Rosetta Drone 2 tested on **DJI Air, Mavic 2 x and Matrice 210 V2, Mavic Pro, Mavic AIR series and supports Android 5.1 and newer, with DJI SDK 4.14 and Androidx lib
=======
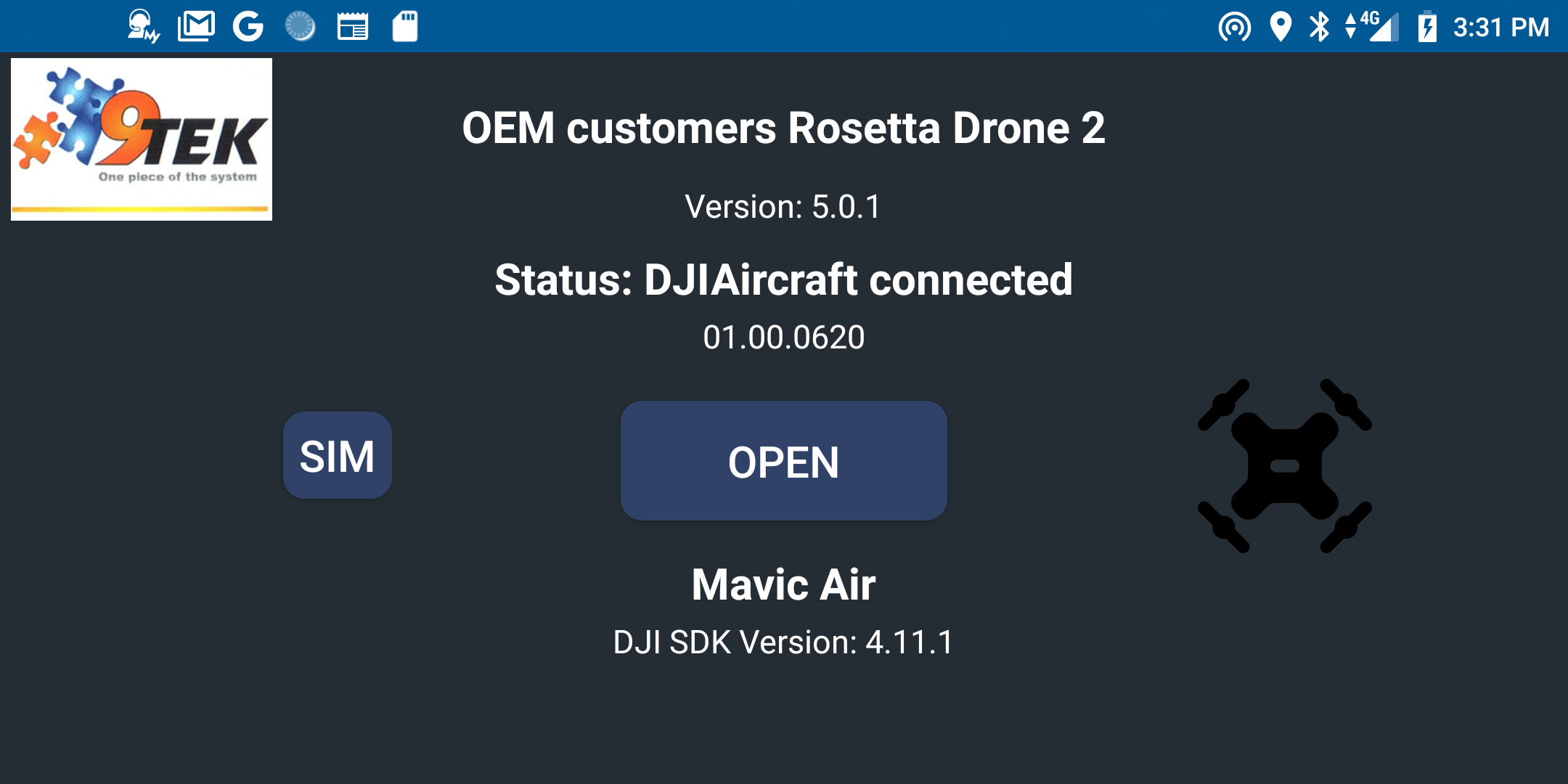 Opening screen, requires DJI login first time...
