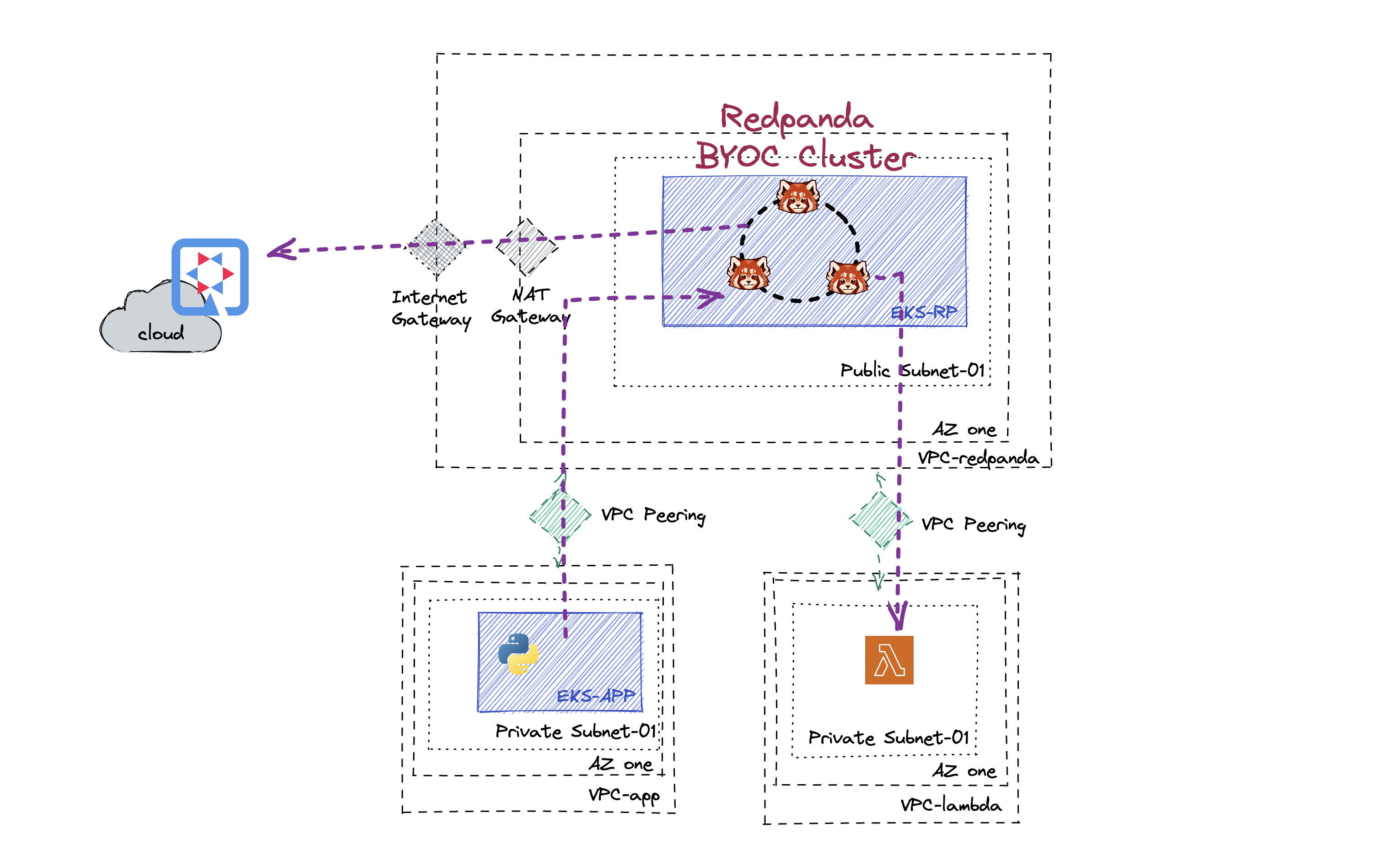
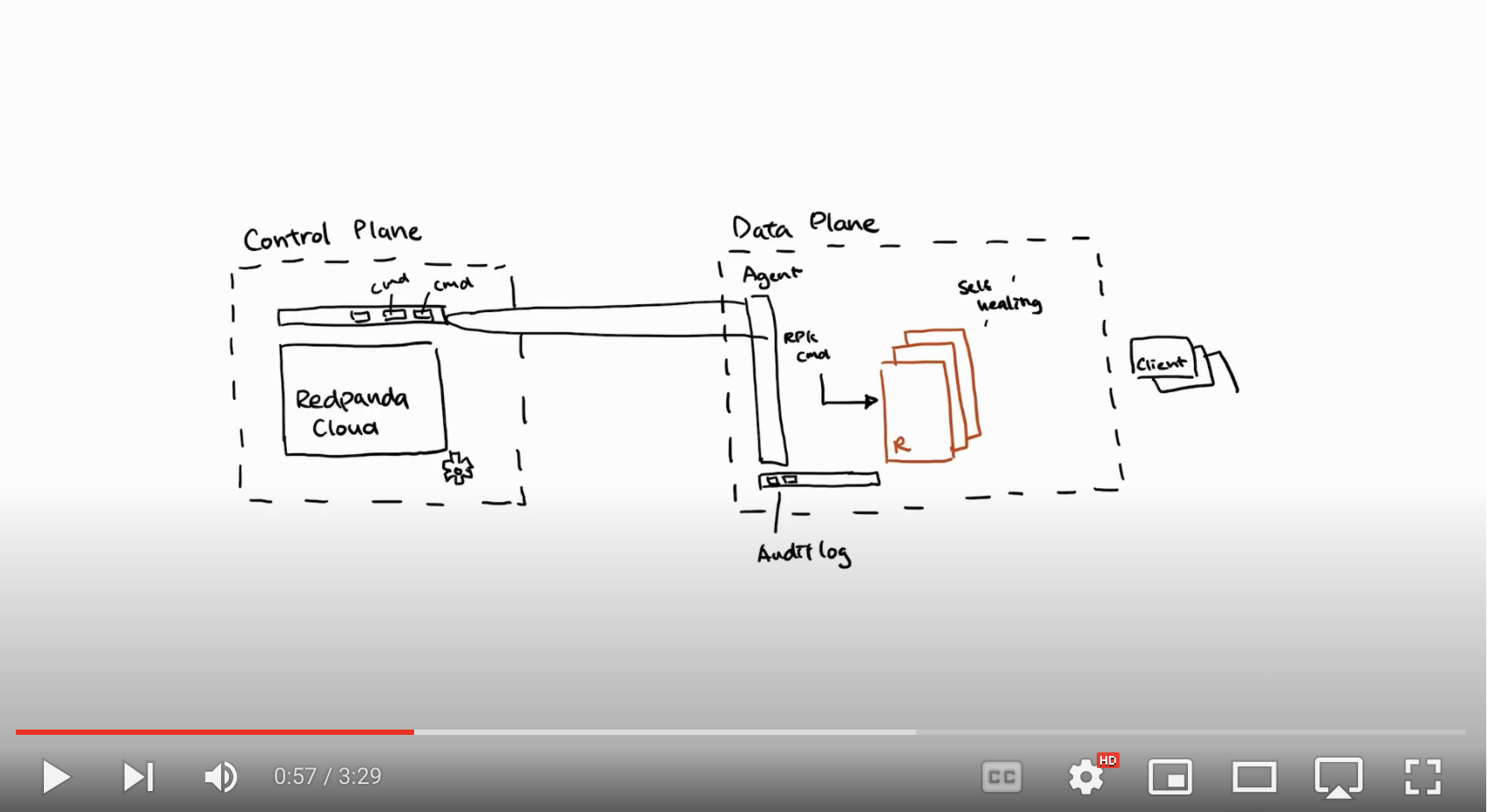
Here is a quick demo showcasing different ways you can connect to the Redpanda BYOC cluster.
A simulator microservices(python) is deployed in Kubernetes and continuously publishes signal events, the Kubernetes cluster sits in its own VPC and is now connecting to the Redpanda cluster via VPC peering. Another consumer client(Java Quarkus) consumes the events externally. I have set up the BYOC in a public subnet, therefore it can connect via the internet gateway.
The signal also triggers a Lambda serverless application, instead of using an MSK or SNS. The Lambda service also sits in its own VPC, in order to connect them, similar to AWS MSK and Kinesis, establishing an VPC peering connection will do the trick. In my example, for better security, I have enabled SASL for authentication purposes. I choose to use the secret manager to store the credentials for Lamba triggers. In this case, make sure you update the access policy for your lambda role, so it has permission to get the credential stored.
