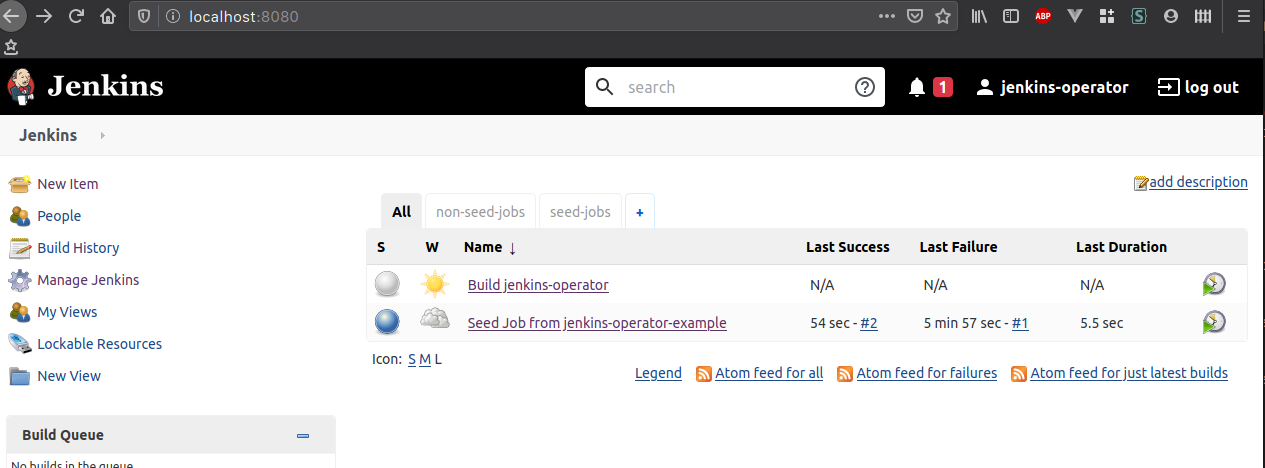
Once you login, you should be able to see a Seed job that has completed and a new "Build jenkins-oeprator" job:
Retrieve your access token key & secret pair from https://my.webhookrelay.com/tokens and set it as an env variable:
export RELAY_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxx
export RELAY_SECRET=xxxxx
Add Webhook Relay Operator Helm repository and install it:
helm repo add webhookrelay https://charts.webhookrelay.com
helm repo update
helm upgrade --install webhookrelay-operator --namespace=jenkins webhookrelay/webhookrelay-operator \
--set credentials.key=$RELAY_KEY --set credentials.secret=$RELAY_SECRETNow, let's check Jenkins service address so we can configure our webhook forwarding CR:
kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
jenkins-operator-http-example ClusterIP 10.102.22.176 <none> 8080/TCP 37m
jenkins-operator-metrics ClusterIP 10.100.220.49 <none> 8383/TCP,8686/TCP 97m
jenkins-operator-slave-example ClusterIP 10.96.229.141 <none> 50000/TCP 37m
Check out the CR in webhookrelay_cr.yaml file and if needed update destination address. Once you are happy with it, let's create it:
kubectl apply -f webhookrelay_cr.yaml
And once it's created you should be able to view the CR status:
$ kubectl describe webhookrelayforwards.forward.webhookrelay.com example-forward
Name: example-forward
Namespace: jenkins
Labels: <none>
Annotations: API Version: forward.webhookrelay.com/v1
Kind: WebhookRelayForward
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2020-07-01T23:33:12Z
Generation: 1
Resource Version: 106773
