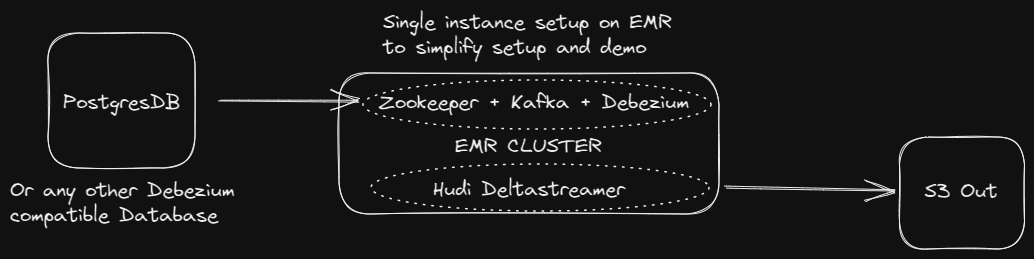
The hardest part of getting real time data from databases to S3 is setting up Debezium correctly. So majority of this course will focus on setting up Debezium and then setting up the rest of the infrastructure to accommodate streaming. Even though this course is focused on streaming from Postgres, it can easily be adapted to any database connection supported by Debezium once set up.
Debezium is a massively scalable realtime database streaming open source project. It achieves this by using Kafka Connectors to hook into each database's binary logstream and sending the changes as Kafka topics. In production environments you should use Kubernetes/AWS EKS to host the required infrastructure for zookeeper, kafka, kafka connect and debezium. There are instructions for setting this up here: https://debezium.io/documentation/reference/stable/operations/kubernetes.html
However, this tutorial will focus on setting up Debezium and it's required services on a single instance for demonstration and development purposes. In our case, we'll use a master EMR node to set up Debezium from scratch (but the steps will be the same for an EC2 instance). We'll assume only Spark is running on your EMR cluster. You can skip steps for services you already have set up.
We are going to be using a MSK cluster from AWS, but the steps should be the same regardless of if you're hosting Kafka yourself, or using Confluent or Redpanda or whatever service you need. We just need the bootstrap server endpoints and the zookeeper connection strings.
- Go to the MSK service in AWS console, and click "Create Cluster"
- Select "Custom Create"
Step1: Cluster Settings
- Give it a cluster name
- Make sure cluster type is "provisioned"
- Select Recommended Kafka Version (At time of writing that was 2.8.1)
- Select the smallest broker type (kafka.t3.small). You can always upgrade this if needed
Step2: Networking
- Select your VPC, security groups etc
Step3: Security
- Choose "Unauthenticated access". I'd recommend just getting everything to work, and then later you can make it more secure by using the recommended "IAM role-based authentication"
- Select "Plaintext" as the encryption between clients and brokers. You can change this later to the recommended "TLS encryption"
- Leave TLS encryption enabled for communication within the cluster
You can leave the rest of the things on default, then click "Create cluster"
When the cluster has been created, click on "View client information" top right on jot down the following:
- Private endpoints under bootstrap servers
- Plaintext Zookeeper connection string
In my case I created a Postgres database from https://railway.app/ (It's fast and free). I created a very simple "employees" database with 2 columns:
id: Serial (Primary Key)
full_name: Text
Make sure you jot down the connection variables from the "Connect" tab.
Now, in order to read from Postgres in real-time we need to enable the WAL (Write-Ahead-log) that will allow us to read the change stream of data. It's the same mechanism that Postgres uses to replicate data across different Postgres servers. To enable it, run the following query:
ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = 'logical';Make sure you restart the postgres server afterwards for the change to take effect.
When logged into your EMR cluster. Make sure you have java v11 or higher.
