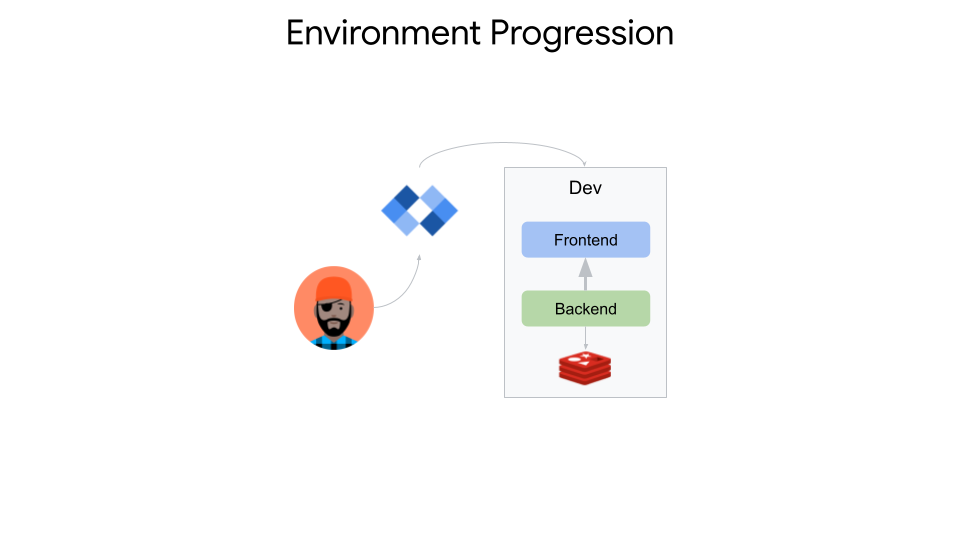
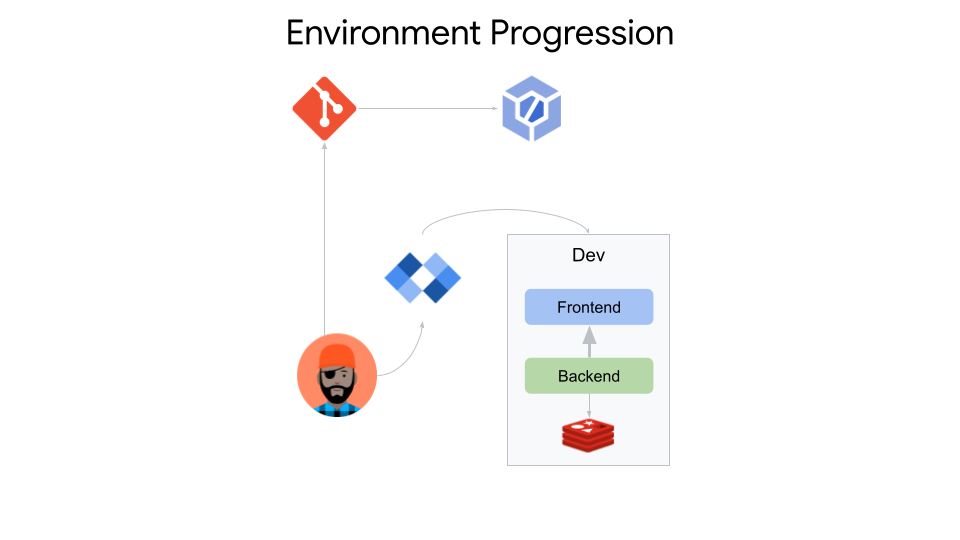
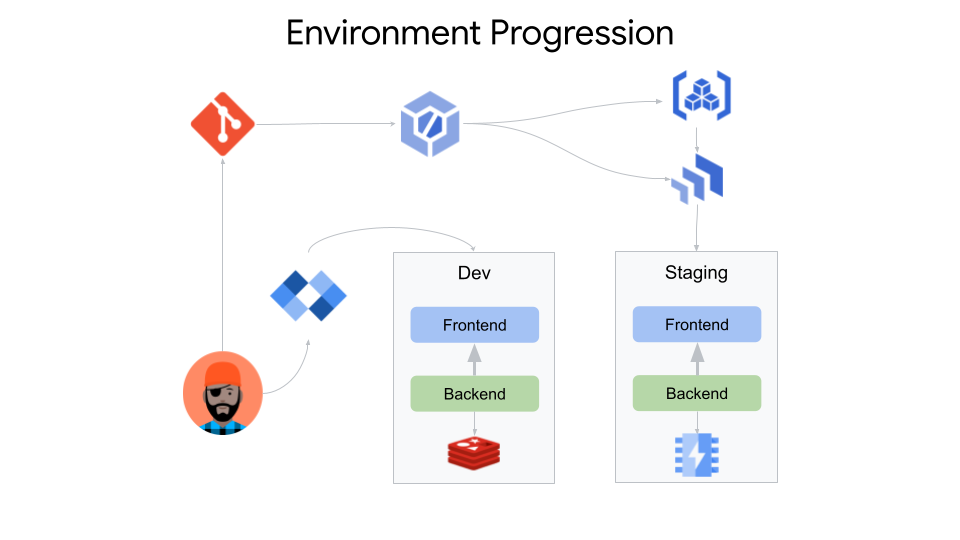
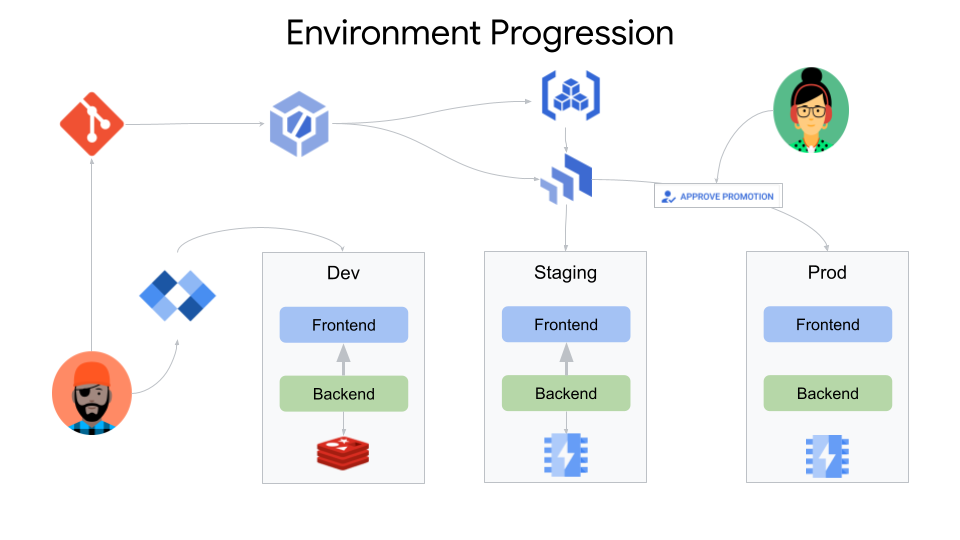
Sample App For End to End Golden Path
Boostrapping your project
- Run
./demo-startup.shto prepare the environment - Auto-generate the skaffold config and kubernetes deployment manifest and enter 8080 when asked about the port.
skaffold init --generate-manifests - Add the following YAML to the end of deployment.yaml to ensure redis is properly deployed and rbac is configured
--- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: name: redis labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:5.0.4 command: - redis-server env: - name: MASTER value: "true" ports: - containerPort: 6379 resources: limits: cpu: "0.3" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /redis-master-data name: data volumes: - name: data emptyDir: {} --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: redis spec: ports: - name: redis port: 6379 protocol: TCP selector: app: redis --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: namespace: default name: info-getter rules: - apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group resources: ["pods"] verbs: ["get"] - apiGroups: ["redis.cnrm.cloud.google.com"] resources: ["redisinstances"] verbs: ["get", "list"] --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: get-info namespace: default subjects: # You can specify more than one "subject" - kind: ServiceAccount name: default # "name" is case sensitive roleRef: # "roleRef" specifies the binding to a