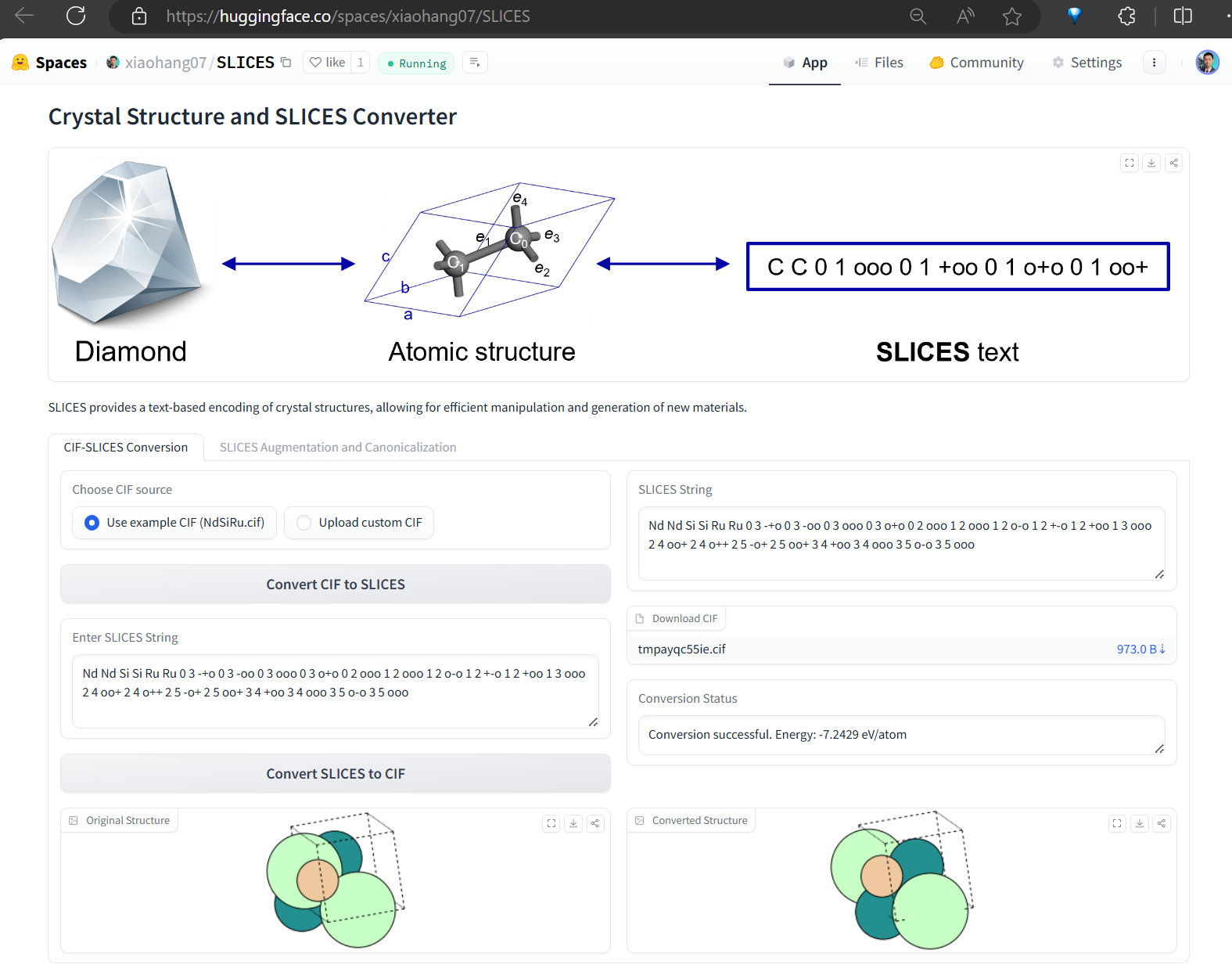
This software implementes Simplified Line-Input Crystal-Encoding System (SLICES), the first invertible and invariant crystal representation.
