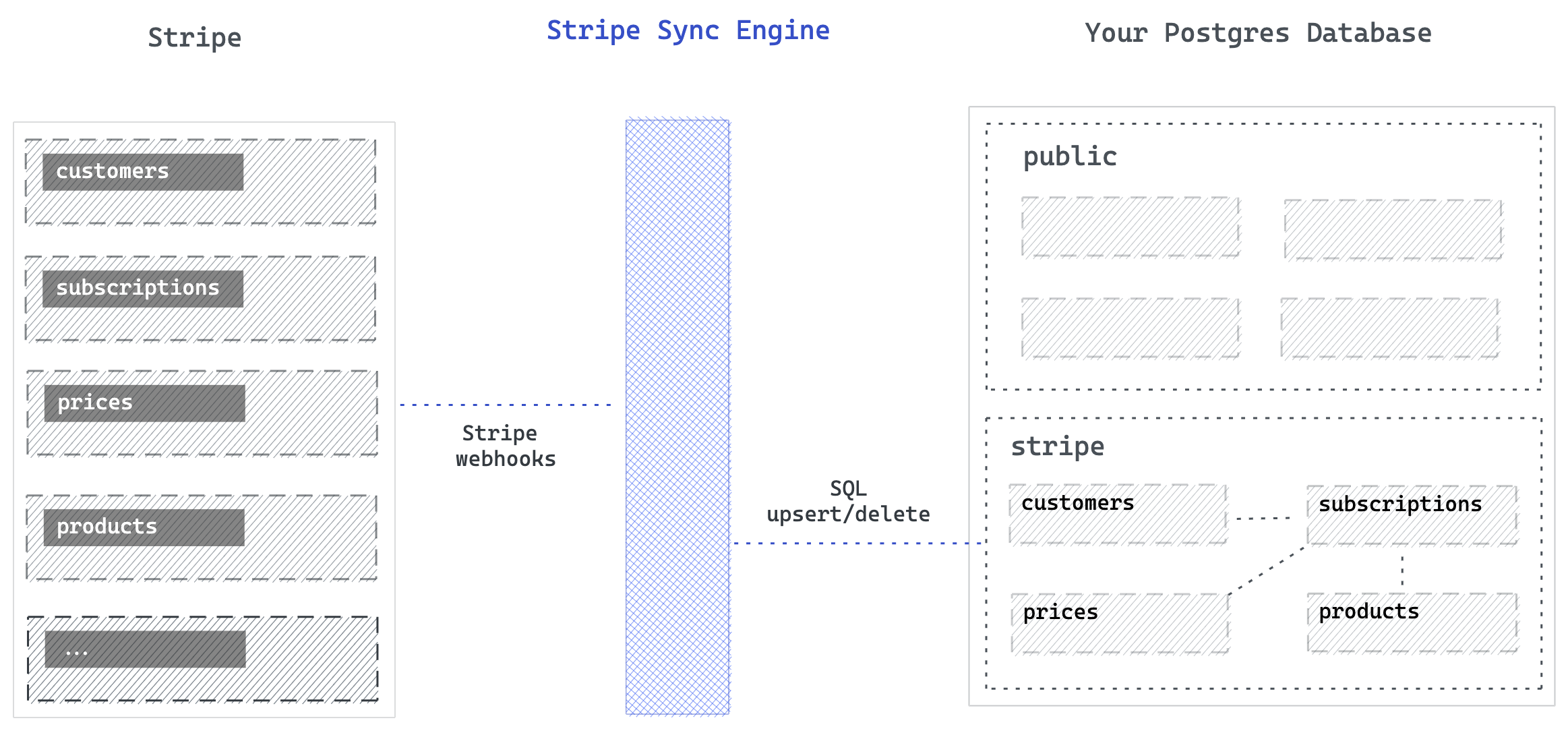
Continuously synchronizes a Stripe account to a Postgres database.
Note: this is experimental. There are no guarantees that it will be supported in the future.
Sometimes you want to analyze your billing data using SQL. Even more importantly, you want to join your billing data to your product/business data.
This server synchronizes your Stripe account to a Postgres database. It can be a new database, or an existing Postgres database.
- Creates a new schema
stripein a Postgres database, with tables & columns matching Stripe. - Exposes a
/webhooksendpoint that listens to any Stripe webhooks. - Inserts/updates/deletes changes into the tables whenever there is a change to Stripe.
Not implemented
- This will not do an initial load of existing Stripe data. You should use CSV loads for this. We might implement this in the future.
