Probabilistic Prediction for PV Systems - P3
Welcome to The P3 System
The Probabilistic Prediction System for PVs (P3 System) is a tool for predicting the short-term power output of a PV system. It available as:
- A Matlab source code.
- An excecutable software with graphical user interface (GUI), which you can simply download and install on your PC. For more information, click here.
- A Python code, which will be implemented over a Raspberry Pi. For more information, click here.
Downloads
Click here to access all the MATLAB codes concerning the P3 system.
The forecasts can be obtained by running Main.m. All the other functions must be present as well.
To obtain the weather forecasts, run AcquireWeather.m. You must provide your API key in order to be able to get the 10-day weather forecast.
About the Code
The diagram below highlights the inputs and the outputs of the MATLAB code.
Input data
In order to predict the generated power of a PV system, three inputs must be provided:
(1) Weather Forecasts: This is obtained from an online service provider (e.g.Weather Underground). In this model, 10-day forecasts of 1-hour resolution are used. The forecasts must cover the training and prediction periods. The temperature and the cloudiness are the critical weather parameters to the code.
(2) PV System’s Parameters: Including location, orientation and technical parameters.
(3) Historic PV System’s Generated Power: The generation for the training horizon is acquired through the energy monitoring system connected to the PV modules.
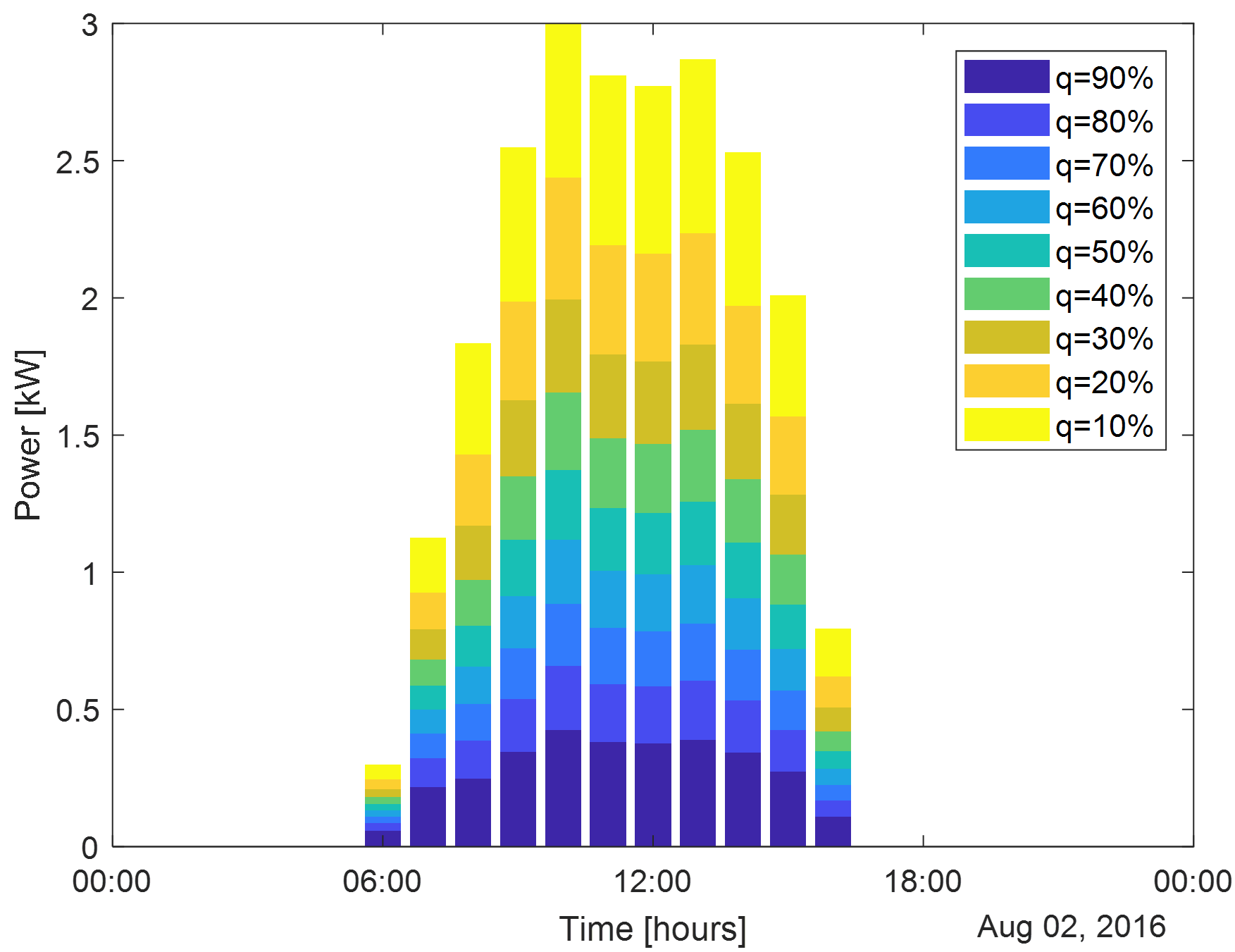
Output Forecasts
(1) Deterministic Forecast: Prediction of only one profile of the PV generated
power with no probability involved.