It has several main functionalities:
- Encode crystal structures into SLICES strings
- Reconstruct original crystal structures from their SLICES strings (Text2Crystal)
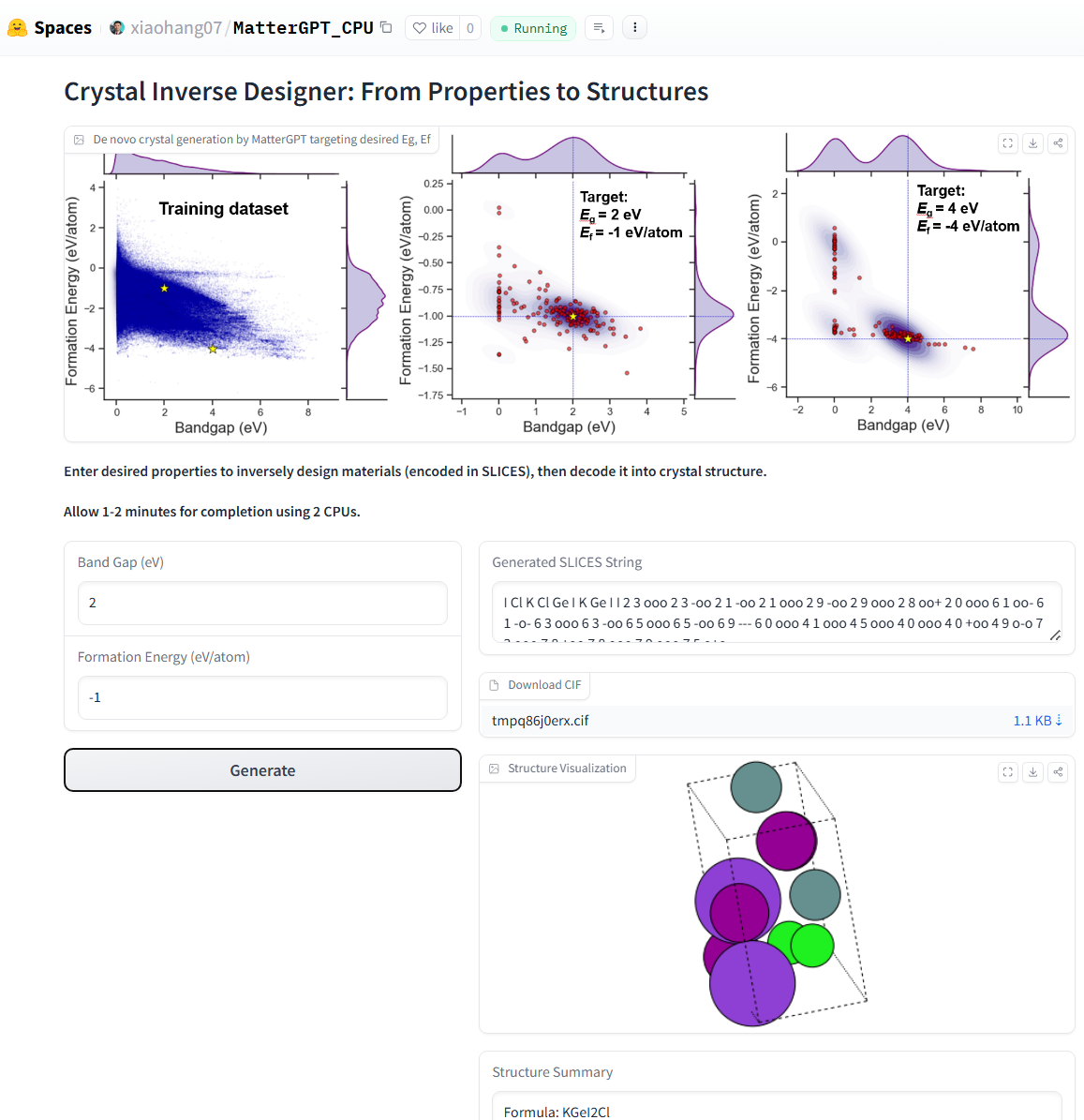
- Generate crystals with desired properties using conditional RNN (Inverse Design)
Developed by Hang Xiao 2023.04 xiaohang07@live.cn
Nature Communications [Paper] [SLICES晶体语言视频介绍][SLICES101] [Data/Results][Source code]
We provide a huggingface space to allow one-click conversion of CIF to SLICES and SLICES to CIF online.
- Installation
- Examples
- SLICES视频教程
- MatterGPT视频教程
- Tutorials
- Documentation
- Reproduction of benchmarks
- Citation
- Contact
# pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple (use this if you are in China)
conda env create --name slices --file=environments.yml
conda activate slices
pip install slices==2.0.2
#If you're in China, use this command instead: "pip install slices -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple".Please note that this installtion method is intended for Linux operating systems like Ubuntu and CentOS. Unfortunately, SLICES is not directly compatible with Windows or MacOS due to the modified XTB binary was compiled on Linux. To run SLICES on Windows or MacOS, one can run SLICES with docker, referring to Jupyter backend setup.