Opening screen, requires DJI login first time...
This version has implemented the new video stream method in DJI SDK that require quite a few modifications. It also includes all the latest libraries, and Androidx. In the unstable code there is also the DJI simulator, to enable testing in the lab. Android Studio is now updated to 3.6
Rosetta Drone is a Mavlink wrapper for the DJI SDK, which allows users to fly DJI drones using Mavlink-speaking ground control stations. In theory it should work with any Mavlink GCS, but all testing so far has been done with QGroundControl.
*** IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTE *** Due to imperfect translation between DJI and Mavlink, props may begin spinning at unexpected times. Always treat props as if they are live. Use Rosetta Drone's "safety" feature, which should prevent the drone from acknowledging unexpected GCS arm or takeoff commands.
The user assumes all responsibility for prevention of harm or damage. This is an evolving, experimental app. See "Known issues" below before use.
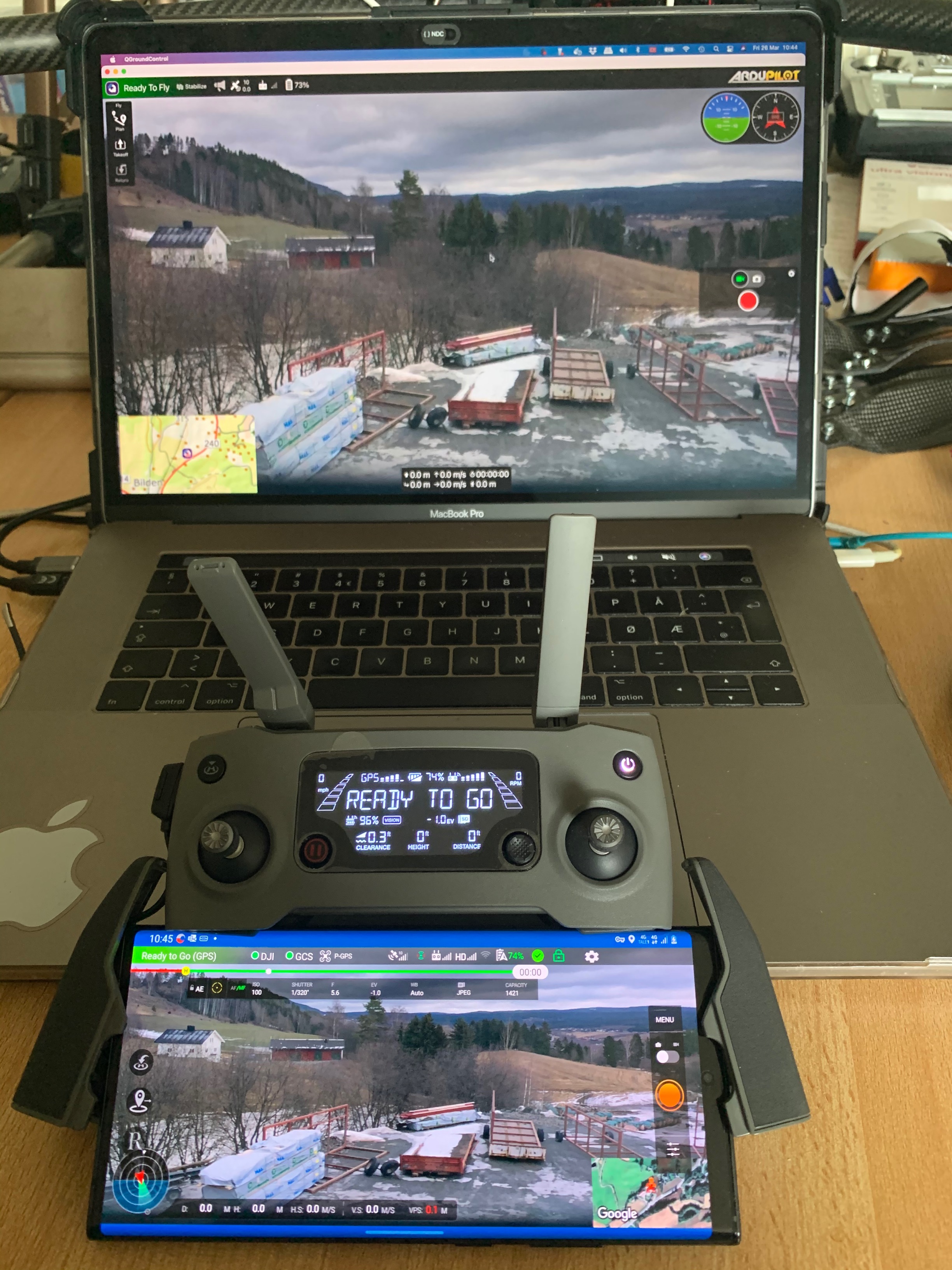 DJI-Rosettadrone-QGC live over 4G-LTE
DJI-Rosettadrone-QGC live over 4G-LTE
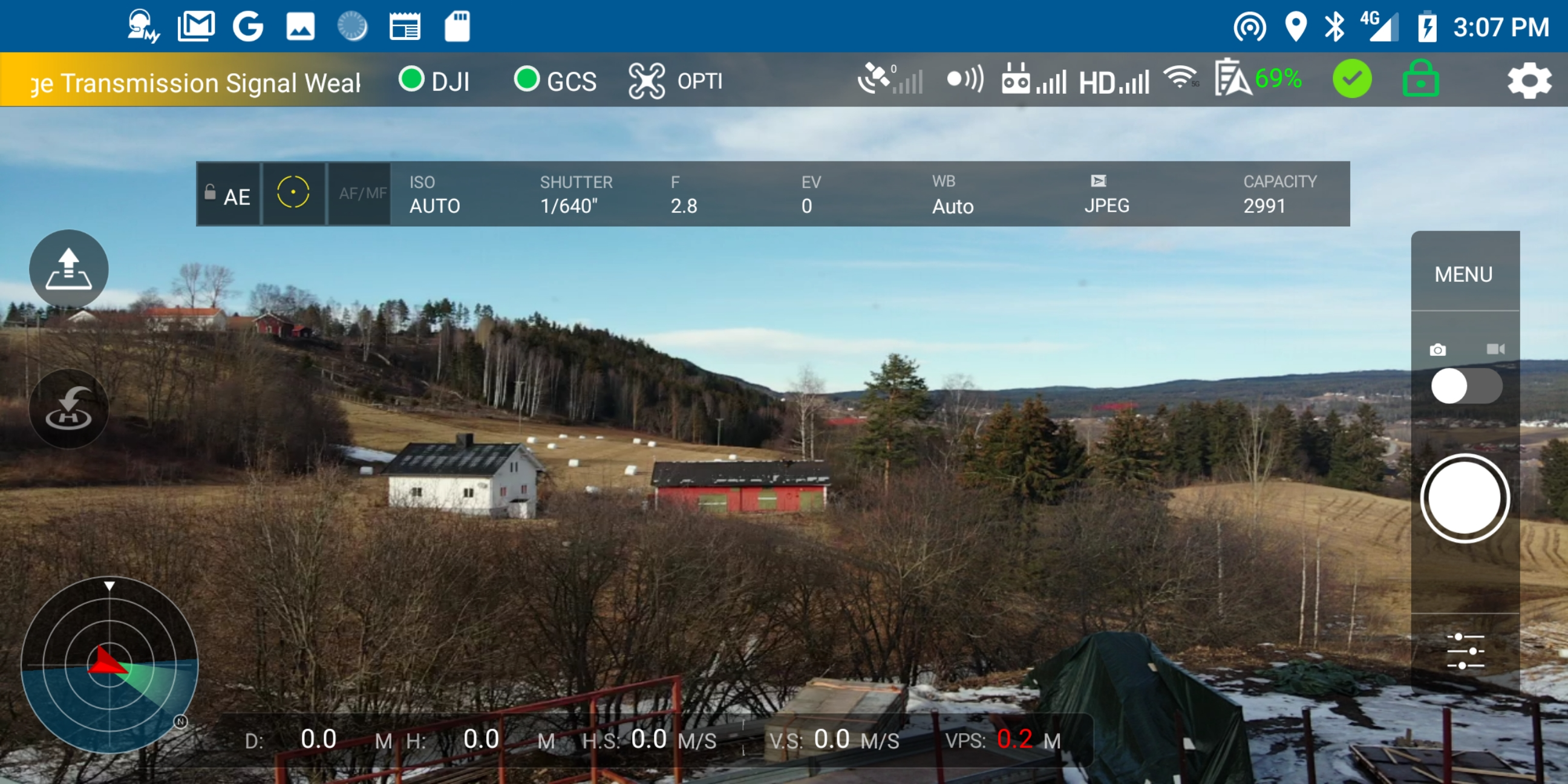 Main screen, with live video on Mavic AIR (from my office)...
Main screen, with live video on Mavic AIR (from my office)...
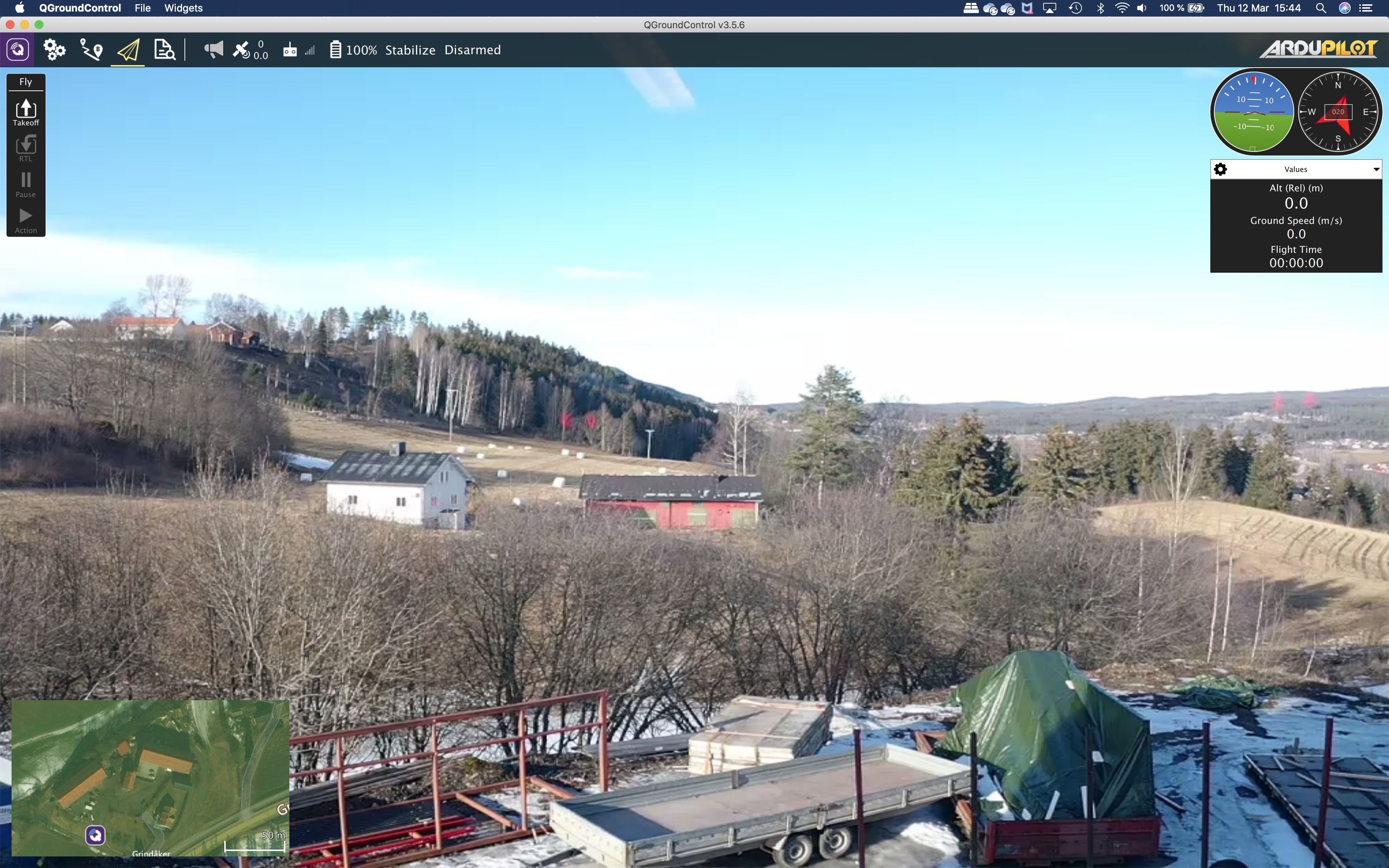 Main screen on QGroundControl with live video and telemetry... (from inside my office)
