- window 10 版本19041
- Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2019 版本 16.6.4
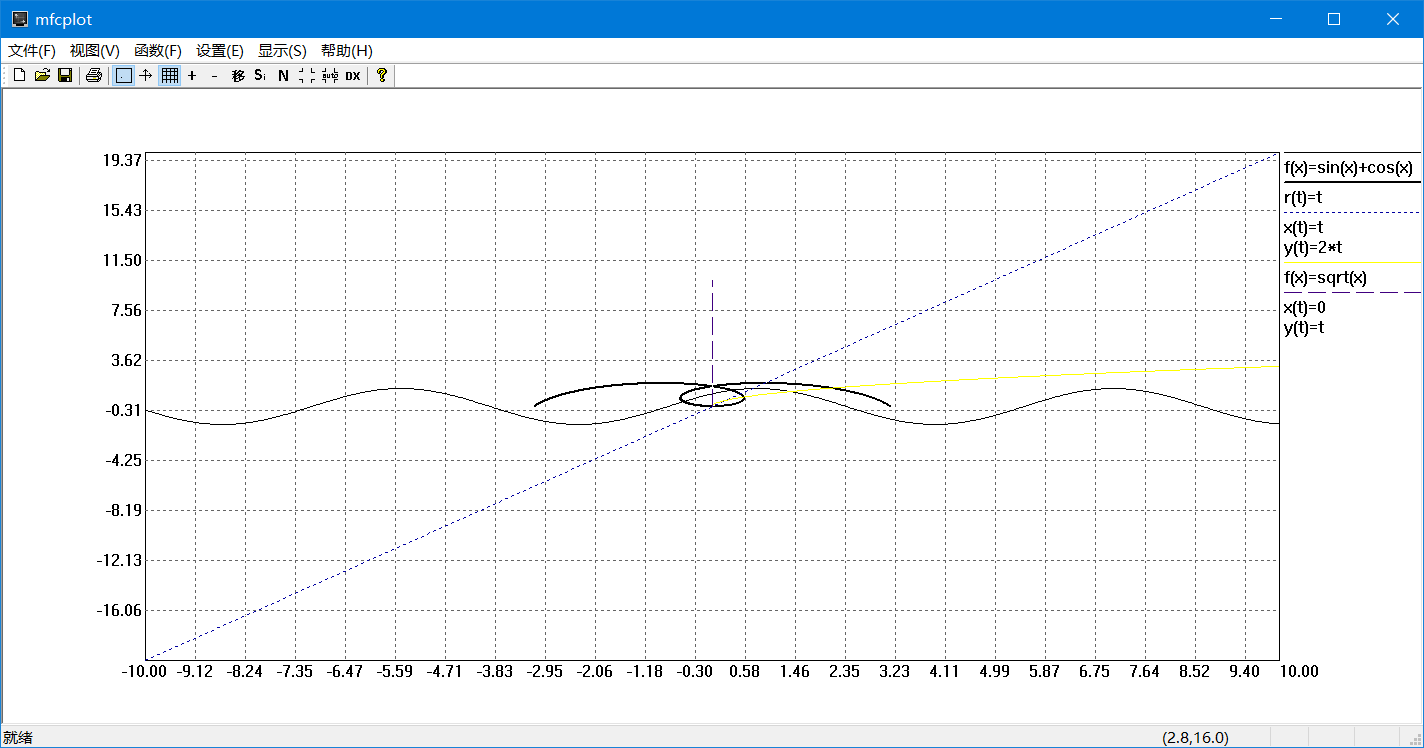
- 绘制常见一元函数的图像
- 支持普通函数,极坐标函数,参数方程,直接输入数据点
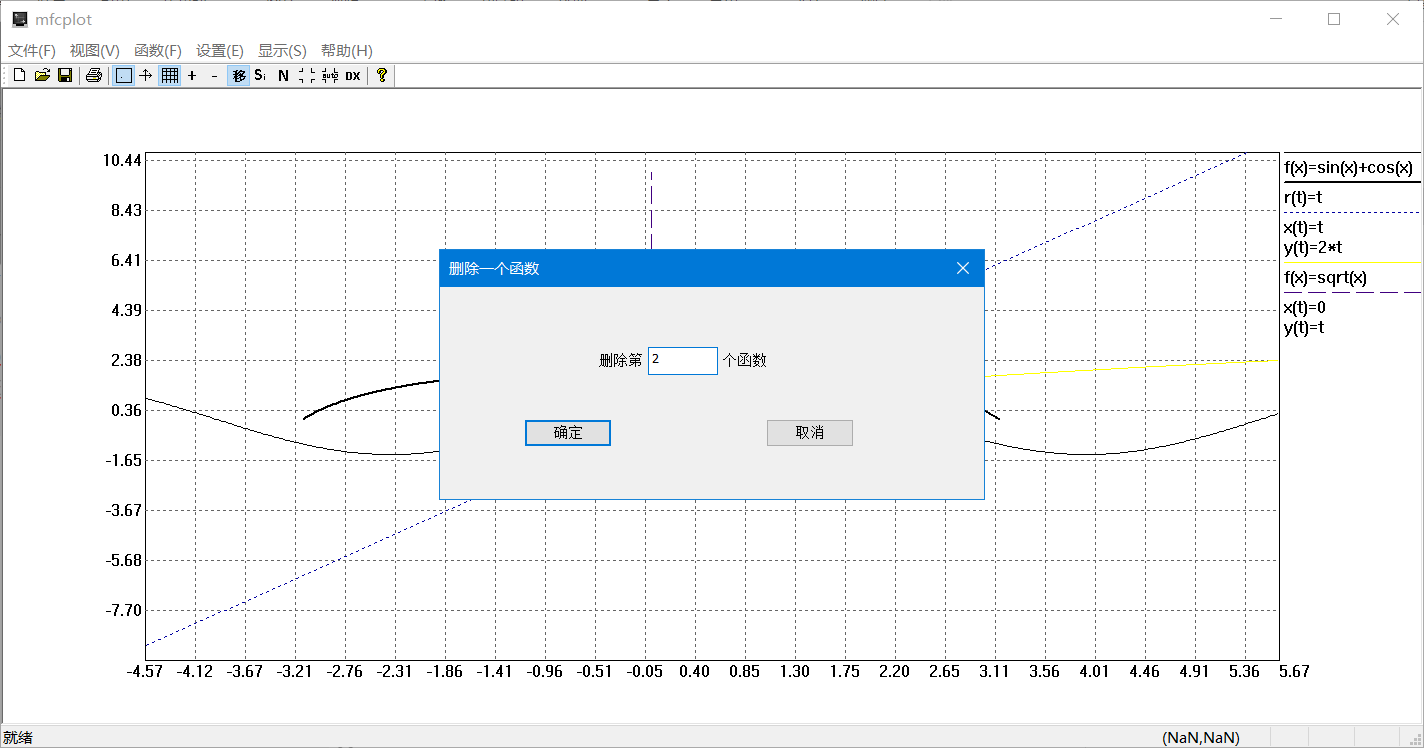
- 可以删除指定函数图像
- 可以在一个坐标系中绘制多条数学曲线
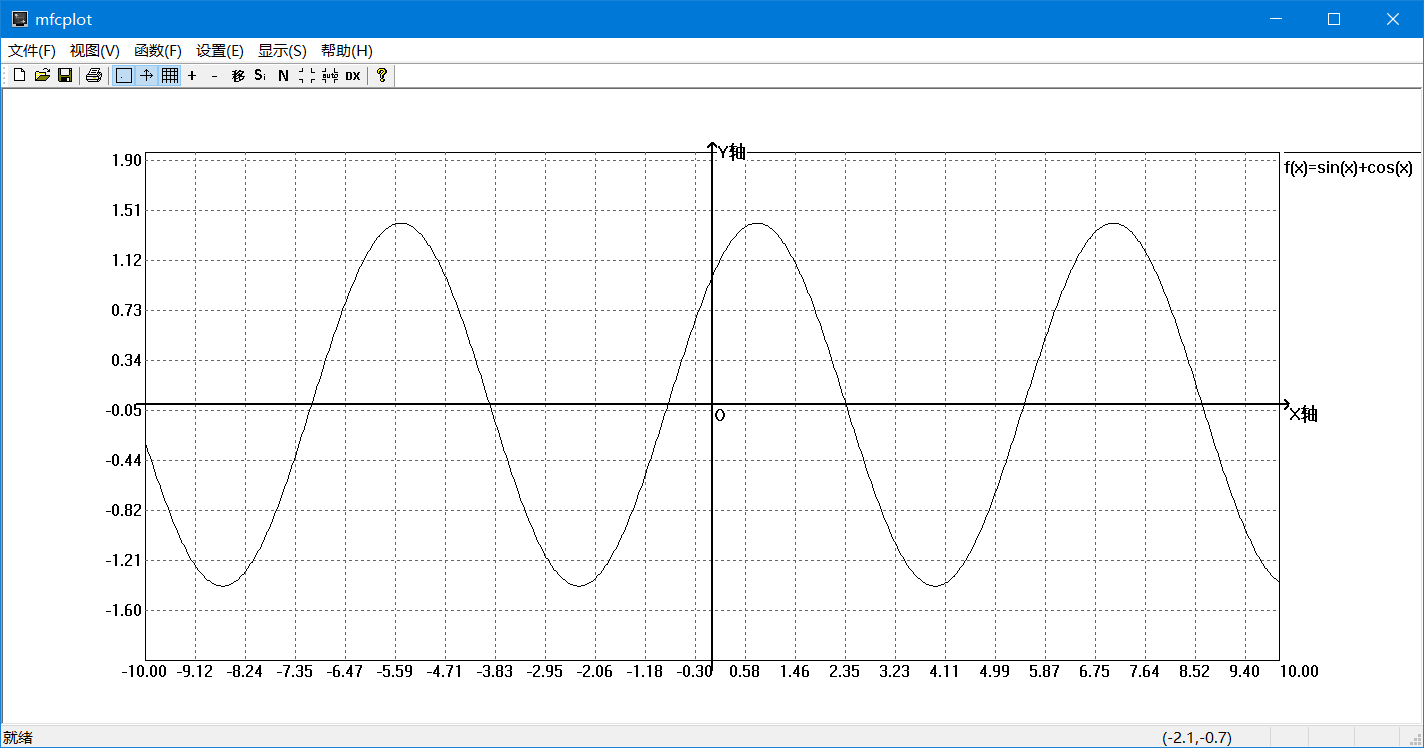
- 显示坐标轴,网格,刻度值,图例
- 可以选择不同颜色线型来绘制不同的曲线
- 当鼠标移动到曲线上某点时,可以显示该点的坐标
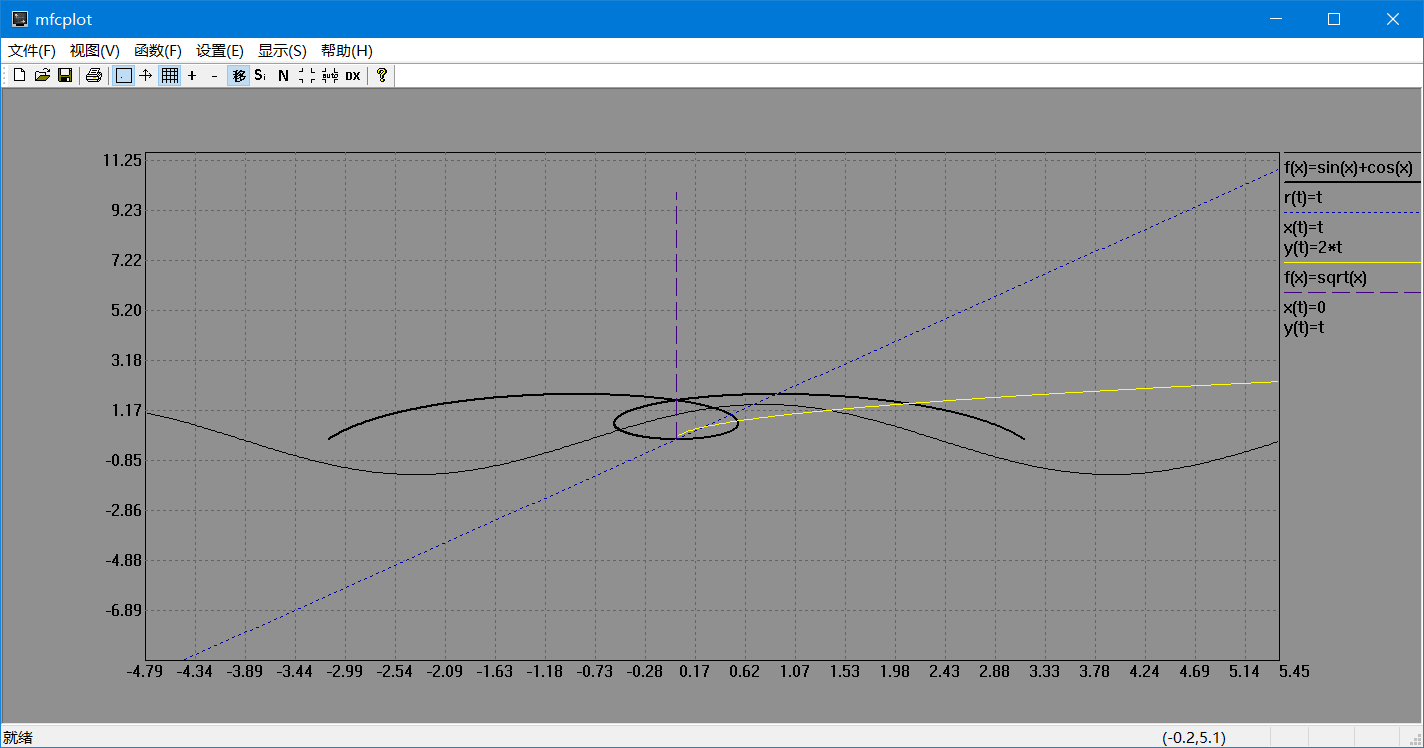
- 可以用鼠标拖动图像
- 可以进行图形的放大,缩小,定量设置显示范围,自动缩放
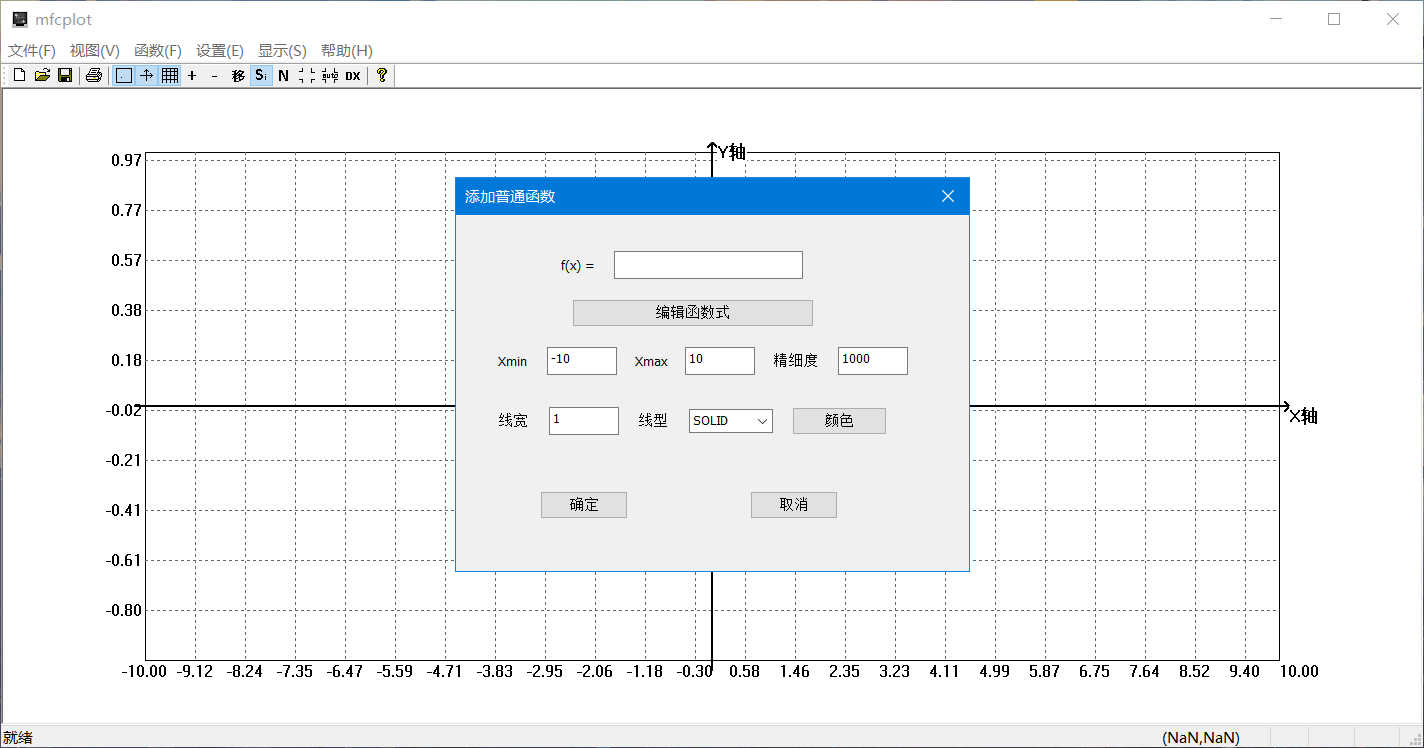
- 普通函数x取值范围可设置为跟随显示范围变化
- 状态栏实时显示鼠标位置,双击显示鼠标精确位置
- 重要数据的序列化和反序列化
- 突变函数(如floor(x))和部分y值接近无穷的函数(如tan(x))无法完美显示
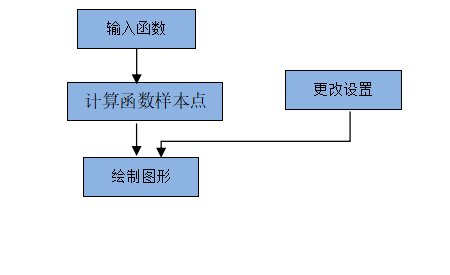
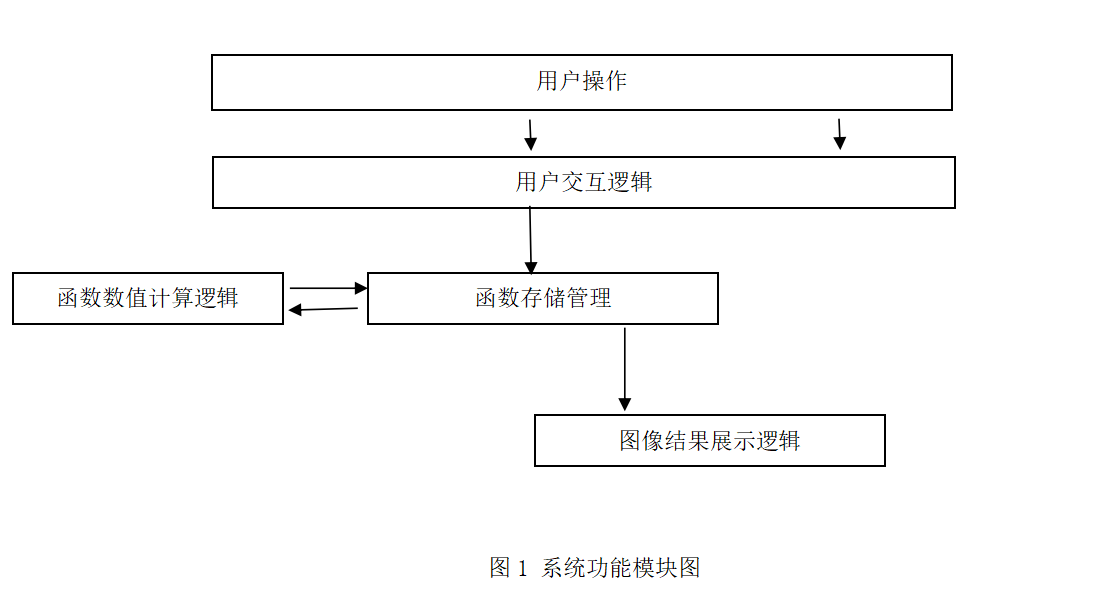
用户输入函数信息,显示函数图像。还可以通过菜单和工具栏更改设置。
通过计算样本点,相邻样本点用直线连接,当样本点数量足够大时,可近似看成曲线。
double CalcEquation(CString m_sEquation, bool& succ, char xKey, double xVal) m_sEquation:表达式 succ:计算是否成功 xKey:未知数是"x"还是"t" xVal:未知数的值
此文件可以单独拿出来(把CString换成string就行)使用 bool succ = true; double ans = CalcEquation("sin(x)+e^x",succ,'x',1.1);
对方程,分为数(常数,未知数x),双目运算符(+ , - ,* , / , ^ ) ,单目运算符(sin,cos等等),单目运算符后面是一个完整的子式,如2+cos(x+1)中,x+1就是一个完整的式子,通过递归调用可以求子式的值,如果已知子式值,这个[单目运算符+子式]就是一个已知数了,那剩下的就等效于只有+ , - , * , / , ^ 的公式,用表达式栈法就可以解决。
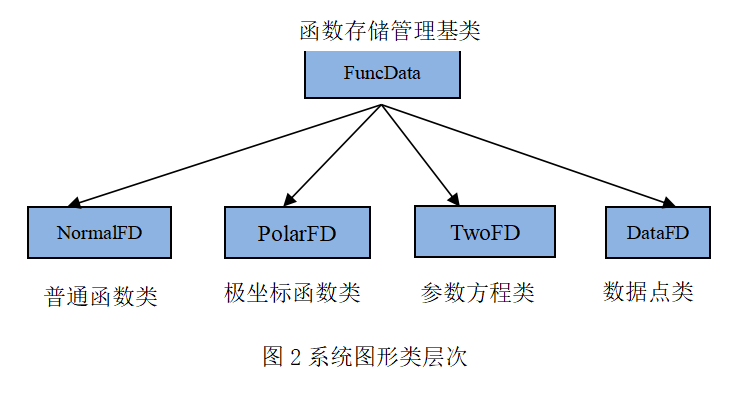
FuncData类
成员变量:
