Conditional density estimation is a fundamental problem in statistics, with various scientific and practical applications such as genetics and economics. We propose a conditional density estimator based on tree boosting and Lindsey’s method (LinCDE). LinCDE admits flexible modeling of the density family and captures distributional characteristics like modality and shape. In particular, LinCDE always produces smooth and non-negative density estimates. Furthermore, in the presence of nuisances, LinCDE identifies the influential covariates to the response distribution.
You can install the development version of LinCDE from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
# devtools::install_github("ZijunGao/LinCDE")Below is a basic example of using LinCDE for conditional mean estimation.
library(LinCDE)
# true conditional density function; LGD stands for locally Gaussian design
density.LGD = function(X, y = NULL){
if(is.null(dim(X))){X = matrix(X, nrow = 1)}
if(!is.null(y)){
dens = dnorm(y, mean = (0.5 * X[, 1] + X[, 1] * X[, 2]), sd = (0.5 + 0.25 * X[, 2]))
}else{
y = 0.5 * X[, 1] + X[, 1] * X[, 2] + rnorm(dim(X)[1], 0, 1) * (0.5 + 0.25 * X[ ,2])
}
}
# feature points for visualization
d = 20; XProfile = matrix(0, nrow = 3^2, ncol = d); colnames(XProfile) = paste("X", seq(1,d), sep = "")
X1 = X2 = c(-0.6,0,0.6); XProfile[, c(1,2)] = as.matrix(expand.grid(X1, X2))
# training data
set.seed(100)
n = 1000; X = matrix(runif(n * d, -1, 1), ncol = d); colnames(X) = paste("X", seq(1,d), sep = "")
y.LGD = density.LGD(X)
# fitting a LinCDE boost model
model.example = LinCDE.boost(X = X, y = y.LGD, verbose = F)
# visualizing LinCDE boost model's predictions at the selected feature points
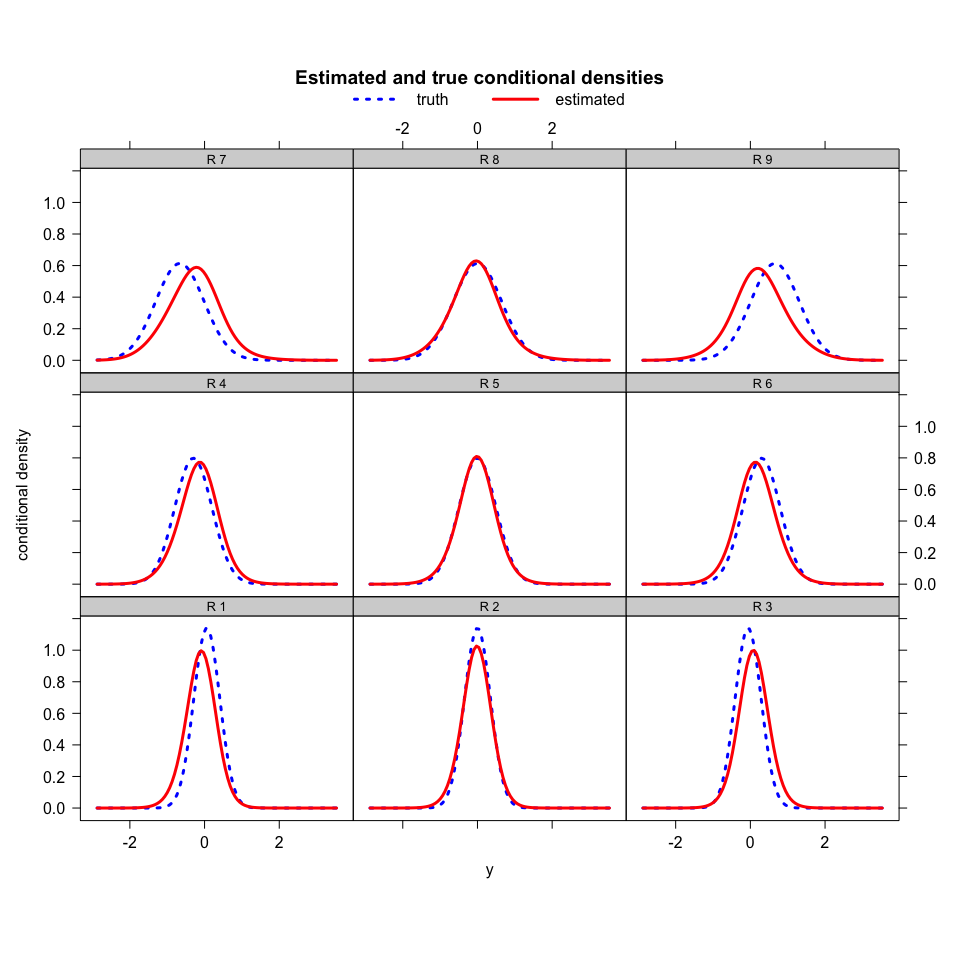
densityPlot(X = XProfile, trueDensity = density.LGD, model = model.example)For more examples, please see the vignette :)