Main screen on QGroundControl with live video and telemetry... (from inside my office)
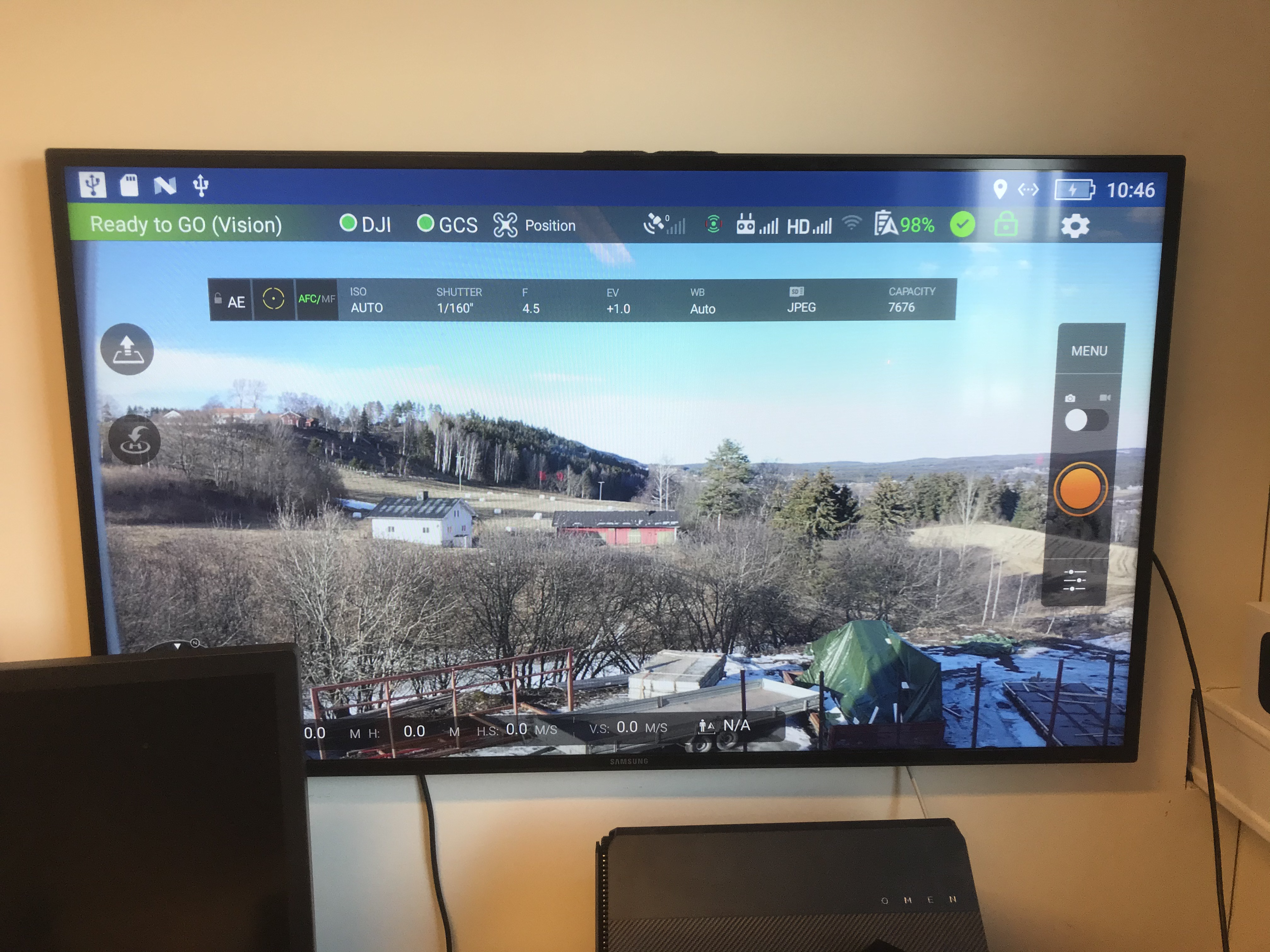 Rosetta Drone 2 on the big screen from DJI Smart Controller
Rosetta Drone 2 on the big screen from DJI Smart Controller
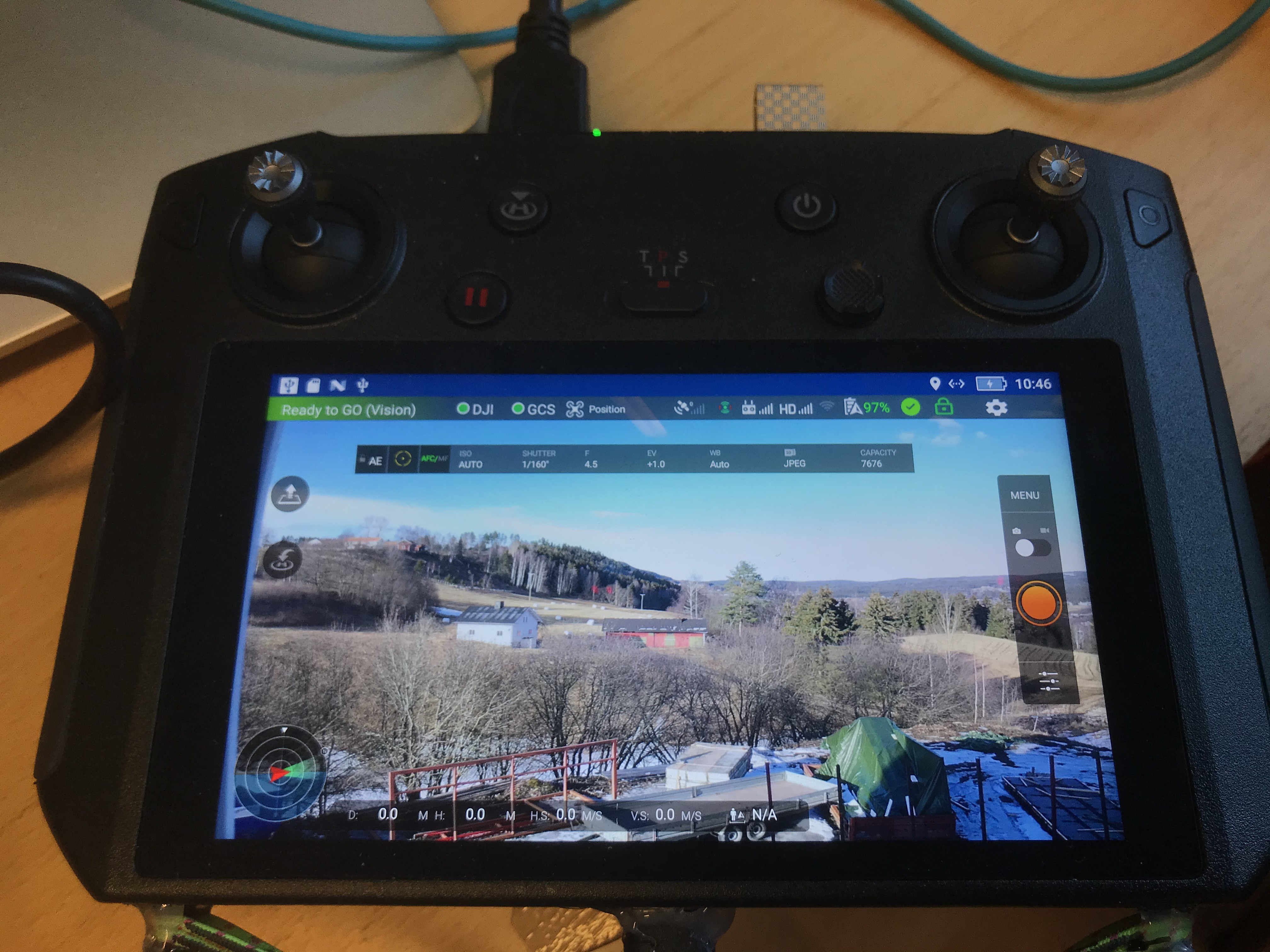 Rosetta Drone 2 on the DJI Smart Controller
Rosetta Drone 2 on the DJI Smart Controller
Latency video:
(https://youtu.be/HAC5OpQQpDI "Click to play in Youtube.com")
- Report telemetry in QGC like position, attitude, relative altitude, heading, and battery remaining
- Command Return-to-Launch from QGC
- View drone video feeds in QGC or forward RTP to an IP address of your choice (currently Mavic Pro 2 only)