int FuncCas; //函数类型
CString m_Equation; //函数表达式
double minX, maxX; //x极值
double maxY, minY; //y极值
int stepX; //可以理解为样本点的数量
int m_penWidth; //画笔宽度
int m_penType; //画笔类型
COLORREF m_color; //画笔颜色
vector<pair<double, double> > vetPoint; //储存所有样本点
成员函数:
virtual double GetY(double xVal, bool& succ) = 0;//得到未知数为xVal时函数值,succ表示计算是否成功
virtual bool CalcList() = 0; //计算vetPoint
virtual bool GetNearest(pair<double,double> NowPoint, pair<double, double> &CmpPoint);//获取本函数与NowPoint最近的点
virtual CString GetEquation2(); //为了得到参数方程第二个函数式
FuncData();
FuncData(CString Equation,double minX,double maxX,int stepX,COLORREF color, int penWidth,int penType);//构造函数
注意:此处派生类只记录特有的成员
NormalFD类
无
PolarFD 类
成员变量
double maxth, minth; //自变量θ取值范围
TwoFD类
成员变量
CString m_EquationY;
double maxT, minT;
成员函数
double GetX(double tVal, bool& succ);//参数方程X也需要求值
virtual double GetY(double tVal, bool& succ);
DataFD类
成员函数
static int DataFD_Cnt; //记录数据点类型函数数量mfcplotDoc中记录着设置信息和函数数据,主要内容如下
public:
bool m_WillShowGrid; //是否显示网格
bool m_WillShowAxis; //是否显示坐标轴
bool m_WillShowEdge; //是否显示边框
bool m_SingelMode; //单函数模式添加函数自动删除上一个函数
bool m_ForceXrange; //普通函数x范围是否固定,不固定的话随显示范围变化
bool m_ShowNearPoint;//鼠标接近函数线时是否显示其坐标
double m_Xmin, m_Xmax, m_Ymin, m_Ymax;//显示范围
