The purpose of this project is to explore and experiment with what it takes to make a website screen-shotting tool. At first it may seem like an easy task, but it becomes complex once you try.
NOTE: If you just want a tool that "just works" then I suggest you try any of the capable services linked below.
- Javascript heavy pages (almost all these days); many sites use JavaScript to load content after the page has downloaded into the browser. Therefore you need to have a modern javascript engine to parse and execute those extra instructions to get the content as it was intented to be seen by humans.
- Geography-restricted content; some sites in the US have blocked visitors from Europe because of GDPR. Do you accept this, or is there a way to work around it?
- Bot and automation detection schemes; some sites use services to protect against automated processes from collecting content. This includes taking screenshots
- Improperly configured domain names, SSL/TLS encryption certificates, and other network-related issues
- Nefarious website owners and hacked sites that attempt to exploit the web browser to mine crypto-currencies. This puts an added load on your resources and can significantly slow your render-times.
- Taking too many screenshots at a time may overload the server and cause timeouts or failure to load pages.
- Temporary network or website failure; If the problem is on the site's end, then how will we know that and schedule another attempt later?
- People using the service as a defacto proxy (eg- pranksters downloading porn at their schools or in public places)
My development evironment is on MacOS, so HomeBrew and PyCharm are my friends here.
- python 3.x stable in Virtual Environment (this is the only version I'm working with)
- Selenium/geckodriver/chrome-driver installed via homebrew
brew install geckodriver - Docker
- Postgres installed via Homebrew.
I don't use Docker on my development machine because I have not figured out how to get PyCharm's awesome debugger working well inside docker containers. IF you can, ping me.
- Check out the repo
- Install a local virtual environment
python -m venv venv/ - Jump into venv/ with
souce venv/bin/activate - Install requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt - Create the postgres database for the project
CREATE DATABASE screenshot - copy the
env.sampletoenvin the root source folder - Check / update values in the
envfolder if needed - Install Selenium geckodriver for your platform
brew install geckodriver - Migrate the database
cd src && ./manage.py migrate - Create the cache table
cd src && ./manage.py createcachetable - Create the superuser
cd src && ./manage.py createsuperuser - Start the worker
cd src && ./manage.py screenshot_worker_ff - Finally, start the webserver
cd src && ./manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
Open a browser onto http://localhost:8000 and see the screenshot app in all its glory.
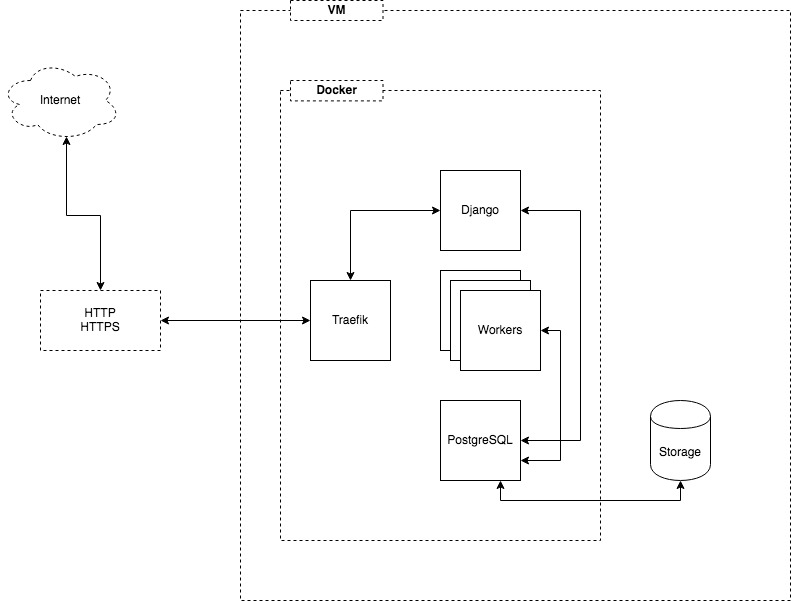
Django runs as usual in either development mode or inside gunicorn (for production).
There is a worker (or a number of workers) that run as parallel, independent processes to the webserver process. They connect to the database and poll for new work on an interval. This pattern obviates the need for Celery, Redis, RabbitMQ, or other complicated moving parts in the system.
The worker processes work like this:
- poll database for new screenshots to make
- find a screenshot, mark it as pending
- launch slenium and take screenshot of resulting page (up to 60 seconds time limit)
- save screenshot to database
- shutdown selenium browser
- sleep
- repeat
In the database! Now, before you lose it -- I know what many of you will say about storing images in the database. I have linked to the StackOverflow here:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3748/storing-images-in-db-yea-or-nay
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54500/storing-images-in-postgresql
My rationale is this:
- All content lives in the database, so there is no syncing issues with regards to the data (screenshots) and the metadata (database).
- Images will be smallish because they are compressed screenshots not more than a 1mb (often far less). But we will need to run many iterations and save as much metadata about the screens to really know.
- Thumbnails will be stored in cache (also a database table), but get purged after 30 days.
- Todays compute, network, and storage capacities are so big that 1TB is no longer considered unreasonable. This means that if we build up a screenshot datbase of 1TB, then that is a good problem to have and we can re-architect from there.
Note: This is a hypothesis, and I am willing to change my mind if this does not work out.
- https://medium.com/@eknkc/how-to-run-headless-chrome-in-scale-7a3c7c83b28f
- https://medium.com/@timotheejeannin/i-built-a-screenshot-api-and-some-guy-was-mining-cryptocurrencies-with-it-cd188dfae773
- Philip Walton - Simple sticky footers using flexbox
Please fork and submit pull requests if you are inspired to do so. Issues are open as well.