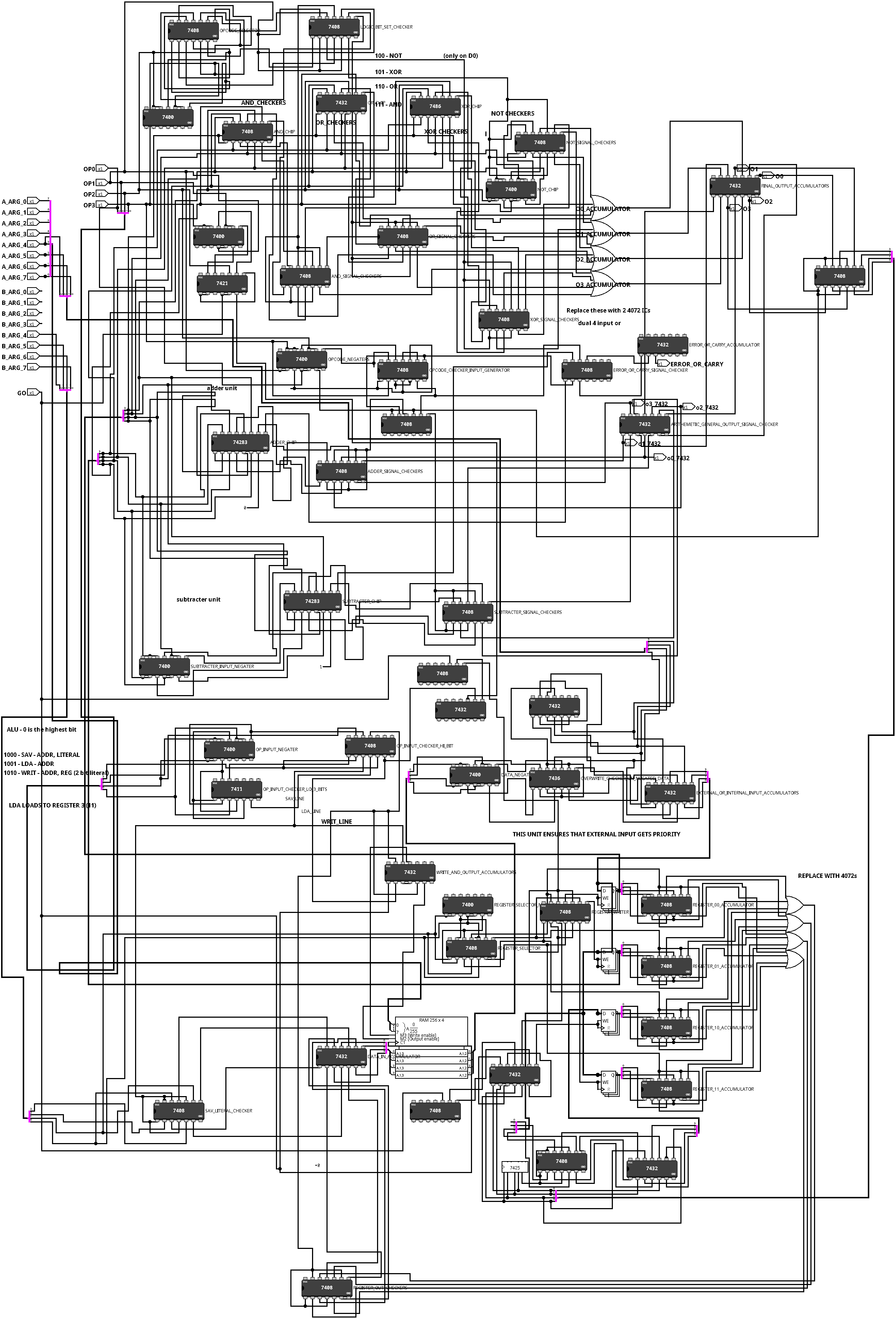
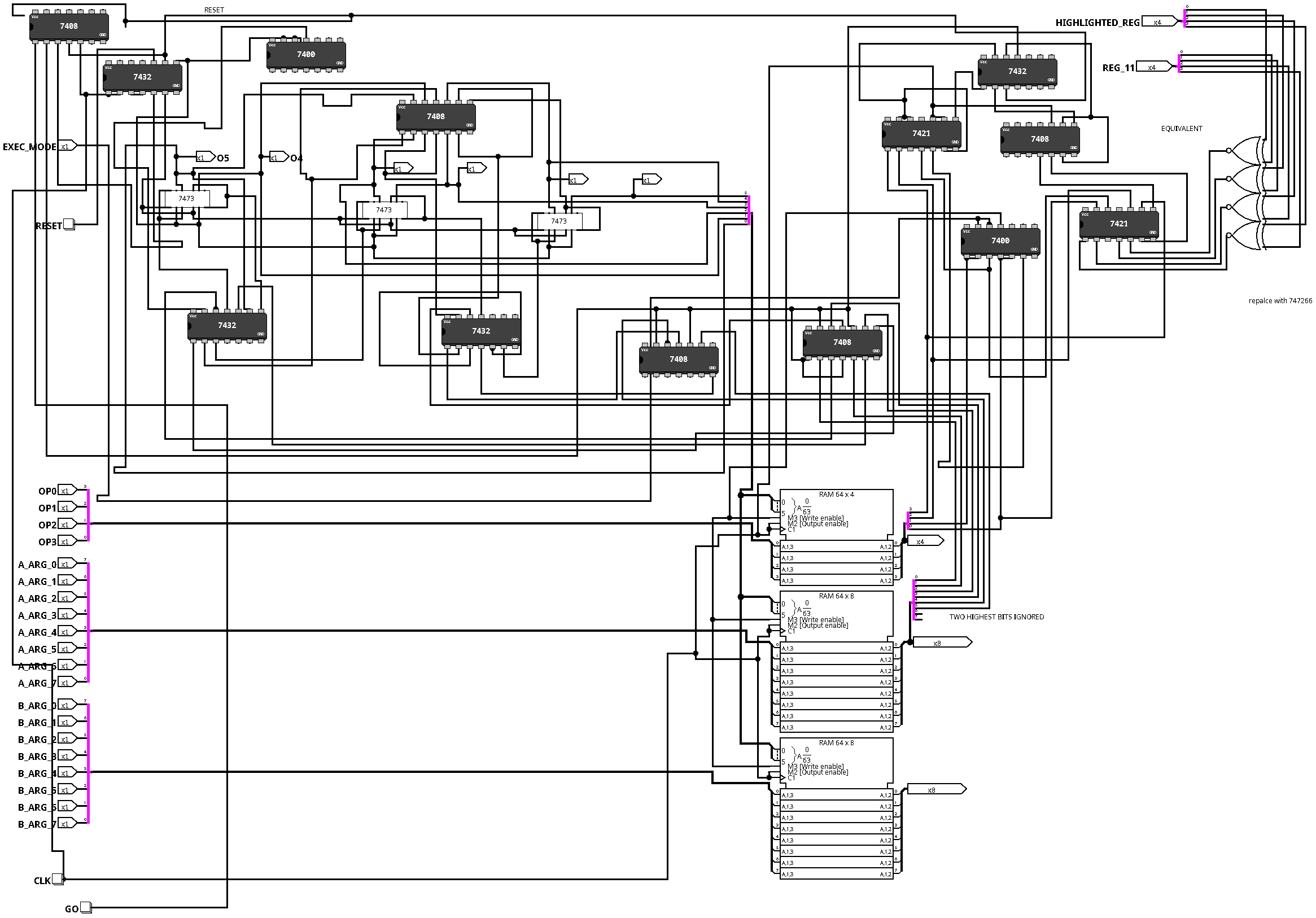
- Custom 4-bit ALU, supporting AND, OR, XOR, NOT, full add and full subtract
- 256 nibbles of general use memory
- Four registers, used for I/O to/from the ALU
- Program counter with jump and jump if zero instructions
| Binary Value | Assembly Mnemonic | A_ARG value |
B_ARG value |
Operation Description | Implemented |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0000 |
ADD |
None | None | Adds reg 00 to reg 01 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
0001 |
SUB |
None | None | Subtracts reg 01 from reg 00 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
0010 |
REG |
4 bit literal | 2 bit register address | Stores A_ARG in reg B_ARG |
Yes |
0011 |
NOP |
None | None | None | Yes |
0100 |
NOT |
None | None | Logically inverts the contents of reg 00 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
0101 |
XOR |
None | None | Performs logical XOR on registers 00 and 01 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
0110 |
OR |
None | None | Performs logical OR on registers 00 and 01 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
0111 |
AND |
None | None | Performs logical AND on registers 00 and 01 and stores in reg 10 | Yes |
1000 |
SAV |
8 bit address | 4 bit literal | Saves B_ARG to memory address B_ARG |
Yes |
1001 |
LDA |
8 bit address | 2 bit register address | Loads memory address A_ARG to reg B_ARG |
Yes |
1010 |
WRIT |
8 bit address | 2 bit register address | Saves reg B_ARG to memory address A_ARG |
Yes |
1011 |
Reserved | - | - | - | No |
1100 |
JMP |
6 bit address | None | Jumps to PC address A_ARG |
Yes |
1101 |
Reserved | - | - | - | No |
1110 |
JCU |