FuncData *m_FD;//临时变量
CObList m_List;//记录所有函数信息
public:
afx_msg void OnAxisMenu();//坐标轴
afx_msg void OnGridMenu();//网格
afx_msg void OnEdgeMenu();//边框
afx_msg void OnSmallerMenu();//显示范围缩小 0.8
afx_msg void OnBiggerMenu();//显示范围放大 1.25
afx_msg void OnNormalFuncMenu();//增加普通函数
afx_msg void OnMenuSetXyrange();//设置显示范围
afx_msg void OnFuncMode();//单/多函数模式
afx_msg void OnPolarFuncMenu();//增加极坐标函数
afx_msg void OnTwoFuncMenu();//增加参数方程函数
afx_msg void OnDataFuncMenu();//增加数据点型函数
afx_msg void OnFroceXrang();//普通函数x范围是否固定
afx_msg void OnNearpointMenu();//是否显示最近点
afx_msg void OnAutorangeMenu();//自动调整显示范围,正好显示完整函数图像
afx_msg void OnDelfunconeMenu();//删除一个函数
afx_msg void OnDelallMenu();//删除所有函数绘图逻辑是在这里实现的,主要内容如下
public:
double m_Xmin, m_Xmax, m_Ymin, m_Ymax;//函数显示范围
int nTop, nButton, nLeft, nRight;//对应的逻辑坐标范围
int isMoving;//拖动状态 0不拖动 1拖动模式 2正在拖动
double tmp_Xmin, tmp_Xmax, tmp_Ymin, tmp_Ymax;
//拖动模式下,单击鼠标左键,记录起点的显示范围
CPoint m_posStart;
//拖动模式下,单击鼠标左键,记录起点的鼠标坐标
//根据鼠标坐标偏移量可以计算显示范围变化量函数中LPxtoFPx表示把函数坐标x变成pDC可以用的逻辑坐标_x,原理函数坐标范围m_Xmin,m_Xmax到逻辑坐标范围nLeft,nRight(下面函数会给出)等比例的映射。
double CmfcplotView::LPxtoFPx(int x) {
return m_Xmin + (1.0 * x - nLeft) * (m_Xmax - m_Xmin) / (1.0 * nRight - nLeft);
}实现坐标转换后就可以进行绘图工作了。