(2) Probabilistic Forecast: Multiple output profiles, each is associated with a
specific probability. For example, for q=30, the probability of generating less
than or equal to the corresponding profile is 30%.
Reference Publications and Developers
The MATLAB code was created at the Chair of Energy Economy and Application Technology in the Technical University of Munich. The code is described in the following publications:
-
W. El-Baz, M. Seufzger, S. Lutzenberger, P. Tzscheutschler and U. Wagner, "Impact of probabilistic small-scale photovoltaic generation forecast on energy management systems," Solar Energy, vol. 165, pp. 136-146, 1 May 2018.
-
W. El-Baz, P. Tzscheutschler and U. Wagner, "Day-ahead probabilistic PV generation forecast for buildings energy management systems," Solar Energy, vol. 171, pp. 478-490, 1 September 2018.
The GUI was developed by Mohamed Eldakadosi, while the Python codes were created by Çağatay Eren.
Available Sources
Matlab Source Code
Matlab GUI
The GUI is developed, through MATLAB’s App Designer, to facilitate the prediction
process to owners of PV systems. The main layout is shown below.
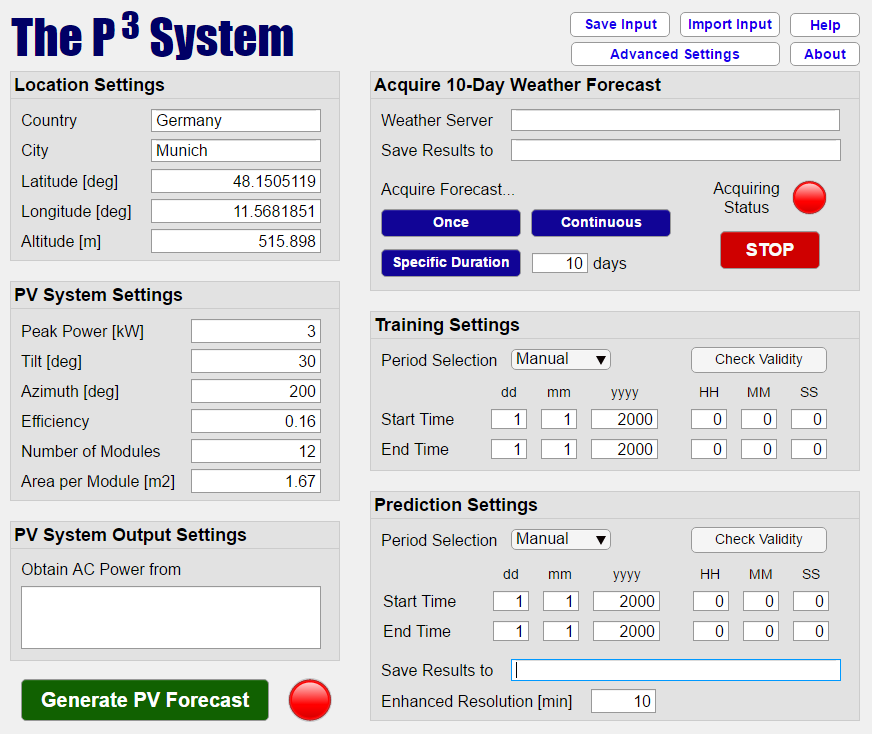 The user is requested to provide information concerning the PV system:
The user is requested to provide information concerning the PV system:
- Location, technical and orientation parameters.
- The server (or address) where the historic output power is obtained.
- The weather server where the weather forecasts are acquired.
- The directory where weather forecasts are stored.
- The training horizon.
- The prediction horizon.
- The directory where PV predicted outputs are stored.
Note: The button ‘Check Validity’ helps the user to verify whether the dates entered comply with the available weather forecasts. If ‘Period Selection’ is chosen as ‘Auto,’ then dates will be automatically filled in.
Downloads
Two sets of files are available to download for this part;
-
MATLAB codes for the GUI. The main code is PVpredictGUI.mlapp, which can be edited/run through MATLAB's App Designer.
-
Executable file to use the GUI as a standalone application. Note: MATLAB Runtime will be downloaded during the installation of the .exe file.
Acquisition of Weather Forecasts
In order to predict the output power of the PV system, the user must acquire weather forecasts for at least 10 days. This is possible through the provided buttons:
- ‘Once’: acquiring the weather forecast once upon the click.
- ‘Continuous’: weather forecasts will be obtained every 24 hour, starting from the first click, until the user presses ‘STOP’.
