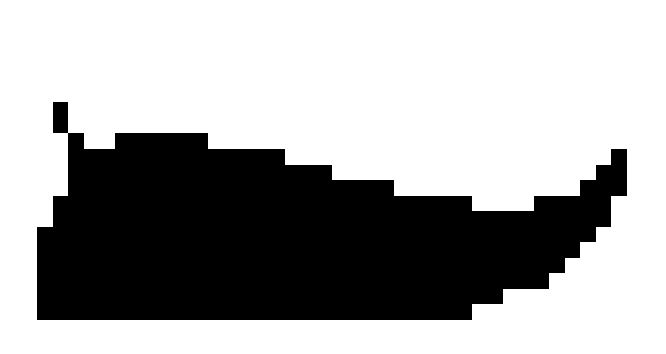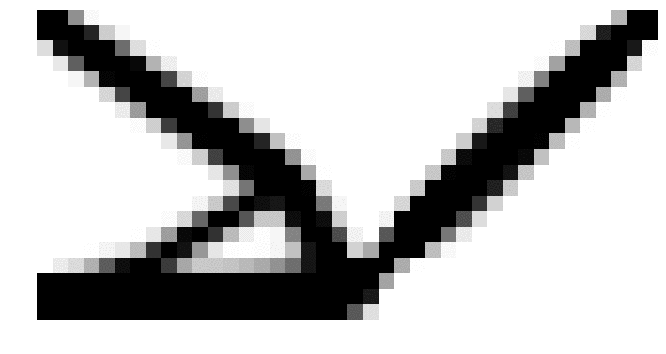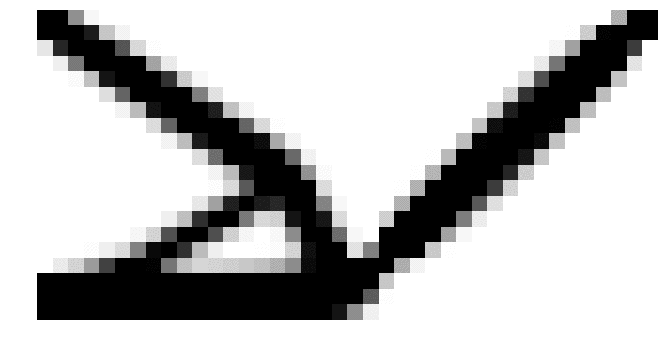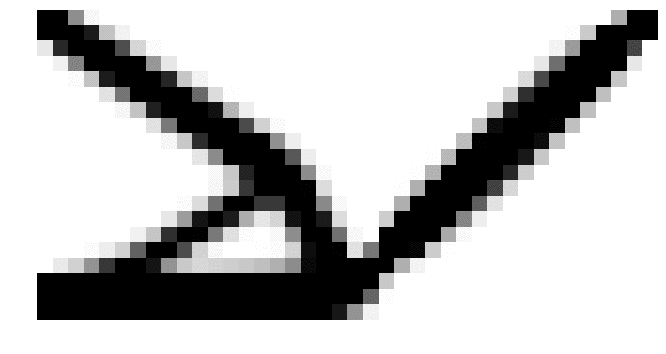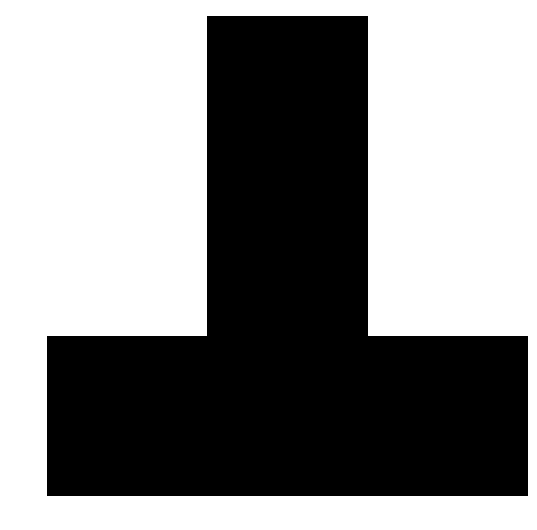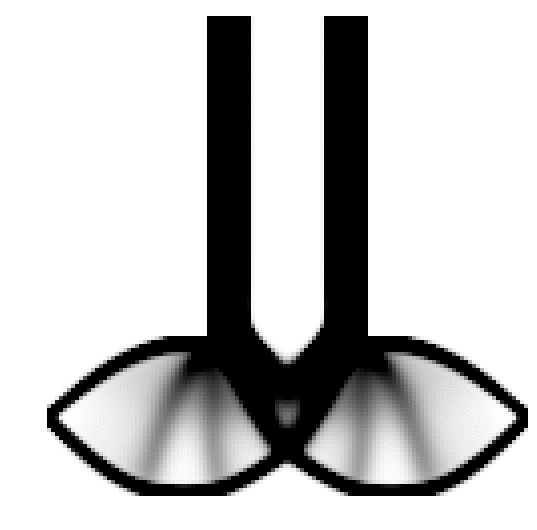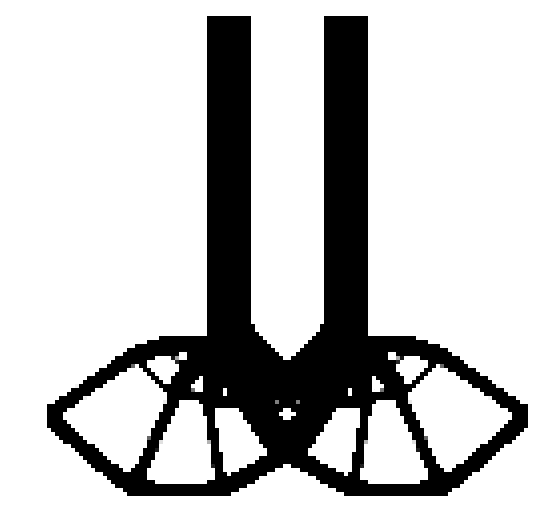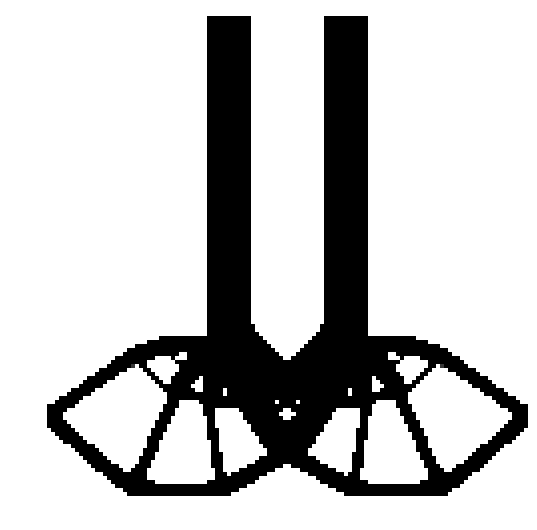ToPy is a lightweight topology optimization framework for Python that can solve compliance (stiffness), mechanism synthesis and heat conduction problems in 2D and 3D. Please refer to the ToPy Wiki for further information.
An example TPD file and solution/result
NOTE: I've added a 0.4.1 release, which is older then the master branch, but will get you up and running with Python 2 and Pysparse if you're willing to use the Anaconda Python distribution
Once you've downloaded the dependencies (see the INSTALL file) all you need to do is the following:
Download the latest stable release from here: https://github.com/williamhunter/topy/releases/latest
Then do
$ cd topy/topy
$ python setup.py installToPy is fairly old. I started working on it in 2005 and finished it around 2009, so that implies that the stable release only works with Python 2. You can however pull the latest "unstable" version, which should work with Python 3 (thanks to the efforts of other people).
The main class of ToPy is 'Topology'. It defines the main constraints, grid and parameters of optimization -- but you don't really have to bother yourself with this if you just want to get some results.
- TPD file: You define the problem with keywords
(see Help) in a simple text file and solve via the command line. The text file must have the extension
.tpd - Config dictionary: This is similar to the TPD file approach, however, you define the problem directly in a Python file; it's very useful if you want to experiment and don't want to keep making changes to a text file. You can later save the Config keywords to a TPD file.
