Project description
Showcase is a sample project that presents modern, 2019 approach to Android application development using Kotlin and latest tech-stack.
The goal of the project is to demonstrate best practices, provide a set of guidelines, and present modern Android application architecture that is modular, scalable, maintainable and testable. This application may look simple, but it has all of these small details that will set the rock-solid foundation of the larger app suitable for bigger teams and long application lifecycle. Many of the project design decisions follow official Google recommendations.
This project is being heavily maintained to match current industry standards. In upcoming weeks (Aug-Dec 2019) I plan to write an extensive series of articles explaining many of this project architectural design decisions, so stay tuned.
Project characteristics
This project brings to table set of best practices, tools, and solutions:
- 100% Kotlin
- Modern architecture (feature modules, Clean Architecture, Model-View-ViewModel)
- Android Jetpack
- A single-activity architecture, using the Navigation component to manage fragment operations
- Reactive UIs
- CI pipeline
- Testing
- Static analysis tools
- Dependency Injection
- Material design
Tech-stack
Min API level is set to 21, so the presented approach is suitable for over
85% of devices running Android. This project takes advantage of many
popular libraries and tools of the Android ecosystem. Most of the libraries are in the stable version, unless there is a
good reason to use non-stable dependency.
- Tech-stack
- Kotlin + Coroutines - Perform background operations
- Kodein - Dependency injection
- Retrofit - Retrieve data from network
- Jetpack
- Navigation - deal with whole in-app navigation
- LiveData - notify views about database change
- Lifecycle - perform action when lifecycle state changes
- ViewModel - store and manage UI-related data in a lifecycle conscious way
- Coil - image loading library with Kotlin idiomatic API
- Lottie - animation library
- Stetho - application debugging tool
- and more...
- Architecture
- Clean Architecture (at module level)
- MVVM + MVI (presentation layer)
- Dynamic feature modules
- Android Architecture components (ViewModel, LiveData, Navigation, SafeArgs plugin)
- Tests
- Gradle
- Gradle Kotlin DSL
- Custom tasks
- Plugins (Ktlint, Detekt, Versions, SafeArgs)
Architecture
Feature related code is placed inside one of the feature modules. This modularized approach provides better separation of concerns in the codebase and allows for feature to be developed in isolation, independently from other features.
Module dependencies
This is a simplified diagram of dependencies between gradle modules.
Note that due usage of Android dynamic-feature module dependencies are reversed (feature modules are depending on
app module, not another way around).
Feature structure
Each feature module contains own set of the Clean Architecture layers:
Each layer has a distinct set of responsibilities:
Presentation layer- responsible for presenting data to a screen and handling user interactions.Domain layer- containsUseCases(business logic) and supporting domain models (entities).Data layer- encapsulates the source of the data (eg. network, memory cache, local database...) and serves as unified access point to the data forDomainlayer.
Clean architecture is the "core architecture" of the application. Presentation layer is as mix of MVVM (Jetpack
ViewModel used to preserve data across activity restart) and MVI (actions modify common state of the view and
then new state is edited to a view via LiveData to be rendered).
common state(for each view) approach derives from Unidirectional Data Flow and Redux principles.
Let's take a look at two common android cases when view state can be lost:
- Activity restart - view state should be restored from
ViewModelstate (last value emitted byLiveData) - Process restart - view state should be restored from
Repository(whatever data comes from the local cache or network)
Data flow
Below diagram presents application data flow when a user interacts with album list screen:
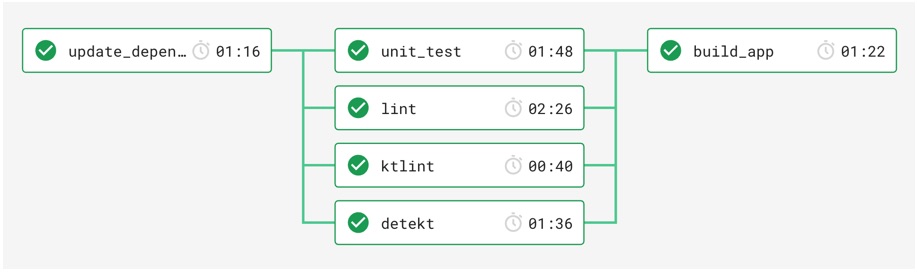
Ci pipeline
CI pipeline verifies project correctness witch each PR. Some of the tasks run in parallel, while
others like app build will not be stared until all static checks and tests complete successfully:
These are all of the Gradle tasks (cmd commands) that are executed by CI:
./gradlew lintDebug- runs Android lint./gradlew detekt- runs detekt./gradlew ktlintCheck- runs ktlint./gradlew testDebugUnitTest- run unit tests./gradlew :app:bundleDebug- create app bundle
On top of that project contains custom ./gradlew staticCheck task that mimics all CI tasks and is intended to run on
local computer.
What this project does not cover?
The interface of the app utilises some of modern material design components, however, is deliberately kept simple to focus on application architecture.
Upcoming improvements
- Android Dynamic delivery
- Caching layer (memory + disk)
- Add Room
- UI tests (including CI pipeline emulator configuration)
- Data binding
- Add Custom
android lint,ktlintanddetektchecks/rules - Add script to update all dependencies in the project, create PR to run all checks
- Continuous deployment (automatically publish app to Google play store using CI)
- Support for DayNight MaterialTheme
- and much more…
Getting started
There are a few ways to open this project.
Android Studio
- Android Studio -> File -> New -> From Version control -> Git
- Enter
https://github.com/igorwojda/android-showcase.gitinto URL field
Command line + Android Studio
- Run
git clone https://github.com/igorwojda/android-showcase.git - Android Studio -> File -> Open
Known issues
- Classes generated by
SafeArgsplugin (AlbumListFragmentDirections,AlbumDetailFragmentArgs...) are not properly recognized by IDE in the multi-module configuration. Code will run however IDE will mark these classes as non- existing. Also sometimes code has to be cleaned before running tests. This needs more investigation.
Inspiration
This is project is just a sample, to inspire you and should handle most of the common cases. I encourage you to also take a look at other high-quality projects to find architecture that works for you and your existing codebase:
- Iosched - official Android application from google IO 2019
- Android Architecture Blueprints v2 - showcase of different Android architecture approaches
- Android sunflower complete
Jetpacksample covering all libraries - GithubBrowserSample - multiple small projects demonstrating usage of Android Architecture Components
- Plaid - showcase of Android material design
- Clean Architecture boilerplate - contains nice diagrams of Clean Architecture layers
- Roxie - solid example of
common stateapproach together witch very good documentation
Contribute
Feedback and new contributions are welcome whether it's through bug reports or new PRs.
Author
License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2019 Igor Wojda
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.