- Create and fly waypoint missions
- Fly by joystick and QGS
- Fly from Python in DroneKit
- Use Mavproxy to connect both QGC and DroneKit at the same time
- Use Gstreamer/OpenCV/FFMPEG and DroneKit to create complex AI functions
-
Connect your Android phone to a DJI transmitter and power on your DJI drone.
-
Start Rosetta Drone. The DJI light in the top-right will turn green if the app is successfully communicating with your drone.
-
If you wish to use QGroundControl on an external device, click the Gear icon to access Settings, check Use GCS on an external device, then specify an IP address.
-
Start QGroundControl. A telemetry connection should be immediately established, and the GCS light in Rosetta Drone will turn green. Note that if you are using QGroundControl on the same device as Rosetta drone, the GCS light may not turn green if QGC is in the background.
-
To start video:
a. Click the "Q" icon in the top-left corner of QGC
b. Under Video change Video Source to UDP Video Stream.
c. Change UDP Port to 5600.
-
Takeoff is recommended using the RC transmitter. To arm or takeoff from the GCS, click the SAFETY ENABLED button. It will turn green and say READY TO FLY. Then use the QGroundControl Takeoff or Start Mission function.
-
After flight, ensure the safety is enabled before approaching props.
-
Support is added for Pan and Tilt of camera gimbal by using RC channel 8 and 9.
###Add this to you're Dronekit python script:
def set_servo(servo,val): msg = vehicle.message_factory.command_long_encode( 0, # time_boot_ms (not used) 0, # target system, target component mavutil.mavlink.MAV_CMD_DO_SET_SERVO, 0, servo, # RC channel... 1500+(val*5.5), # RC value 0, 0, 0, 0, 0) vehicle.send_mavlink(msg) vehicle.flush()
And then use: set_servo(8,-45.0) to set the gimbal....
-
Support for joystick is added and tested with QGroundcontrol, using the now built in simulator.
-
By taping on the drone icon 5 times, you enable test mode and can open the software with no drone connected. For GUI work.
-
Install git lfs as specified at https://github.com/git-lfs/git-lfs/wiki/Installation
-
Clone or download the repository.