You will need to have an EKS already running in it's own VPC and an empty VPC with one AZ, private subnet.
Create a small EKS cluster
eksctl create cluster --name redpanda \
--external-dns-access \
--nodegroup-name standard-workers \
--node-type t2.small \
--nodes 3
Create VPC peering between
- Lambda VPC to the VPC that runs the BYOC Redpanda Cluster
- Newly created EKS's VPC to the VPC that runs the BYOC Redpanda Cluster
TODO: automate above instructions
Request yours BYOC cluster here
After Redpanda cluster started, create a Topic name plants
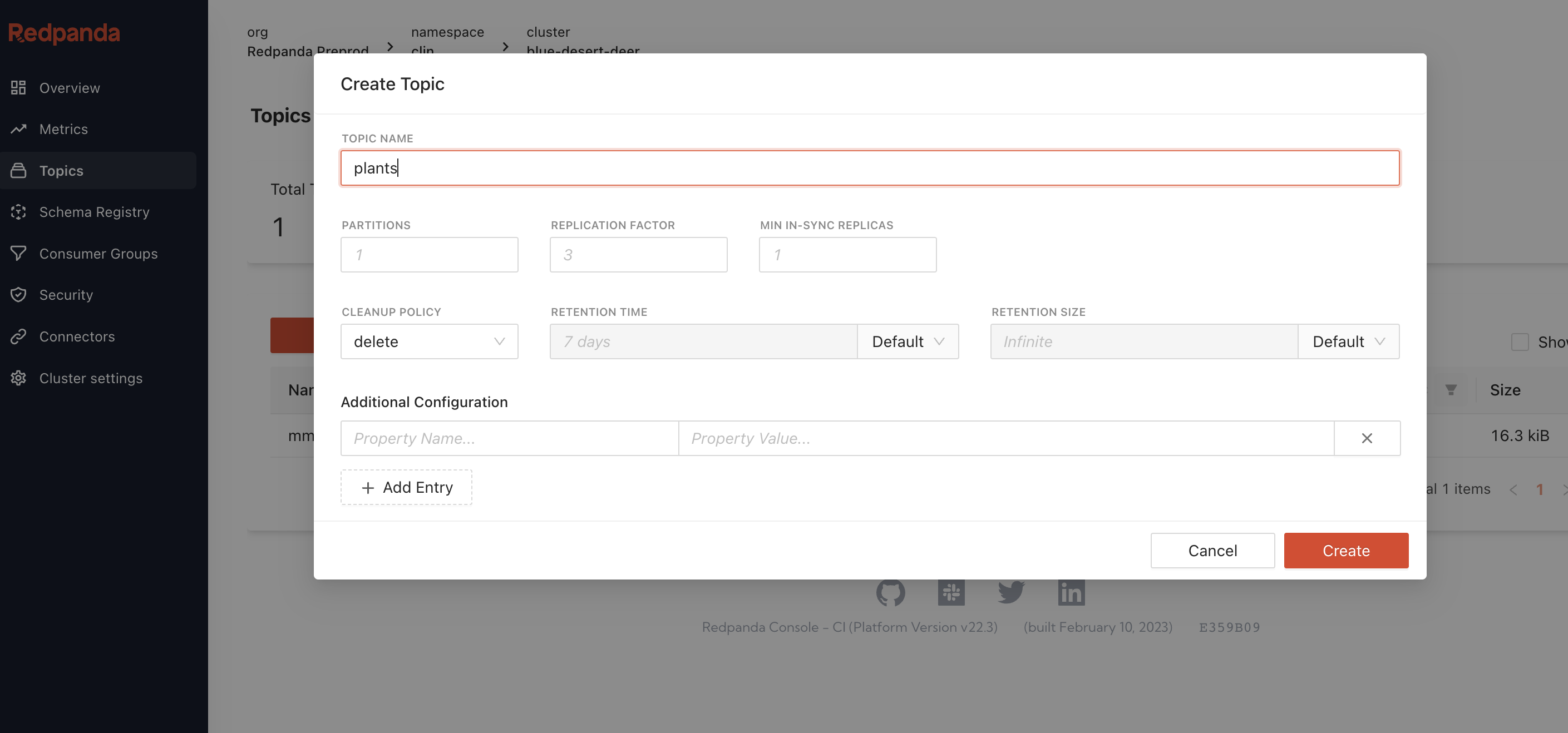
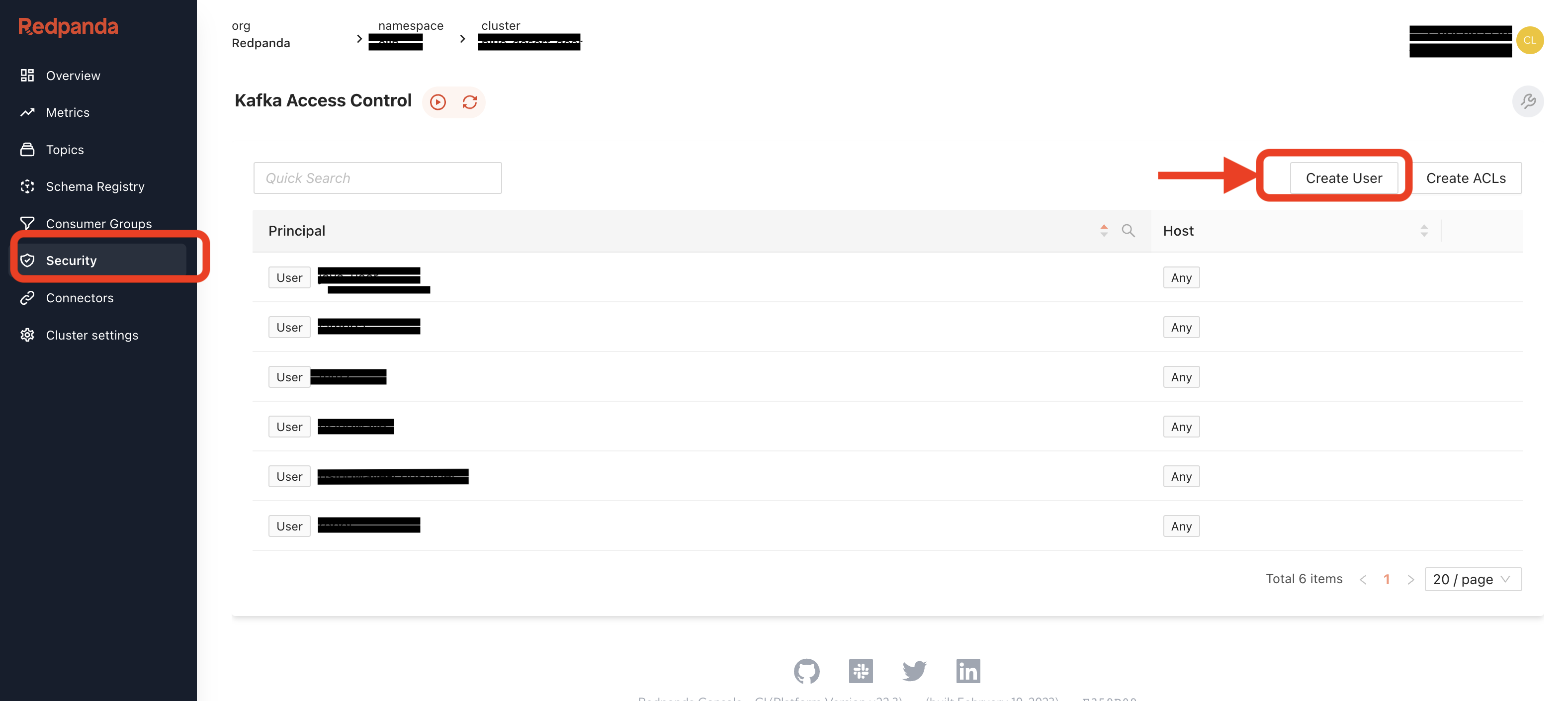
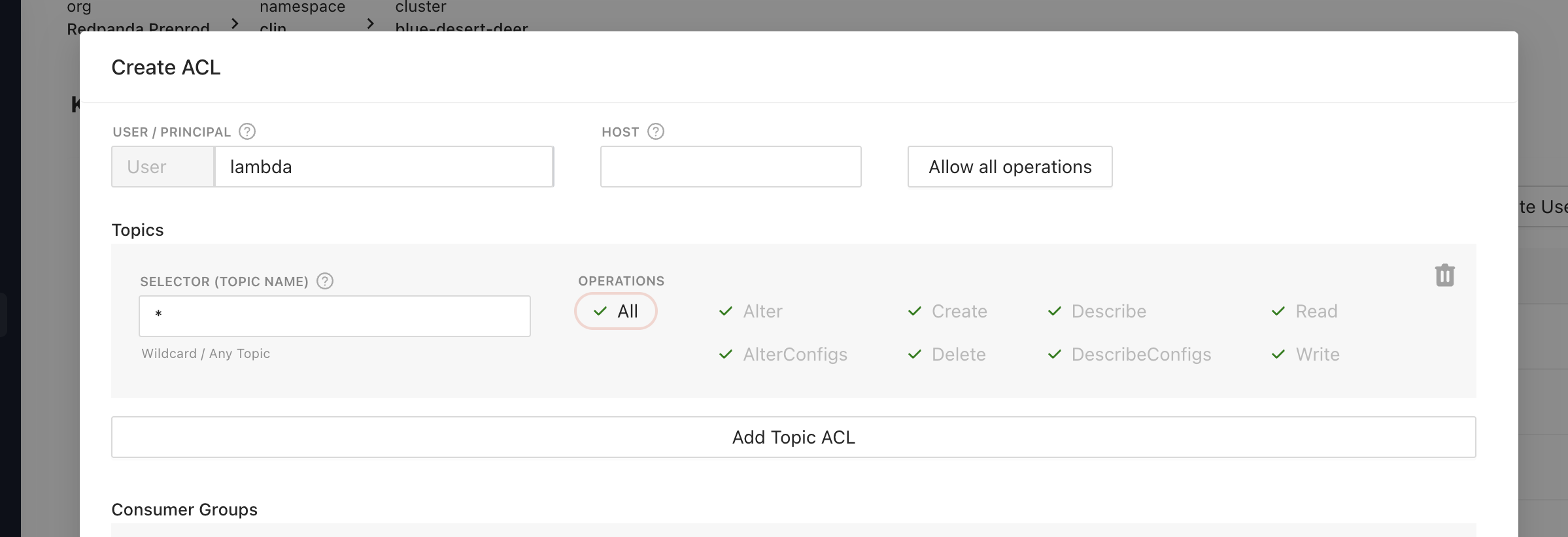
Click on the Security in the left menu, setup the access control to the cluster by creating a new user with Mechanism SCRAM-SHA-256.
Remember your id & password.
Create three sets of the credential, for all three clients
- Python publisher (for example ID/PWD robot/xxxxxx)