There is a minimal set of parameters which is required for successful definition of a ToPy problem:
PROB_TYPE : comp
PROB_NAME : mbb_beam_minimal
ETA : 0.5
DOF_PN : 2
VOL_FRAC : 0.5
FILT_RAD : 1.5
P_FAC : 3
ELEM_K : Q4
NUM_ELEM_X : 60
NUM_ELEM_Y : 20
NUM_ELEM_Z : 0
NUM_ITER : 10
FXTR_NODE_X: 1|21
FXTR_NODE_Y: 1281
LOAD_NODE_Y: 1
LOAD_VALU_Y: -1
You can read more about successful problem definition here.
When the TPD file is defined, then the rest is simple:
from topy import Topology
topology = Topology()
topology.load_tpd_file('file.tpd')First you have to define a config dictionary (note the similarity with a TPD file, especially the keywords):
config = {
'DOF_PN': 2,
'ELEM_K': 'Q4',
'ETA': '0.5',
'FILT_RAD': 1.5,
'FXTR_NODE_X': range(1, 22),
'FXTR_NODE_Y': 1281,
'LOAD_NODE_Y': 1,
'LOAD_VALU_Y': -1,
'NUM_ELEM_X': 60,
'NUM_ELEM_Y': 20,
'NUM_ELEM_Z': 0,
'NUM_ITER': 94,
'PROB_NAME': 'beam_2d_reci',
'PROB_TYPE': 'comp',
'P_FAC': 3.0,
'VOL_FRAC': 0.5
}The requirements are the same as for the TPD file.
topology = Topology(config=config)You can use the command line solution:
$ python topy/scripts/optimise.py <filename>.tpdOr you can use a Python script:
import topy
config = {...}
t = topy.Topology(config)
t.set_top_params()
topy.optimise(t)Module topy.visualization allows one to save the output as a .png image for 2D problems or as a .vtk file for 3D.
The VTK files can be viewed with Mayavi or ParaView.
You can animate the PNG images with
the convert tool.
convert -delay 35 *.png anim.gifIf you've used ToPy in your research work or find it useful in any way, please consider to cite:
@misc{Hunter2007william,
author = {Hunter, William and others},
title = {ToPy - Topology optimization with Python},
year = {2017},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/williamhunter/topy}},
}