Self Link: /apis/forward.webhookrelay.com/v1/namespaces/jenkins/webhookrelayforwards/example-forward
UID: d56de305-240f-4222-8f89-0dfee70fa804
Spec:
Buckets:
Inputs:
Description: Endpoint for GitHub
Name: public-endpoint
Response Body: OK
Response Status Code: 200
Name: jenkins-whr-operator
Outputs:
Destination: http://jenkins-operator-http-example:8080/github-webhook/
Name: jenkins
Status:
Agent Status: Running
Public Endpoints:
https://k0yv9ip5sxxp55ncsu936k.hooks.webhookrelay.com
Ready: true
Routing Status: Configured
Events: <none>
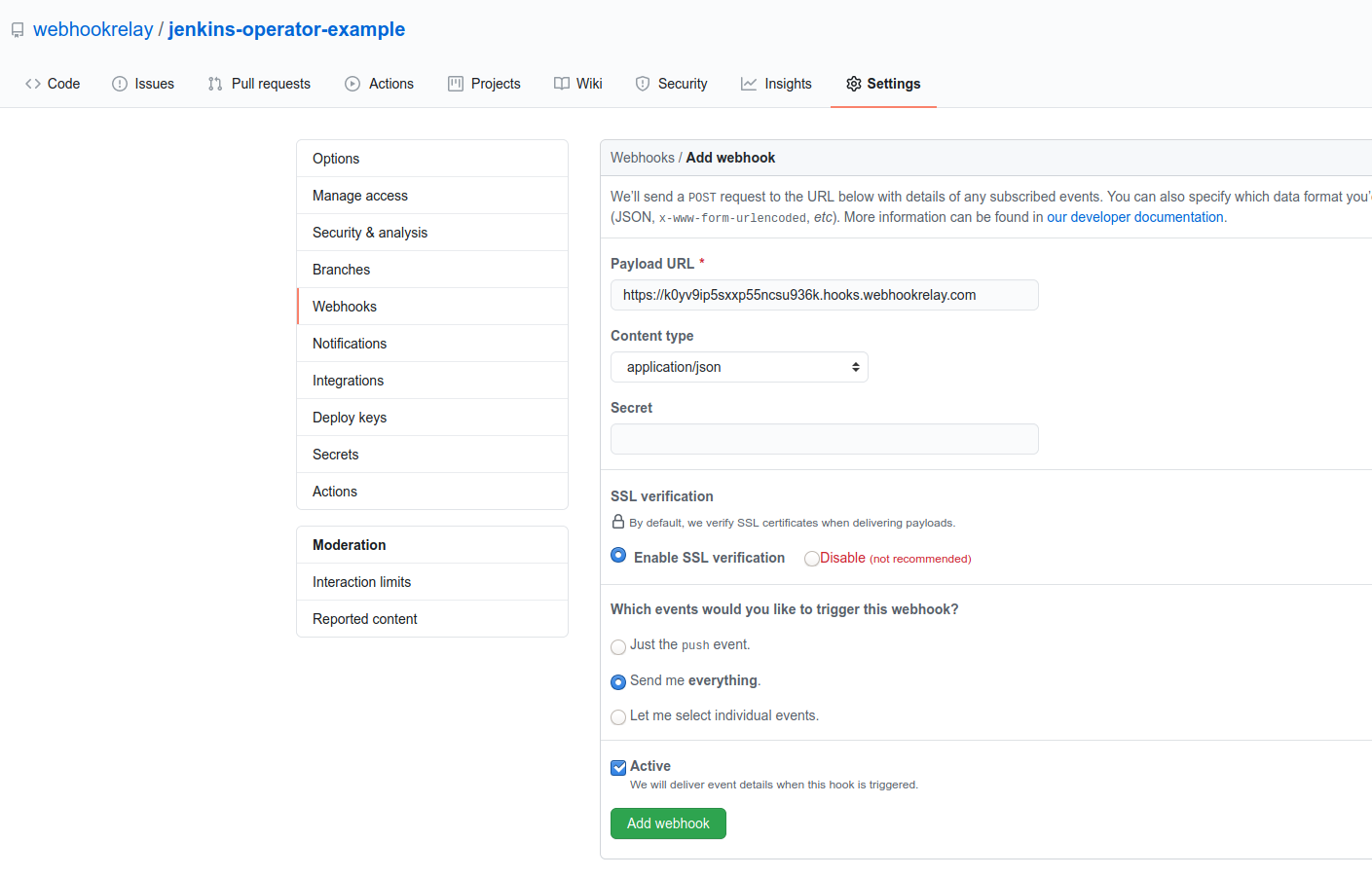
Take the public endpoint URL and add it to your GitHub repository:
Now, any push to your GitHub repository will send a webhook through Webhook Relay to your Jenkins instance that's running inside a Kubernetes cluster.
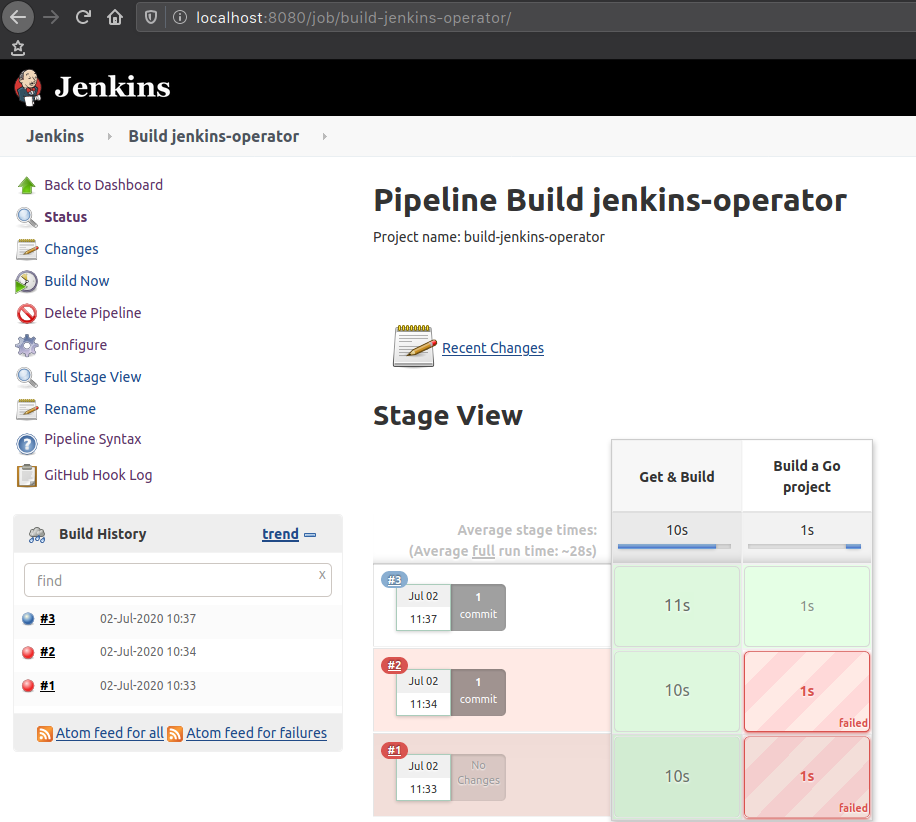
After a first push or if you trigger the seed job, it will ensure that the pipeline project is set up. At least on the version that I have tested, you first need to start job manually. After it, webhooks will automatically trigger any subsequent builds:
Reference:
- Jenkins Kubernetes Operator: https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-operator
- Jenkins Operator docs: https://jenkinsci.github.io/kubernetes-operator/docs/getting-started/latest/configuration/
- Jenkins Kubernetes plugin: https://plugins.jenkins.io/kubernetes/
- Jenkins Kubernetes plugin source: https://github.com/jenkinsci/kubernetes-plugin
- Webhook Relay Operator: https://github.com/webhookrelay/webhookrelay-operator/
- Helm (package manager): https://helm.sh/