Role / ClusterRole kind: Role #this must be Role or ClusterRole name: info-getter # this must match the name of the Role or ClusterRole you wish to bind to apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io - The app will need an environment variable called
VERSIONin order to correctly find redis. Edit deployment.yaml and ensure the appropriate section matches the below YAMLspec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: go-mod-image template: metadata: labels: app: go-mod-image spec: containers: - name: go-mod-image image: go-mod-image env: - name: VERSION value: staging - Edit skaffold.yaml and add testing between the build and deploy YAML so the file looks like this
build: ... test: - image: go-mod-image custom: - command: go test deploy: ... - Edit skaffold.yaml and change the
apiVersiontoskaffold/v2beta16- Note: this step shouldnt be necessary once Cloud Deploy exits beta
- On the bar at the absolute bottom of the IDE, click Cloud Code > Run on Kubernetes and watch the app build and deploy to minikube in the console output
- See the app running at http://localhost:8080
- Open main.go and change the value of
var colorto blue/red and watch the app rebuild in the console output - See the change running at http://localhost:8080
- You can debug the app by doing the following:
- Click the Cloud Code stop button at the top of the IDE
- Open main.go and add a breakpoint on the line
counter, err := incrCounter(c) - On the bar at the absolute bottom of the IDE, click Cloud Code > Debug on Kubernetes
Your app is now deployed locally on minikube with redis.