java -version
Otherwise install Java. For Amazon Linux 2 on EMR:
sudo yum install java-11-amazon-corretto
sudo update-alternatives --set java /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-amazon-corretto.aarch64/bin/java
You can find the latest version here: https://debezium.io/documentation/reference/stable/operations/debezium-server.html. At the time of writing, the latest version is 2.2, so we'll use that. Run this from your EMR cluster from any folder. In my case I'm assuming that's /home/hadoop
wget https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/io/debezium/debezium-server-dist/2.2.0.Final/debezium-server-dist-2.2.0.Final.tar.gz
tar -xzf debezium-server-dist-2.2.0.Final.tar.gz
rm debezium-server-dist-2.2.0.Final.tar.gz
You should now have a "debezium-server" folder in /home/hadoop/
We are going to install the kafka binaries on this EMR cluster to use the cli to create topics on the MSK cluster. There are various ways of doing this though. Remember to use the closest Kafka version to the one you created in the MSK console. You can see the available releases here: https://dlcdn.apache.org/kafka/
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/kafka/2.8.2/kafka_2.12-2.8.2.tgz
tar -xf kafka_2.12-2.8.2.tgz
cd kafka_2.12-2.8.2/bin
# Remember to replace the bootstrap server with any one of your bootstrap servers
# And also replace "debezium1" with the "debezium.source.topic.prefix" you'll need in the next step
./kafka-topics --bootstrap-server b-1.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092 --create --topic debezium1.public.employees
Now we'll configure and start the debezium connection to listen for changes in our Postgres database and post it to Kafka
On your EMR cluster, for each connection you want, you can copy the "debezium-server" folder created above. I'm calling my connection debezium-test1, but you should call it something more descriptive.
cp -R debezium-server debezium-test1
Create a "data" folder inside this folder for capturing offsets:
cd debezium-test1
mkdir data
chmod -R 777 data
Keep duplicating the "debezium-server" folder for each connection you want to set up.
Now create a configuration file with the content below inside the conf folder called "application.properties". In my case the file location is here: /home/hadoop/debezium-test1/conf/application.properties
You can find the list of available Postgres configuration settings, and what they do here: https://debezium.io/documentation/reference/stable/connectors/postgresql.html#postgresql-connector-properties
Please review each of these settings and make sure it correlates to your postgres and kafka settings created above. I'm just using mine here as an example:
debezium.source.connector.class=io.debezium.connector.postgresql.PostgresConnector
debezium.source.offset.storage.file.filename=./data/offsets.dat
debezium.source.offset.flush.interval.ms=1000
debezium.source.database.hostname=containers-us-west-180.railway.app
debezium.source.database.port=7866
debezium.source.database.user=xxxxx
debezium.source.database.password=xxxxx
debezium.source.database.dbname=railway
debezium.source.topic.prefix=debezium1
debezium.source.table.include.list=public.employees
debezium.source.plugin.name=pgoutput
debezium.source.database.encrypt=false
debezium.sink.type=kafka
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.key.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.value.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.bootstrap.servers=b-1.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-3.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-2.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.security.protocol=PLAINTEXT
quarkus.log.console.json=false
Once you've saved your configuration file, you can now run this connection by executing the run.sh command in the folder:
cd /home/hadoop/debezium-test1
./run.sh
Look at the output log and make sure there aren't any errors. You can now add that run command as a step on the EMR cluster to make sure it's always running. There are detailed instructions for that later.
Create a script.py somewhere on the EMR cluster (I placed mine at /home/hadoop/script.py) with the following basic code to test:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import *
from pyspark.sql.types import *
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("KafkaToS3").getOrCreate()
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN")
def process(df, batch_id):
schema = spark.read.json(df.rdd.map(lambda row: row.value)).schema
df = df \
.withColumn('json', from_json(col("value"), schema)) \
.withColumn('id', col("json.payload.after.id")) \
.withColumn('full_name', col("json.payload.after.full_name")) \
.drop('json', 'value')
df.show(vertical=True, truncate=False)
df.write.mode('append').parquet("s3://oml-dp-debezium-datalabs/output/")
# Set up the Kafka read stream
kafka_df = spark.readStream.format("kafka") \
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "b-1.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-3.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-2.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092") \
.option("subscribePattern", "debezium1.*") \
.load() \
.selectExpr("CAST(value AS STRING)")
# Write the data to S3 in Parquet format
query = kafka_df.writeStream \
.option("checkpointLocation", "s3://oml-dp-debezium-datalabs/checkpoints/") \
.foreachBatch(process) \
.start() \
.awaitTermination()Then run the script with:
spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.3.1 script.py
We need the 2 scripts (Pyspark and Debezium Connector) to be continuously running on the EMR cluster to listen for database change events and stream the results. Go to your EMR cluster in AWS console and select "Steps"
Step Type: "Custom JAR"
Name: Can be anything. I named mine "Debezium1" JAR location: command-runner.jar Arguments: bash -c /home/hadoop/debezium-test1/run.sh
Step Type: "Custom JAR"
Name: Can be anything. I named mine "PysparkDebezium1" JAR location: command-runner.jar Arguments: spark-submit --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.3.1 /home/hadoop/script.py
Please review each argument and make sure you understand each one before adding the steps and adapt it to your needs. You can add additional steps for additional Debezium Connectors.