- We are progressively working through webhooks.
-
balance.available -
charge.captured🟢 -
charge.expired🟢 -
charge.failed🟢 -
charge.pending🟢 -
charge.refunded🟢 -
charge.succeeded🟢 -
charge.updated🟢 -
charge.dispute.closed🟢 -
charge.dispute.created🟢 -
charge.dispute.funds_reinstated🟢 -
charge.dispute.funds_withdrawn🟢 -
charge.dispute.updated🟢 -
checkout.session.async_payment_failed -
checkout.session.async_payment_succeeded -
checkout.session.completed -
customer.created🟢 -
customer.deleted🟢 -
customer.source.created -
customer.source.updated -
customer.subscription.created🟢 -
customer.subscription.deleted🟢 -
customer.subscription.paused🟢 -
customer.subscription.pending_update_applied🟢 -
customer.subscription.pending_update_expired🟢 -
customer.subscription.resumed🟢 -
customer.subscription.trial_will_end🟢 -
customer.subscription.updated🟢 -
customer.updated🟢 -
invoice.created🟢 -
invoice.deleted🟢 -
invoice.finalized🟢 -
invoice.finalization_failed🟢 -
invoice.paid🟢 -
invoice.payment_action_required🟢 -
invoice.payment_failed🟢 -
invoice.payment_succeeded🟢 -
invoice.upcoming🟢 -
invoice.updated🟢 -
issuing_authorization.request -
issuing_card.created -
issuing_cardholder.created -
payment_intent.amount_capturable_updated🟢 -
payment_intent.canceled🟢 -
payment_intent.created🟢 -
payment_intent.partially_refunded🟢 -
payment_intent.payment_failed🟢 -
payment_intent.processing🟢 -
payment_intent.requires_action🟢 -
payment_intent.succeeded🟢 -
payment_method.attached🟢 -
payment_method.automatically_updated🟢 -
payment_method.detached🟢 -
payment_method.updated🟢 -
plan.created🟢 -
plan.deleted🟢 -
plan.updated🟢 -
price.created🟢 -
price.deleted🟢 -
price.updated🟢 -
product.created🟢 -
product.deleted🟢 -
product.updated🟢 -
setup_intent.canceled🟢 -
setup_intent.created🟢 -
setup_intent.requires_action🟢 -
setup_intent.setup_failed🟢 -
setup_intent.succeeded🟢 -
subscription_schedule.aborted🟢 -
subscription_schedule.canceled🟢 -
subscription_schedule.completed🟢 -
subscription_schedule.created🟢 -
subscription_schedule.expiring🟢 -
subscription_schedule.released🟢 -
subscription_schedule.updated🟢
- Update your Stripe account with all valid webhooks and get the webhook secret
mv .env.sample .envand then rename all the variables- Make sure the database URL has search_path
stripe. eg:DATABASE_URL=postgres://postgres:postgres@hostname:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable&search_path=stripe - Deploy the docker image to your favourite hosting service and expose port
8080- eg:
docker run -e PORT=8080 --env-file .env supabase/stripe-sync-engine - This will automatically run any migrations on your database
- eg:
- Point your Stripe webooks to your deployed app.
POST /sync
body: {
"object": "product",
"created": {
"gte": 1643872333
}
}
objectall | charge | customer | dispute | invoice | payment_method | payment_intent | plan | price | product | setup_intent | subscriptioncreatedis Stripe.RangeQueryParam. It supports gt, gte, lt, lte
POST /sync/daily
---
POST /sync/daily
body: {
"object": "product"
}
To backfill/update a single entity, you can use
POST /sync/single/cus_12345
The entity type is recognized automatically, based on the prefix.
- Expose an "initialize" endpoint that will fetch data from Stripe and do an initial load (or perhaps
POSTa CSV to an endpoint).
Set up
- Create a Postgres database on supabase.com (or another Postgres provider)
- Update Stripe with all valid webhooks and get the webhook secret
mv .env.sample .envand then rename all the variables
Develop
npm run devto start the local servernpm run testto run tests
Building Docker
docker build -t stripe-sync-engine .
docker run -p 8080:8080 stripe-sync-engineRelease
Handled by GitHub actions whenever their is a commit to the main branch with fix or feat in the description.
Apache 2.0
Supabase is building the features of Firebase using enterprise-grade, open source products. We support existing communities wherever possible, and if the products don’t exist we build them and open source them ourselves.