void CmfcplotView::OnDraw(CDC* pDC)
{
CmfcplotDoc* pDoc = GetDocument();
ASSERT_VALID(pDoc);
if (!pDoc)
return;
m_Xmin = pDoc->m_Xmin;//极值保存在Doc中
m_Xmax = pDoc->m_Xmax;
m_Ymin = pDoc->m_Ymin;
m_Ymax = pDoc->m_Ymax;
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);//获得视图区
nTop = (int)round(rect.bottom * 0.1); //函数图像不会占据整个视图区
nButton = (int)round(rect.bottom * 0.9);
nLeft = (int)round(rect.right * 0.1);
nRight = (int)round(rect.right * 0.9);
if (pDoc->m_WillShowEdge) {//画边框
pDC->MoveTo(nLeft, nTop);
pDC->LineTo(nLeft, nButton);
pDC->LineTo(nRight, nButton);
pDC->LineTo(nRight, nTop);
pDC->LineTo(nLeft, nTop);
}
//画x坐标信息
int nX,nY;
bool BIGX = abs(m_Xmin) > 100 || abs(m_Xmax) > 100;//x坐标值比较大时,标注更稀
for (nX = nLeft; nX < nRight; nX += (BIGX ? 100 : 50)) { //每隔100/50像素一个标注
CRect textRect(nX - (BIGX ? 50 : 25), nButton + 1, nX + (BIGX ? 50 : 25), nButton + 20);//显示区域
CString xInfo;
xInfo.Format(_T("%.2f"),LPxtoFPx(nX));
pDC->DrawText(xInfo, &textRect, DT_SINGLELINE | DT_CENTER);
//单行,上下左右居中显示
}
if (nX - nRight <= (BIGX ? 50 : 25)) {//最后一个x坐标,与前一个标注距离太近则不显示
CRect textRect(nRight, nButton + 1, nRight + 50, nButton + 20);
CString xInfo;
xInfo.Format(_T("%.2f"),m_Xmax);
pDC->DrawText(xInfo, &textRect, DT_SINGLELINE | DT_LEFT | DT_TOP);