Configure Cloud Build Trigger
- Log into GitHub, fork this repository, and follow these steps to connect the forked repository to Cloud Build
- Create a file called cloudbuild.yaml and add the following to it:
substitutions: _REGION: us-central1 steps: - name: 'gcr.io/k8s-skaffold/skaffold' entrypoint: 'sh' args: - -xe - -c - | # Build and push images skaffold build --file-output=/workspace/artifacts.json \ --default-repo=${_REGION}-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/sample-app-repo \ --push=true # Test images skaffold test --build-artifacts=/workspace/artifacts.json - name: 'google/cloud-sdk:latest' entrypoint: 'sh' args: - -xe - -c - | gcloud alpha deploy releases create $SHORT_SHA-$(date +%s) \ --delivery-pipeline sample-app \ --description "$(git log -1 --pretty='%s')" \ --region ${_REGION} \ --build-artifacts /workspace/artifacts.json artifacts: objects: location: 'gs://$PROJECT_ID-gceme-artifacts/' paths: - '/workspace/artifacts.json' options: machineType: E2_HIGHCPU_8 timeout: 3600s - Create the Cloud Build trigger for whenever a push is made to the main branch
gcloud beta builds triggers create github \ --name="sample-app-repo" \ --repo-owner="willisc7" \ --repo-name="next21-demo-golden-path" \ --branch-pattern="main" \ --build-config="cloudbuild.yaml"
You now have Cloud Build configured for continuous integration.
Configure Cloud Deploy and Rollout to Staging
- Create the deployment manifest for the staging environment
cp deployment.yaml deployment-staging.yaml - Edit deployment-staging.yaml and remove the redis service and deployment sections shown below
--- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: redis spec: selector: matchLabels: app: redis template: metadata: name: redis labels: app: redis spec: containers: - name: redis image: redis:5.0.4 command: - redis-server env: - name: MASTER value: "true" ports: - containerPort: 6379 resources: limits: cpu: "0.3" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /redis-master-data name: data volumes: - name: data emptyDir: {} --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: redis spec: ports: - name: redis port: 6379 protocol: TCP selector: app: redis - Still editing deployment-staging.yaml, add the following YAML to the end of the file to deploy a redis in GCP using GCP Config Connector
--- apiVersion: redis.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: RedisInstance metadata: name: redis-staging spec: displayName: Redis Instance region: us-central1 authorizedNetworkRef: name: default tier: BASIC memorySizeGb: 16 connectMode: PRIVATE_SERVICE_ACCESS - Edit skaffold.yaml and add the staging, canary, and prod profiles to the end of the file
profiles: - name: staging deploy: kubectl: manifests: - deployment-staging.yaml - name: canary deploy: kubectl: manifests: - deployment-canary.yaml - name: prod deploy: kubectl: manifests: - deployment-prod.yaml - Create a file called pipeline.yaml and add the following YAML to it. This will be the pipeline for deploying to staging and prod
apiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: DeliveryPipeline metadata: name: sample-app labels: app: sample-app description: sample-app delivery pipeline serialPipeline: stages: - targetId: staging profiles: - staging - targetId: canary profiles: - canary - targetId: prod profiles: - prod - Create the Cloud Deploy pipeline
gcloud alpha deploy apply --region us-central1 --file ./pipeline.yaml - Create the staging deployment file called staging-deploy.yaml replacing
PROJECT_NAMEwith your GCP projectapiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: Target metadata: name: staging annotations: {} labels: {} description: staging gkeCluster: project: PROJECT_NAME cluster: staging location: us-central1 - Configure the staging step of the CD pipeline
gcloud alpha deploy apply --region us-central1 --file ./staging-deploy.yaml - Trigger Cloud Build (CI) and Cloud Deply (CD) processes
git add . && git commit -am "Trigger build and deploy to staging" && git push - Navigate to the Cloud Build console to watch the build and then the Cloud Deploy console to watch the deploy
- You can check the app deployed in staging by running the following command and copy/pasting the link in the comment into your browser
kubectl proxy --port 8001 --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_staging # http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/default/services/go-mod-image:8080/proxy/
You now have Cloud Build pushing artifacts to Artifact Registry and triggering a Cloud Deploy pipeline to deploy your application to the staging environment.
