lrucache
1. 原理
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高。
依据此原理,可以设计微服务的二级缓存结构,用于存储经常访问的热数据,实现避免频繁访问后端数据库的相同数据逻辑。当使用该缓存当做二级缓存时,需要保证缓存中数据和后端数据的一致性。
2. 实现
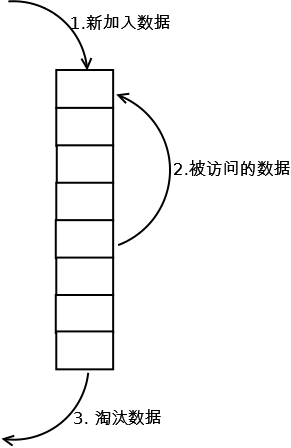
lrucache实现是使用一个链表保存缓存数据,详细算法实现如下:
-
新数据插入到链表尾部;
-
每当缓存命中(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表尾部;
-
当链表满的时候,将链表头部的数据丢弃。
3. 分析
【命中率】 当存在热点数据时,LRU的效率很好,但偶发性的、周期性的批量操作会导致LRU命中率急剧下降,缓存污染情况比较严重。
【复杂度】
O(1)-O(n)
【代价】
命中时需要遍历链表,找到命中的数据块索引,然后需要将数据移到头部。
4. 使用
4.1 How to use it?
import (
"github.com/wonderivan/lrucache"
)
cache := lrucache.NewLruCache()
err := cache.StartAndGC(`{
"name" : "testCache",
"low": 858993459,
"high": 1073741824,
"interval": 3600
}`)
// then use it like this:
cache.Put("key", "value:123abc*#+", 10)
cache.Get("key")
cache.IsExist("key")
cache.Delete("key")
// last free when process defer
cache.Destroy()4.2 LRUCache config
LRUCache config like this:
{
"name" : "testCache",
"low": 858993459,
"high": 1073741824,
"interval": 3600
}| 参数名 | 释义 | 默认 |
|---|---|---|
| name | 缓存名称 | "" |
| low | 缓存压缩最低阈值限制 | 800 MB |
| high | 缓存触发压缩最高阈值 | 1 GB |
| interval | 缓存有效数据检查间隔 | 1天 |
name: Specify the name of the current Lrucache low: Minimum buffer size when cache shrinkage high: Maximum buffer size when cache growth interval: Cycle to detect whether the time expired
If config is not set, the default low is equal to 0.8GB, high equal to 1GB
Note: the low must be less than high, otherwise it would be panic
LRUCache performance test
test config:
cpu : one intel x64 2.7GHz
memory: 4G x 2
low : 140000000
high : 200000000
key : 1-1000W string
value : 1-1000W string
Execute 10000000 times Put
PUT : 50W/s
Execute 10000000 times Get
GET : 220W/s
5. 未来
为了解决偶发性的、周期性的批量操作lrucache而导致的命中率急剧下降,可以考虑使用LRU-K缓存算法。
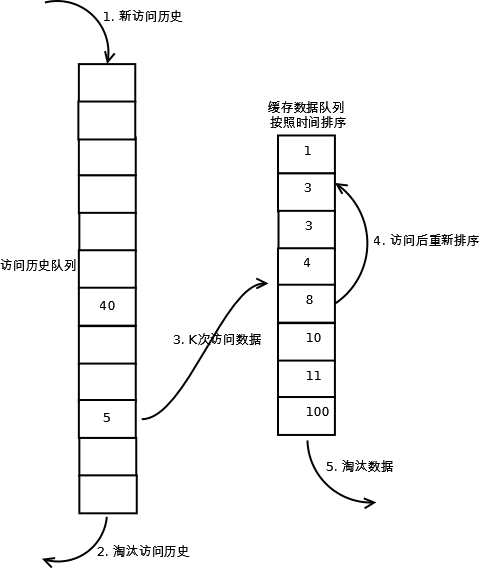
核心:将热数据标准”最近使用过的“判断标准扩展为“最近使用过K次”,只有最近使用过K次才认为是热数据,为了保存热数据,需要再引入一个队列存储。
实现: 只有当数据的访问次数达到K次的时候,才将数据放入缓存。当需要淘汰数据时,LRU-K会淘汰第K次访问时间距当前时间最大的数据,详细算法实现如下:
-
数据第一次被访问,加入到左侧的访问历史列表;
-
如果数据在访问历史列表里后没有达到K次访问,则按照原来的lrucache方式淘汰;
-
当访问历史队列中的数据访问次数达到K次后,将左侧数据迁移到右侧缓存队列中,右侧缓存队列重新按照时间排序;
-
右侧缓存数据队列中被再次访问后,重新排序;
-
需要淘汰数据时,淘汰缓存队列中排在末尾的数据,即:淘汰“倒数第K次访问离现在最久”的数据。