}
//y坐标
for (nY = nButton - 50; nY > nTop; nY -= 50) {
CRect textRect(nLeft - 200, nY-10, nLeft - 3, nY + 10);
CString yInfo;
yInfo.Format(_T("%.2f"), LPytoFPy(nY));
pDC->DrawText(yInfo, &textRect, DT_SINGLELINE | DT_RIGHT);
}
if (nTop - nY <= 25) {
CRect textRect(nLeft - 200, nTop - 10, nLeft - 3, nTop + 10);
CString yInfo;
yInfo.Format(_T("%.2f"),m_Ymax);
pDC->DrawText(yInfo, &textRect, DT_SINGLELINE | DT_BOTTOM | DT_RIGHT);
}
// 显示网格
if (pDoc->m_WillShowGrid) {
CPen pen(PS_DOT, 1, RGB(100, 100, 100)); //创建笔,虚线,并调整坐标颜色灰色
CPen *pOldPen = (CPen *)pDC->SelectObject(&pen);
for (nX = nLeft+50; nX < nRight; nX += 50) {
pDC->MoveTo(nX, nTop);
pDC->LineTo(nX, nButton);
}
for (nY = nButton - 50; nY > nTop; nY -= 50) {
pDC->MoveTo(nLeft, nY);
pDC->LineTo(nRight, nY);
}
pDC->SelectObject(pOldPen);
}
// 显示坐标轴
if (pDoc->m_WillShowAxis) {
CPen pen(PS_SOLID, 2, RGB(0, 0, 0));
CPen* pOldPen = (CPen*)pDC->SelectObject(&pen);
int oX = FPxtoLPx(0);
int oY = FPytoLPy(0);
bool showY = oX >= nLeft && oX <= nRight;
bool showX = oY >= nTop && oY <= nButton;//判断x,y轴是否在范围内
if (showX) {
pDC->MoveTo(nLeft - 10, oY);
pDC->LineTo(nRight + 10, oY);
}
if (showY) {
pDC->MoveTo(oX, nButton + 10);