If "TypeError: bases must be types" occurs when you use SLICES library, then do this:
pip install protobuf==3.20.0If errors still occur, then you can run SLICES with docker, referring to Jupyter backend setup.
Converting a crystal structure to its SLICES string and converting this SLICES string back to its original crystal structure. Suppose we wish to convert the crystal structure of NdSiRu (mp-5239,https://next-gen.materialsproject.org/materials/mp-5239?material_ids=mp-5239) to its SLICES string and converting this SLICES string back to its original crystal structure. The python code below accomplishes this:
from slices.core import SLICES
from pymatgen.core.structure import Structure
# obtaining the pymatgen Structure instance of NdSiRu
original_structure = Structure.from_file(filename='NdSiRu.cif')
# creating an instance of the InvCryRep Class (initialization)
backend=SLICES()
# converting a crystal structure to its SLICES string
slices_NdSiRu=backend.structure2SLICES(original_structure)
# converting a SLICES string back to its original crystal structure and obtaining its M3GNet_IAP-predicted energy_per_atom
reconstructed_structure,final_energy_per_atom_IAP = backend.SLICES2structure(slices_NdSiRu)
print('SLICES string of NdSiRu is: ',slices_NdSiRu)
print('\nReconstructed_structure is: ',reconstructed_structure)
print('\nfinal_energy_per_atom_IAP is: ',final_energy_per_atom_IAP,' eV/atom')
# if final_energy_per_atom_IAP is 0, it means the M3GNet_IAP refinement failed, and the reconstructed_structure is the ZL*-optimized structure.Converting a crystal structure to its SLICES string and perform data augmentation (50x), then reduce these 50 SLICES to 1 canonical SLICES with get_canonical_SLICES.
from slices.core import SLICES
from pymatgen.core.structure import Structure
from pymatgen.analysis.structure_matcher import StructureMatcher, ElementComparator
# obtaining the pymatgen Structure instance of Sr3Ru2O7
original_structure = Structure.from_file(filename='Sr3Ru2O7.cif')
# creating an instance of the InvCryRep Class (initialization)
backend=SLICES(graph_method='crystalnn')
# converting a crystal structure to its SLICES string and perform data augmentation (50x)
slices_list=backend.structure2SLICESAug_atom_order(structure=original_structure,num=50)
slices_list_unique=list(set(slices_list))
cannon_slices_list=[]
for i in slices_list_unique:
cannon_slices_list.append(backend.get_canonical_SLICES(i))
# test get_canonical_SLICES
print(len(slices_list),len(set(cannon_slices_list)))
# 50 SLICES generated by data augmentation has been reduced to 1 canonical SLICES(1) Download this repo and unzipped it.
(2) Put Materials Project's new API key in "APIKEY.ini".
(3) Edit "CPUs" in "slurm.conf" to set up the number of CPU threads available for the docker container.
(4) Run following commands in terminal (Linux or WSL2 Ubuntu on Win11)
# Download SLICES_docker with pre-installed SLICES and other relevant packages.
docker pull xiaohang07/slices:v9
# You can download the compressed docker image v9 at https://figshare.com/s/260701a1accd0192de20 if docker pull does not work.
