Protecting a public Minecraft server by requiring authentication through web-interface.
Note, that there was a previous version which also talked to to Minecrat Server instance using the SwiftApi (allowing to monitor player stats etc.). But since the Swift stuff was very unstable for me, I dropped this. However, the mentioned version is archived in this branch.
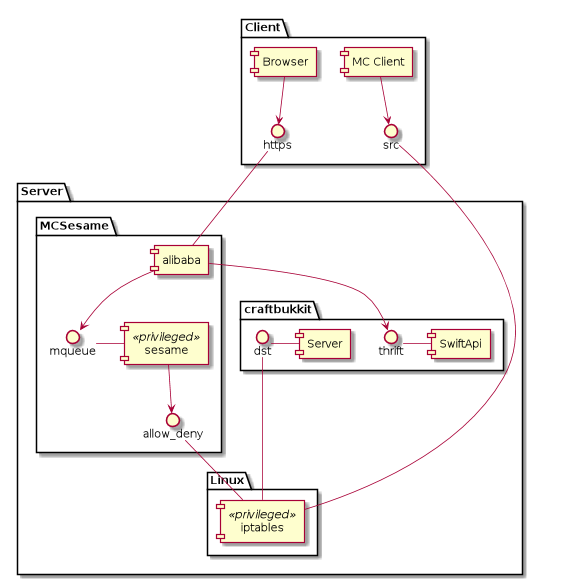
It is assumed that by default access to all ports on the server is denied by IPTables. Thus, when a MCServer is run, it's port will not be accessible from outside.
MCSesame has two daemons. sesame which adds or removes IP addresses to the IPTables
for player machines who authenticated through a web frontend provided by alibaba daemon.
User with the admin flag are allowed to add/remove/change users via the web frontend.
The figure below shows the main components of MC Sesame:
Since changing IPTables needs root rights, but it is not a a good idea (in terms of security)
to run the web serving part (alibaba) with root rights, MC Sesame needs a second daemon, sesame.
Its only purpose is to listen via posix IPC message queue to commands from alibaba and add or
remove an IP from/to the IPTables.
The openssl command is needed to create the SSL devcert. On Ubuntu/Debian it could
be added with:
sudo apt install openssl
Also a craftbukkit server on the same machine as MCSesame is needed.
First, install dependencies from requirements.txt:
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt
Next, install the MCSesame Python modules:
sudo python setup.py install
The install will also create a SSL devcert and a basic configuration and user DB under
/etc/mcsesame.
To run the daemons from this source directory, the following command has to be executed once:
python setup.py build
First start the alibaba daemon with:
sudo alibaba --user $USER
The alibaba daemon needs to be started as root, but after it accessed all the needed
files, it will drop privileges to the user given with --user.
Note, that a logfile is written to /var/log/alibaba.log.
Next, start the sesame daemon with:
sudo sesame
Again, a log file is written to /var/log/sesame.log.
Now, you could access the Alibaba web-page with the following URL:
https://<hostname>:8088/
The default login is admin with password admin.
Note: since we use only a SSL dev-cert, the browser will complain about the cert and you need to ignore this warning.
To stop the daemons use:
sudo sesame -c stop
sudo alibaba -c stop
To use a virtual environment, virualenv needs to be installed. For details
see this guide.
In brief, it could be done by:
sudo pip install virtualenv
Then, a virtual environment with all dependencies could be created like this:
sudo ./mkvenv.sh /opt/mcsesame-venv
Since the daemons need to be run as root, we need to activate the environment in a root shell:
sudo su
source /opt/mcsesame-venv/bin/activate
Now install MCSesame into that environment:
python setup.py install
Launch the daemons as described above for the system wide installation.