pDC->LineTo(oX, nTop - 10);
}
if (showX && showY) {
pDC->TextOutW(oX + 1, oY + 1, _T("O"));
}
if (showX) {
pDC->MoveTo(nRight + 10, oY);
pDC->LineTo(nRight + 5, oY + 5);
pDC->MoveTo(nRight + 10, oY);
pDC->LineTo(nRight + 5, oY - 5);
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 10, oY, _T("X轴"));
}
if (showY) {
pDC->MoveTo(oX, nTop - 10);
pDC->LineTo(oX - 5, nTop - 5);
pDC->MoveTo(oX, nTop - 10);
pDC->LineTo(oX + 5, nTop - 5);
pDC->TextOutW(oX + 5, nTop - 10, _T("Y轴"));
}
pDC->SelectObject(pOldPen);
}
POSITION p = pDoc->m_List.GetHeadPosition();
int showTop = nTop;
while (p != nullptr) {
bool shouldMov = true;//一段曲线第一个点MoveTo,其他都是LineTo
FuncData* tmpFD = (FuncData*)pDoc->m_List.GetNext(p);
CPen pen(tmpFD->m_penType, tmpFD->m_penWidth, tmpFD->m_color);
CPen* pOldPen = (CPen*)pDC->SelectObject(&pen);
if (tmpFD->FuncCas == CAS_NORMAL) {//动态X坐标模式下,普通函数x范围与视图不同时自动同步
if (pDoc->m_ForceXrange && isMoving!=2)
if (tmpFD->minX != m_Xmin || tmpFD->maxX != m_Xmax) {
tmpFD->minX = m_Xmin;
tmpFD->maxX = m_Xmax;
tmpFD->CalcList();
}
}
for (auto dot : tmpFD->vetPoint) {
if (dot.first < m_Xmin || dot.first > m_Xmax || dot.second < m_Ymin || dot.second > m_Ymax || dot.second != dot.second) {
shouldMov = true;
continue;
}