- Quarkus consumer (for example ID/PWD java-user/yyyyyy)
- Lambda consumer (for example ID/PWD lamabda/zzzzzzz)
and configure all three ACLs, we'll grant all permissions to all topics for now.
Go to folder quarkus_app
cd quarkus_app
edit the application.properties and update the bootstrap server & login credential (pick one of the user created in the previous section)
- kafka.bootstrap.servers=<BYOC_SEED_SERVERADDR>
- sasl.username=<CONSUMER_USERNAME>
- sasl.password=<CONSUMER_PASSWORD>
Run following commend to start the consumer:
mvn quarkus:dev
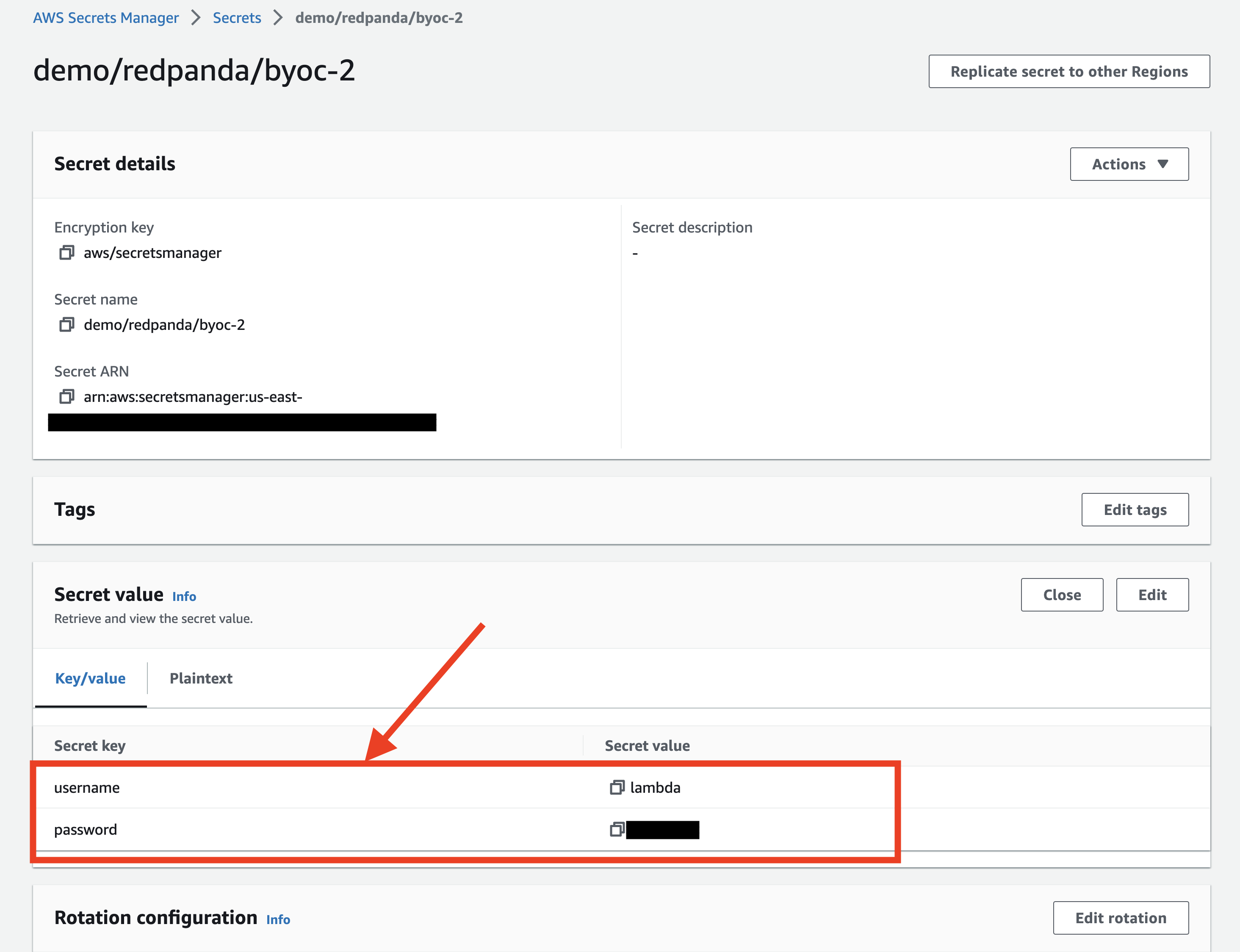
Let's first setup the credential for lambda to access the redpanda cluster.
Create new Lambda function with the runtime of your choice. Do whatever you want in the function, in my case, I simple created a Ruby app that log the events.
Let's setup the lambda function's role permission,
Add the secretsmanager read permission to above role.