Follow the same steps as "Step 6: Set up debezium connection between Postgres and Kafka" and create a new folder. I'm calling mine /home/hadoop/debezium-test2. Change your conf/application.properties to the following:
debezium.source.connector.class=io.debezium.connector.postgresql.PostgresConnector
debezium.source.offset.storage.file.filename=./data/offsets.dat
debezium.source.offset.flush.interval.ms=1000
debezium.source.database.hostname=containers-us-west-180.railway.app
debezium.source.database.port=7866
debezium.source.database.user=xxxx
debezium.source.database.password=xxxx
debezium.source.database.dbname=railway
debezium.source.topic.prefix=debezium1
debezium.source.table.include.list=public.employees
debezium.source.plugin.name=pgoutput
debezium.source.database.encrypt=false
debezium.sink.type=kafka
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.key.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.value.serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.bootstrap.servers=b-1.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-3.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-2.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.security.protocol=PLAINTEXT
quarkus.log.console.json=false
tombstones.on.delete=false
publication.autocreate.mode=filtered
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.key.converter=io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
debezium.sink.kafka.producer.value.converter=io.confluent.connect.avro.AvroConverter
When you're happy, then run the debezium connector:
cd /home/hadoop/debezium-test2
./run.sh
Ensure this EMR instance profile's IAM policy has access to Glue Catalogs!
Then create a hudi script to do the ingestion, I've placed mine at /home/hadoop/hudi_script.py.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import *
spark = SparkSession \
.builder \
.config("spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer") \
.config("spark.sql.hive.convertMetastoreParquet", "false") \
.getOrCreate()
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN")
database_name = "hudi"
table_name = "hudi_out"
checkpoint_location = 's3://oml-dp-debezium-datalabs/checkpoints_hudi/'
out_path = "s3://oml-dp-debezium-datalabs/output_hudi/"
prefix = 'debezium1'
kafka_topic = f'{prefix}.public.employees'
hudi_streaming_options = {
'hoodie.table.name': table_name,
'hoodie.database.name': database_name,
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.database': database_name,
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.table': table_name,
'hoodie.datasource.write.table.type': 'COPY_ON_WRITE',
'hoodie.datasource.write.operation': 'upsert',
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.create_managed_table': 'true',
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.enable': 'true',
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.mode': 'hms',
'hoodie.datasource.write.recordkey.field': 'timestamp',
'hoodie.datasource.write.precombine.field': 'timestamp',
'hoodie.datasource.write.hive_style_partitioning': 'true',
'hoodie.datasource.write.reconcile.schema': 'true',
'hoodie.deltastreamer.source.kafka.value.deserializer.class': 'io.confluent.kafka.serializers.KafkaAvroDeserializer',
'hoodie.deltastreamer.source.kafka.topic': kafka_topic,
'hoodie.datasource.hive_sync.partition_extractor_class': 'org.apache.hudi.hive.MultiPartKeysValueExtractor',
'auto.offset.reset': 'earliest'
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Read stream and do transformations
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def process(df, batch_id):
schema = spark.read.json(df.rdd.map(lambda row: row.value)).schema
df = df \
.withColumn('json', from_json(col("value"), schema)) \
.withColumn('id', col("json.payload.after.id")) \
.withColumn('full_name', col("json.payload.after.full_name")) \
.drop('json', 'value')
df.show(vertical=True, truncate=False)
df.write.mode('append').parquet(out_path)
df = spark.readStream.format("kafka") \
.option("kafka.bootstrap.servers", "b-1.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-3.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092,b-2.debeziummsk.d1e4h8.c6.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9092") \
.option("subscribePattern", f"{prefix}.*") \
.load() \
.selectExpr("timestamp", "CAST(value AS STRING)")
df.writeStream.format("hudi") \
.options(**hudi_streaming_options) \
.option("checkpointLocation", checkpoint_location) \
.foreachBatch(process) \
.start() \
.awaitTermination()And then run it like before, but with the additional hudi packages. You can also run this as a step instead.
clear && spark-submit --jars /usr/lib/hudi/hudi-spark-bundle.jar --packages org.apache.spark:spark-sql-kafka-0-10_2.12:3.3.1,org.apache.spark:spark-avro_2.13:3.3.1 --class org.apache.hudi.utilities.deltastreamer.HoodieDeltaStreamer hudi_script.py --source-class org.apache.hudi.utilities.sources.debezium.PostgresDebeziumSource --source-ordering-field _event_lsn --payload-class org.apache.hudi.common.model.debezium.PostgresDebeziumAvroPayload