if (shouldMov) {
pDC->MoveTo(FPxtoLPx(dot.first), FPytoLPy(dot.second));
shouldMov = false;
}
else
pDC->LineTo(FPxtoLPx(dot.first), FPytoLPy(dot.second));
}
pDC->MoveTo(nRight+5, showTop);//显示图例
pDC->LineTo(rect.right, showTop);
showTop += 5;
if (tmpFD->FuncCas == CAS_NORMAL)
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 5, showTop, _T("f(x)=")+tmpFD->m_Equation);
else if (tmpFD->FuncCas == CAS_POLAR)
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 5, showTop, _T("r(t)=") + tmpFD->m_Equation);
else if (tmpFD->FuncCas == CAS_TWO) {
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 5, showTop, _T("x(t)=") + tmpFD->m_Equation);
showTop += 20;
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 5, showTop, _T("y(t)=") + tmpFD->GetEquation2());
} else if (tmpFD->FuncCas == CAS_DATA)
pDC->TextOutW(nRight + 5, showTop, _T("y(t)=") + tmpFD->m_Equation);
showTop += 25;
pDC->SelectObject(pOldPen);
}
}值得一提的是OnMouseMove的代码,拖动模式下,起点信息已经在OnLButtonDown更新,拖动过程使用了双缓冲绘图防止闪烁。具体原理可参看文末参考资料。
void CmfcplotView::OnMouseMove(UINT nFlags, CPoint point)
{
// TODO: 在此添加消息处理程序代码和/或调用默认值
更新状态栏,此处省略
if (isMoving==2) {
::SetCursor(LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_SIZEALL));
CmfcplotDoc* pDoc = GetDocument();