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"secretsmanager:GetResourcePolicy",
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"secretsmanager:DescribeSecret",
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"secretsmanager:ListSecretVersionIds"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:secretsmanager:us-xx-x:xxxx:secret:demo/redpanda/byoc-2-xxxxx"
]
}
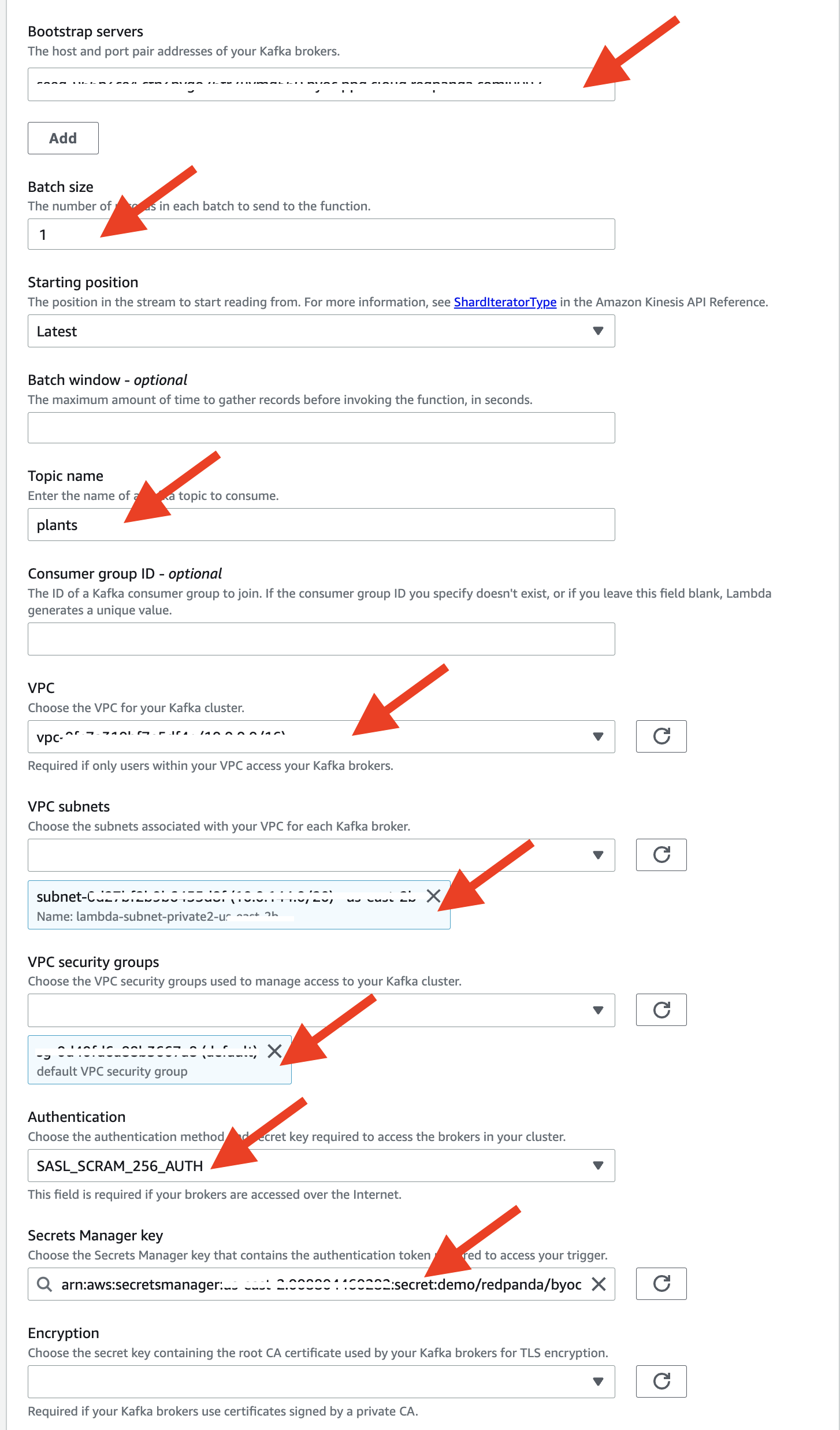
Now,we are ready to setup the trigger, select Apache Kafka as source. And configure the following:
- Bootstrap servers : Your Redpanda seed server address
- Batch size: 1 (For demo purpose)
- Topic name: plants
- VPC: Choose the VPC you created for Lambda functions in prerequisite step
- VPC Subnets: Pick any of the private subnet
- VPC security groups: In my case, I just picked the default group (Change this base on your security policies)
- Authentication: SASL_SCRAM_256_AUTH
- Secrets Manager key: Choose the credential you just added in Secrets Manager in the previous step
Make sure you have access and logged into the EKS for running the microservice applications. (check your kubeconfig file if you have problem accessing the cluster)
Create a new namespace to run the microservices.
kubectl create -f namespace.yml
Add configuration with credentials needed to communicate to Redpanda cluster.
kubectl create -f configmap.yml -n plants
Deploy the python application and start sending random events into the cluster.
kubectl create -f deployment.yml -n plants
Check if deployed successfully.
