This repository contains the cloud infrastructure used in the hackathon. Additionally, it contains the IoT example configured by the Asset Interface Description discussed during session. This repository is self-contained, meaning that you should be able to recreate the exercise at home after the event.
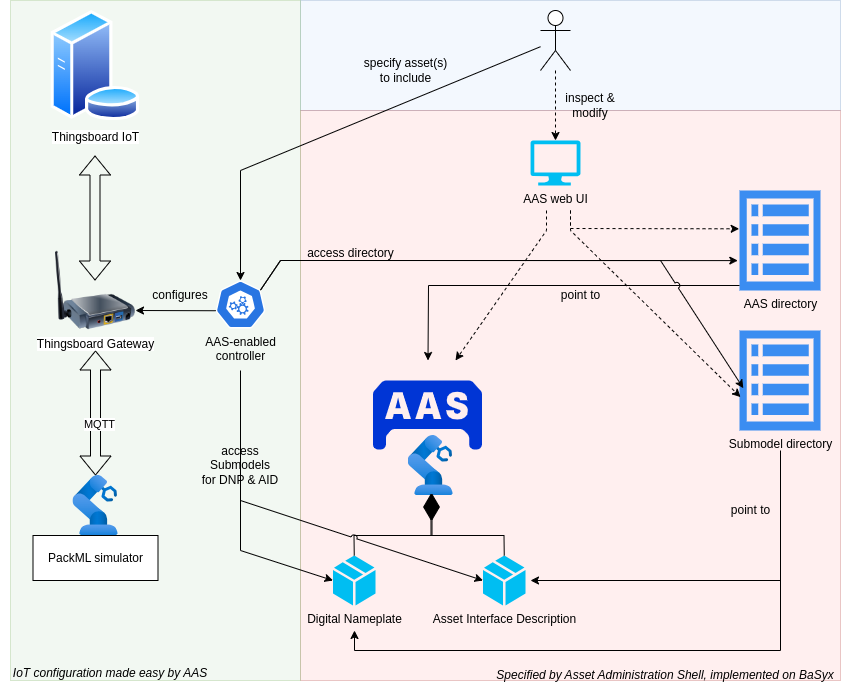 In this example we configure a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) tool, i.e. Thingsboard, with information from one or several AASs.
For this purpose a small controller was written in Python, which continuously compares the Asset Interface Description with the running configuration in the thingsboard-gateway.
Upon changes the gateway configuration files are adjusted and the gateway software is restarted to activate the updated configuration.
Hereafter, the gateway software connects directly to the MQTT topics of the asset.
In this example we configure a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) tool, i.e. Thingsboard, with information from one or several AASs.
For this purpose a small controller was written in Python, which continuously compares the Asset Interface Description with the running configuration in the thingsboard-gateway.
Upon changes the gateway configuration files are adjusted and the gateway software is restarted to activate the updated configuration.
Hereafter, the gateway software connects directly to the MQTT topics of the asset.
This deployment uses multiple docker-compose files to somewhat separate the various products and concepts used. If you are unfamiliar with Docker, please stick to the suggested commands and ask for help early.
-
Install Docker, see https://docs.docker.com/desktop/
Note:
docker composeis required for the setup, please check that your distribution includes this application. -
On Linux, don't forget the postinstall: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/
- Run
docker network create -d bridge ah-backend
- Please change the
PUBLIC_IPvariable in thedefault.envfile to your public IP address. The AAS registry will advertise this IP-address later to clients, hencelocalhostdoes not work.
- Run
docker compose -f docker-compose.basyx.yml --env-file default.env up -d
- Run
docker compose -f docker-compose.iot.yml --env-file default.env up -d
- Open the Thingsboard web UI on
http://{PUBLIC_IP}:8888, use usernametenant@thingsboard.organd passwordtenant. - Navigate
Entities->Devices - Add a new device by clicking on the
+in the top-right corner - Use name
hackaschool-gatewayand toggle theIs gatewayto 'on'. - Click
Next: Credentials(NOTAddyet) - Use access token
1234 - Click
Addand thenClose
Note: If you open the device (by clicking on it) then you can inspect the Last telemetry, which is the telemetry of the gateway software.
After the gateway software starts there should be some entries shown here.
Similarly, when thingsboard adds the asset (after connection) there will be a new device with similar tabs.
- Install the Postman tool to work with REST+JSON.
- A so-called Postman collection (
AAS.postman_collection.json) is supplied for your convenience to work with AASs. Basically it lists a few basic AAS REST calls with parameters and parses JSON return values. - Import the collection into Postman.
- Please change the
IP_ADDRvariable to the same IP-address asPUBLIC_IPin the Basyx section.
Most of the configuration has already been done during the setup or has been pre-configured in the automation scripts. The last remaining step is to upload the AASX describing the asset.
- Open Postman
- Select the
Upload AASXPOST call - Navigate to the
Bodytab - Select
form-dataand add a new key-value pair. For the key writefile, selectFilefrom the dropdown and select the supplied AASX fileSpruik_AID.aasxwhich can be found in theaasxfolder. - Click
Sendand you should gettruein theResponsebox. A blank response or 40X response usually points to trouble, please ask for help.
Please check if the AAS and Submodels have been added correctly in the registries and if they can be accessed. Hint: Use the Postman collection and navigate in the JSON response.
The AID specifies where the mqtt broker can be found, but this needs the public ip address used earlier. Since the AAS is created using a static file the address still needs to be added.
- Open the Basyx AAS UI on
http://localhost:8080, Here you can inspect all you AASes availble. - Click in the left column on
SpruikPackMLSimulator - Click in the second column on the arrow in frond of
AssetInterfaceDescription. - Follow the tree down untill you can click on at
AssetInterfaceDescription/MQTT/EndpointMetadata/base - In the third colomn change
localhost:1884to{PUBLIC_IP}:1884and click the blue upload button to the right. - Refresh the page and verify that the value remains
{PUBLIC_IP}:1884
In the end this step should be automatic. Can you think of a good way to achieve this?
Now data from the asset should be collected by the gateway and transferred to Thingsboard. Open the Thingsboard web UI again and navigate to the devices to see if a new device was added. Does the device also have telemetry data?
To restart the PackML simulator you need to install mosquitto and can use the following commands:
- Reset with mosquitto (MQTT client)
mosquitto_pub -h localhost -p 1884 -t "Site/Area/Line/Command/Reset" -m 1 - Start (after reset) with
mosquitto_pub -h localhost -p 1884 -t "Site/Area/Line/Command/Start" -m 1
Note: You might need to change the -h parameter to point to the broker.
- This project is made possible by a contribution from the National Growth Fund program NXTGEN Hightech.
- Spruik/PackML-MQTT-Simulator
- BaSyx
- AAS web UI