double detx = LPxtoFPx(point.x) - LPxtoFPx(m_posStart.x);
pDoc->m_Xmin = tmp_Xmin - detx;
pDoc->m_Xmax = tmp_Xmax - detx;
double dety = LPytoFPy(point.y) - LPytoFPy(m_posStart.y);
pDoc->m_Ymin = tmp_Ymin - dety;
pDoc->m_Ymax = tmp_Ymax - dety;
CDC* pDC = GetDC();
//创建一个内存中的显示设备
CDC MemDC;
MemDC.CreateCompatibleDC(NULL);
//创建一个内存中的图像
CBitmap MemBitmap;
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);
MemBitmap.CreateCompatibleBitmap(pDC, rect.right, rect.bottom);
//指定内存显示设备在内存中的图像上画图
MemDC.SelectObject(&MemBitmap);
//先用一种颜色作为内存显示设备的背景色
MemDC.FillSolidRect(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom, RGB(144, 144, 144));
this->OnDraw(&MemDC);
//将内存中画好的图像直接拷贝到屏幕指定区域上
pDC->BitBlt(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom, &MemDC, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
//释放相关资源
ReleaseDC(pDC);
}
else if (isMoving == 1) {
::SetCursor(LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_HAND));
}
显示函数最近点部分,此处省略
CView::OnMouseMove(nFlags, point);
}
- DrawText函数的讲解
- VC双缓冲绘图技术介绍
- 阎光伟,彭文,徐琳茜. 基于案例的Visual C++程序设计教程[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2012
- 张晓民. VC++2010应用开发技术[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2013