- ‘Specific Duration’: similar to ‘Continuous’; however, the acquirement will stop after the desired duration.
One possible format for the weather server is the following:
http://api.wunderground.com/api/User_API/hourly10day/q/Germany/Munich.json
Output
When ‘Generate PV Forecast’ is clicked, computations of the forecasted power start.
The resulting outcome should be similar to the figure below.
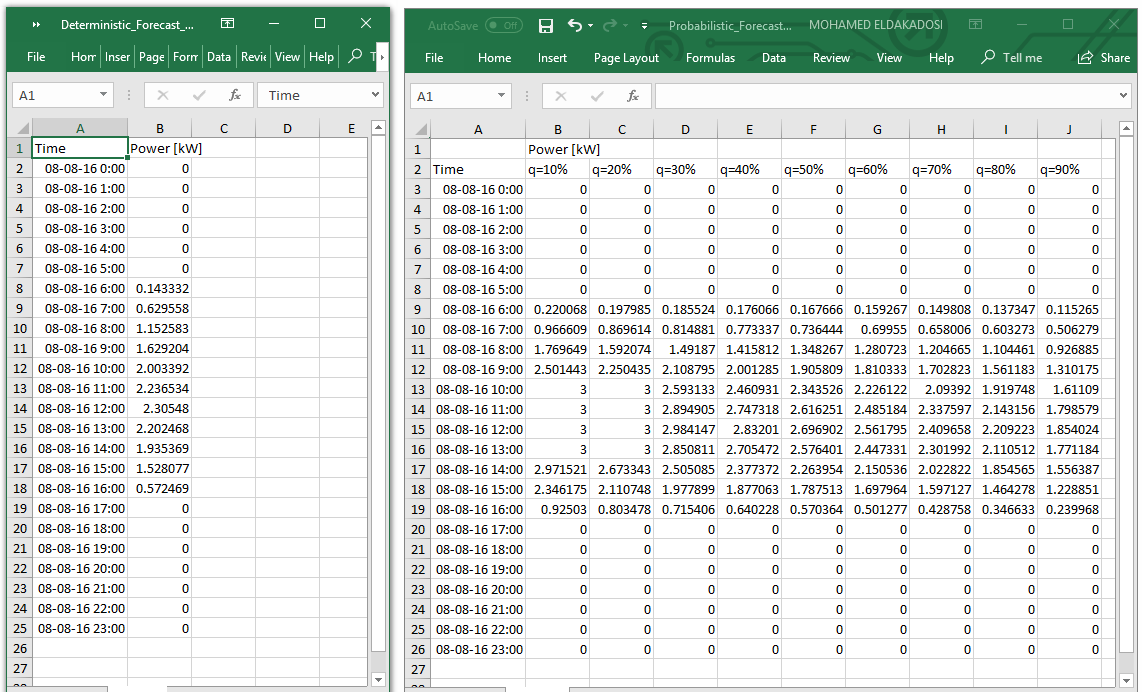
 In addition, the 1-hour deterministic and probabilistic forecasts are stored as
Excel sheets.
In addition, the 1-hour deterministic and probabilistic forecasts are stored as
Excel sheets.
The Python Codes
About Python Implementation
Python code puts into action the same algorithm as in the MATLAB code in Python language.
To run the code on your local machine, you need:
-
Python version 3.x.x, available for download here.
-
Code in this repository. Simply clone/download the code inside this repository.
Current Progress
There are fourteen core .m files that work on the probabilistic PV prediction algorithm. They are given in the list below with their rewriting-in-Python work statuses:
| Function | Progress |
|---|---|
| Main.m | in progress |
| DataAcq.m | completed |
| PVtrain.m | future work |
| clearskygen.m | future work |
| clearsky.m | future work |
| emoncms.m | future work |
| missingData.m | future work |
| unixtime.m | future work |
| weatherset.m | future work |
| PVpredict.m | future work |
| errorcalc.m | future work |
| TrainProp.m | future work |
| allfitdist_woFig.m | future work |
| GenPro.m | future work |
DataAcq.m
Data acquisition function gathers weather data from a directory on the local machine. This weather data is stored in form of a .mat file. The function keeps track of missing .mat files. Temperature, UV index, weather condition, etc., data are stored in matrices.
Python form of this function imitates this behavior. It uses numpy arrays for matrix manipulations, it uses pandas time series for putting a timestamp on individual data points. In the end, Python data acquisition function returns a dictionary data (To be reworked)
Support and Contact
Please review the mentioned publications above for theoretical queries about the forecasting system. For further queries:
- Wessam El-Baz (wessam.elbaz@tum.de)
- concerning the GUI: Mohamed Eldakadosi (m.eldakadosi@tum.de)
- concerning the python codes: Çağatay Eren (c.eren@tum.de)
License Information
Copyright (C) 2018 Wessam El-Baz
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/