> kubectl get pod -n plants
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
plant-bot-6d84f54c98-2d8v9 1/1 Running 0 12s
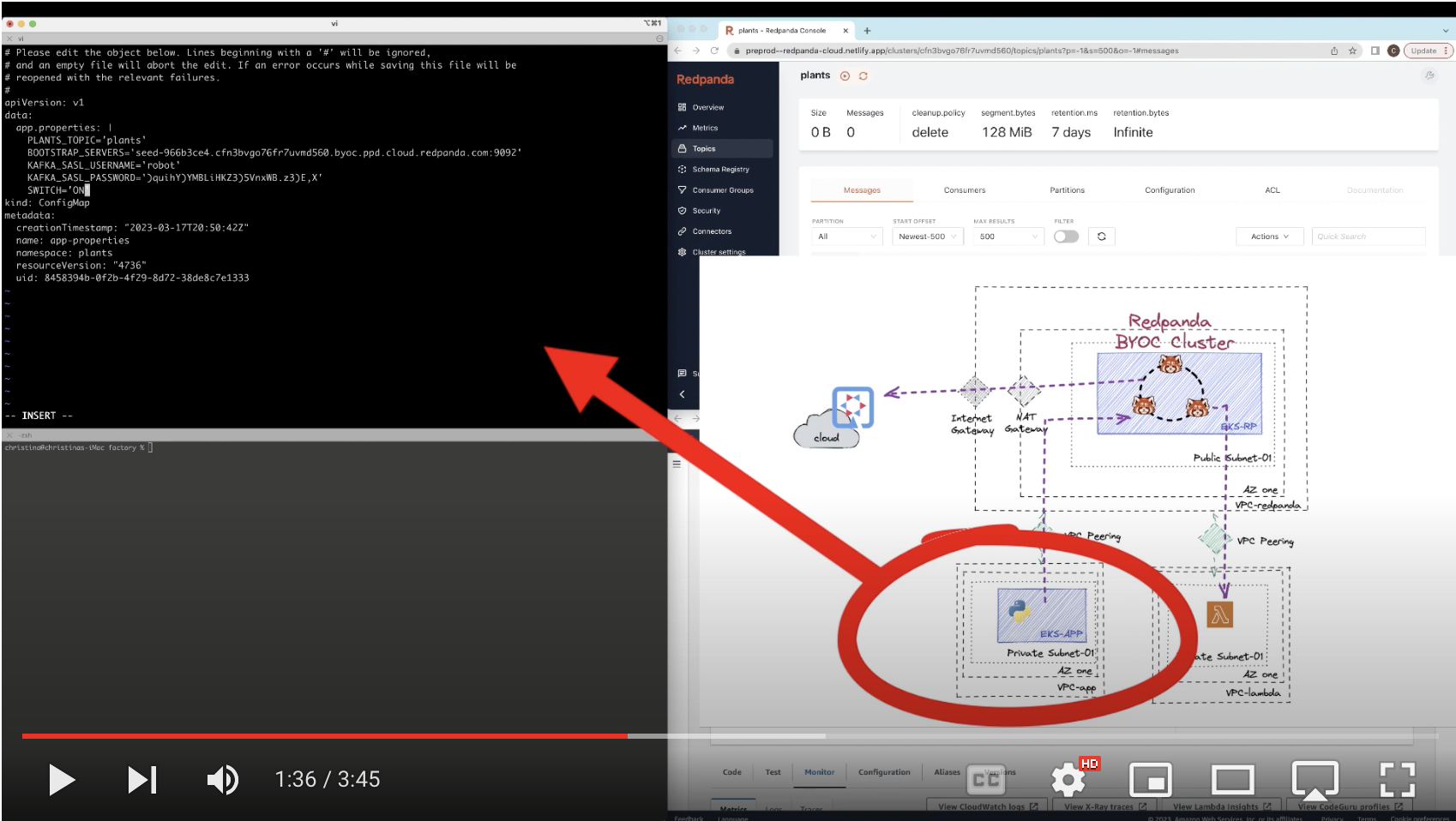
Edit the configmap and turn on the switch to start publishing data
kubectl edit configmap app-properties -n plants
Start consuming localing using the Quarkus Java client
mvn quarkus:dev
View changes in your Lambda monitoring dashboard and Redpanda Cloud UI.
Join our Redpanda Community on Slack, you’ll have access to Redpanda experts and fellow Redpanda users!! Try out Redpanda’s BYOC, take it for a spin ! Request yours here or contact us for more information. Happy streaming!