-
In Android Studio, select File->New->Import Project and navigate to the downloaded folder.
-
Sign up for the DJI Developer Program at https://developer.dji.com/mobile-sdk/ and create an Application key. The package name should be sq.rogue.rosettadrone.
-
Generate Google Maps API key using instructions at https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/get-api-key#creating-api-keys
-
Create a new file called keys.xml in the /app/src/main/res/values/ folder, and insert the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="dji_key">INSERT KEY HERE</string> <string name="google_key">INSERT KEY HERE</string> </resources> -
Run Build->Make Project
Anyone who speaks multiple languages knows that translations are rarely perfect. The same is the case here.
-
The ARM button in QGC does not work, by design. Sending a "Takeoff" or "Start Mission" command from QGC will arm the motors and takeoff.
-
DJI reports heading in True, which Rosetta drone 2 passes along in vfr_hud.hdg. The mavlink protocol does not specify magnetic or true.
-
DJI and Mavlink use different scales to characterise GPS accuracy. DJI also does not report hdop or vdop.
-
Radio signal strength is not yet implemented
-
Rosetta drone 2 reports groundspeed and airspeed as the same, and does no wind correction
-
There is currently no way to turn the video camera on or off in QGC, but DJI controllers will still work fine, Mavlink support for this is now added.
-
The only implemented waypoint actions include delaying at a waypoint, taking a photo, or changing the gimbal pitch
-
Battery % is now show in the GUI on the main screen.
-
Battery Warnings for both Drone and Controller at 20% 10% and 5%. No sound as the moment.
-
Controller stick positions and C1, C2 and C3 switch states are now reported as RC RAW messages over Mavlink
-
A working DJI simulator is added for testing and training. The simulator is Hardware In the Loop (HIL), and this require both a controller and a drone connected.
-
A test mode is added by hitting 5 times on the drone icon. This will enable GUI testing only.
-
The message on the boot/login screen can now be modified in "settings/drone configuration/App Name" , to make tha app more private.
-
The switch C3 is now both reported as switch 3 and also performa a auto takeoff is the system is armed. This to allow flying from Rosetta Drone 2, might be reverted.
-
If you change the UDP port while QGC is running, you may need to restart QGC.
-
If you change the video UDP port while QGC is running, you may need to restart Rosetta drone 2
-
Some times the Rosetta Drone 2 stopps and restarts, work are in progress to eliminate this. Seems to be related to the Mavlik layer.
-
If you takeoff using the QGC, and then sett a point and hit goto, the Rosetta drone 2 enters an error state. Work are in progress.
-
Fix goto position.
-
Fix mission plan flight.
-
Add more actions to mission waypoint
-
Test and prepare official relase, add to play store.
RosettaDrone 2 uses MAVLink code generated by the MAVLink code generator, using the ArduPilot dialect. The Java code generator contains errors (see issues #805 and #806), and the code required manual tweaking after generation. This means that simply dropping in updated auto-generated files will likely produce errors. At the moment this seems only to apply for setting and getting double that is missing. It is quite easy to copy the float function and modify it to double. The only usage for this is for ROV wheel distance, so someone should fix that in Mavlink.
The use of an ArduPilot dialect over PX4 is not intended to be a statement of preference. The author believes strongly in the importance of maintaining maximum compatibility across both projects.
Rosetta Drone was brought to you by developers from Rogue Squadron, a UAS/C-UAS red team at the Defense Innovation Unit Experimental. The Rosetta Drone 2 version was brought to you by the Drone depatment at 9Tek AS, Norway.
Icons made by Pixel Perfect & Freepik at flaticon
Rosetta Drone 2 is licensed under BSD3. For particularities related to U.S. federal government code release, please read Intent.MD. For more information, visit code.mil or code.gov.
Rosetta Drone 2 uses a modified version of DJI's Android Video Stream Decoding Sample, which is released under the MIT License.
Video RTP packing uses code modified from the libstreamer library, licensed under Apache 2.