6 bit address | 2 bit register address | If register B_ARG is equal to register 11, jumps to memory address A_ARG |
Yes |
1111 |
Reserved | - | - | - | No |
- There are 4 "namespaces" (bitfields)
Binary range |
Use |
# uses |
|---|---|---|
0000 - 0011 |
Arithmetic uses | 2 + NOP |
0100 - 0111 |
Logical operations | 4 |
1000 - 1011 |
Memory manipulation operations | 3 |
1100 - 1111 |
Control flow operations | 3 (only 1 implemented) |
- I think it is Turing-complete or near to it? I am pretty sure it is with manual instruction entry on the ALU/Memory Unit, but the PC I am less sure of
A simple program that adds 1 to a number in memory address 0x00 and stores it in memory address 0x01
LDA 0x00 00 ; Load the number from memory address 0x00 into reg 00
REG 1 01 ; Store the literal 1 in reg 01
ADD ; Add reg 00 to reg 01 and store in reg 10
WRIT 0x01 10 ; Write the result to memory address 0x01Fully designed in Logisim, using the built in TTL library and also this library. A few logic gates are included for more obscure ICs, but they will be replaced either with said ICs or with equivalent chips in series.
The ALU/MU is the heart of the computer, and is where all the computation is done. It is a 4-bit ALU, with 256 nibbles of general use memory. The ALU/MU is connected to the program counter, and is where the instructions are executed. The MU contains the registers and the memory.
The program counter is a simple counter that increments by one each clock cycle. It is connected to the ALU/MU, and is where the instructions are fetched from memory. The CLK input loads the current instruction into the ALU/MU, and the GO input executes the instruction. It is programmable, and can jump to any address in memory, using the JMP and JCU instructions.