Rollout to Canary and Prod
- Create the canary and prod deployment manifests
cp deployment-staging.yaml deployment-canary.yaml cp deployment-staging.yaml deployment-prod.yaml - Edit deployment-canary.yaml and deployment-prod.yaml and remove the redis YAML shown below. The canary deployment will use the prod version of redis and we will be spinning up the prod version of redis separately in a moment. IMPORTANT: also make sure you change the value of
VERSIONtocanaryorprodas appropriate.apiVersion: redis.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: RedisInstance metadata: name: redis-staging spec: displayName: Redis Instance region: us-central1 authorizedNetworkRef: name: default tier: BASIC memorySizeGb: 16 connectMode: PRIVATE_SERVICE_ACCESS - Push the changes so Cloud Deploy can use these files
git add . && git commit -am "Trigger build" && git push - Create a file called redis.yaml and paste the following YAML into it
apiVersion: redis.cnrm.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: RedisInstance metadata: name: redis-prod spec: displayName: Redis Instance region: us-central1 authorizedNetworkRef: name: default tier: BASIC memorySizeGb: 16 connectMode: PRIVATE_SERVICE_ACCESS - Deploy redis in prod before rolling out the canary deploy. In a real environment redis would already be in prod and you would not want to be automating the deployment alongside an application release.
kubectl apply -f redis.yaml --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod - Watch until the prod deployment of redis has a
READYstatus ofTruekubectl get redisinstances -w --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod - Create a file called canary-deploy.yaml. This will be the canary deployment configuration file. Copy the following YAML into it, replacing
PROJECT_NAMEwith the appropriate nameapiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: Target metadata: name: canary annotations: {} labels: {} description: canary gkeCluster: project: PROJECT_NAME cluster: prod location: us-central1 - Create a file called prod-deploy.yaml. This will be the prod deployment configuration file. Copy the following YAML into it, replacing
PROJECT_NAMEwith the appropriate nameapiVersion: deploy.cloud.google.com/v1beta1 kind: Target metadata: name: prod annotations: {} labels: {} description: prod requireApproval: true gkeCluster: project: PROJECT_NAME cluster: prod location: us-central1 - Configure the canary and prod steps of the CD pipeline
gcloud alpha deploy apply --region us-central1 --file ./canary-deploy.yaml gcloud alpha deploy apply --region us-central1 --file ./prod-deploy.yaml - Promote to canary. Hit Enter at the prompt.
RELEASE_NAME=$(gcloud alpha deploy releases list --delivery-pipeline sample-app --region us-central1 --format json | jq -r '.[0].name' | cut -d '/' -f8) gcloud alpha deploy releases promote --release $RELEASE_NAME \ --delivery-pipeline sample-app \ --region us-central1 - You can check the app deployed as a canary in prod by running the following command and copy/pasting the link in the comment into your browser
kubectl proxy --port 8002 --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod # http://localhost:8002/api/v1/namespaces/default/services/go-mod-image:8080/proxy/ - Navigate to the Cloud Deploy console and see that the canary deployment is green
- Promote the app from canary to prod. Hit Enter at the prompt.
RELEASE_NAME=$(gcloud alpha deploy releases list --delivery-pipeline sample-app --region us-central1 --format json | jq -r '.[0].name' | cut -d '/' -f8) gcloud alpha deploy releases promote --release $RELEASE_NAME \ --delivery-pipeline sample-app \ --region us-central1 - Check the Cloud Deploy console again to see that the release is pending approval before it can be deployed to prod
- Approve the rollout to prod
RELEASE_NAME=$(gcloud alpha deploy releases list --delivery-pipeline sample-app --region us-central1 --format json | jq -r '.[0].name' | cut -d '/' -f8) ROLLOUT_NAME=$(gcloud alpha deploy rollouts list --delivery-pipeline sample-app --region us-central1 --release $RELEASE_NAME --format json | jq -r '.[0].name' | cut -d '/' -f10) gcloud alpha deploy rollouts approve $ROLLOUT_NAME \ --delivery-pipeline=sample-app \ --release $RELEASE_NAME \ --region us-central1 - Navigate to the Cloud Deploy console and see that the prod deployment is green
- You can check the app deployed in prod by running the following command and copy/pasting the link in the comment into your browser
kubectl proxy --port 8002 --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod # http://localhost:8002/api/v1/namespaces/default/services/go-mod-image:8080/proxy/
You now have Cloud Deploy creating canary releases on prod that can be approved by the appropriate person and deployed to prod.
Optional: Reset to Beginning
- Delete the Cloud Deploy pipeline
gcloud alpha deploy delete --file ./pipeline.yaml --region us-central1 --force - Delete the Cloud Build trigger here
- Either delete the prod and staging clusters or do the following on the prod, staging, and minikube clusters if you want to keep them running
kubectl delete deploy go-mod-image --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod kubectl delete deploy go-mod-image --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_staging kubectl delete redisinstances redis-prod --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_prod kubectl delete redisinstances redis-staging --context gke_$(gcloud config get-value project)_us-central1_staging - Delete the redis instances here
- Remove all the files we created and push the changes
rm *.yaml git add . && git commit -am "reset" && git push