# Then you can load this docker image using the following command:
xz -dc slices_v9.tar.xz | docker load
# Make entrypoint_set_cpus.sh executable
sudo chmod +x entrypoint_set_cpus_jupyter.sh
# Repalce "[]" with the absolute path of this repo's unzipped folder to setup share folder for the docker container.
# e.g. for windows cmd: -v C:\Users\admin\Desktop\SLICES:/crystal
# e.g. for windows wsl: -v /mnt/c/Users/admin/Desktop/SLICES:/crystal
# e.g. for linux: -v /home/admin/Desktop/SLICES:/crystal
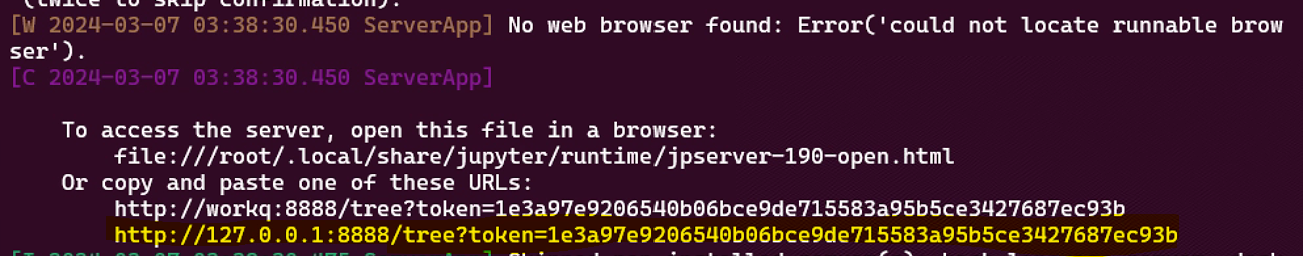
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 -h workq --shm-size=0.5gb --gpus all -v /[]:/crystal xiaohang07/slices:v9 /crystal/entrypoint_set_cpus_jupyter.sh(5) Press CTRL (or Command on Mac) and click the link that starts with http://127.0.0.1 in your terminal (highlighted in yellow in the image below).
This will open the Jupyter notebook in your web browser. Click on the Tutorial_*.ipynb file to load the relevant tutorial notebook.
The SLICES documentation is hosted at read-the-docs.
Reproduction of benchmarks and inverse design case study using a docker image [as an example]. One can run these calculaitons without the docker environment but one need to edit the *.pbs files to make sure the job management system on your PC/HPC work.
Download this repo and unzipped it.
Put Materials Project's new API key in "APIKEY.ini".
Edit "CPUs" in "slurm.conf" to set up the number of CPU threads available for the docker container.
docker pull xiaohang07/slices:v9 # Download SLICES_docker with pre-installed SLICES and other relevant packages.
# Make entrypoint_set_cpus.sh executable
sudo chmod +x entrypoint_set_cpus.sh
# Repalce "[]" with the absolute path of this repo's unzipped folder to setup share folder for the docker container.
docker run -it --privileged=true -h workq --gpus all --shm-size=0.1gb -v /[]:/crystal -w /crystal xiaohang07/slices:v9 /crystal/entrypoint_set_cpus.shConvert MP-20 dataset to json (cdvae/data/mp_20 at main · txie-93/cdvae. GitHub. https://github.com/txie-93/cdvae (accessed 2023-03-12))
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/get_json/0_get_mp20_json
python 0_mp20.pyRule out unsupported elements
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/get_json/1_element_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Convert to primitive cell
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/get_json/2_primitive_cell_conversion
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Rule out crystals with low-dimensional units (e.g. molecular crystals or layered crystals)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/get_json/3_3d_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Calculate reconstruction rate of IAP-refined structures, ZL*-optimized structures, rescaled structures under strict and coarse setting.
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/matchcheck3
python 1_ini.py
#After running python 1_ini.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_grid_new.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_grid_new.py to get "results_collection_matchcheck3.csv"Calculate reconstruction rate of IAP-refined structures, ZL*-optimized structures, IAP-refined rescaled structures, rescaled structures under strict and coarse setting.
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-20/matchcheck4
python 1_ini.py
#After running python 1_ini.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_grid_new.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_grid_new.py to get "results_collection_matchcheck4.csv"Reproduction of Table 1: the table below illustrates the correspondence between the data in "results_collection_matchcheck4.csv" and the match rates of SLI2Cry for the filtered MP-20 dataset (40,330 crystals) presented in Table 1.
| Setting | Rescaled Structure | 𝑍𝐿∗-Optimized Structure | IAP-Refined Structure | IAP-Refined Rescaled Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strict | std_match_sum | opt_match_sum | opt2_match_sum | std2_match_sum |
| Loose | std_match2_sum | opt_match2_sum | opt2_match2_sum | std2_match2_sum |
Reproduction of Table 2: the match rate of SLI2Cry for the MP-20 dataset (45,229 crystals) = opt2_match2_sum*40330/45229.
Download entries to build the filtered MP-21-40 dataset
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-21-40/0_get_json_mp_api
python 0_mp21-40_dataset.py
!!! If “mp_api.client.core.client.MPRestError: REST query returned with error status code” occurs. The solution is:
pip install -U mp-apiRule out crystals with low-dimensional units (e.g. molecular crystals or layered crystals) in general dataset
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-21-40/0_get_json_mp_api/1_filter_prior_3d
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Calculate reconstruction rate of IAP-refined structures, ZL*-optimized structures, rescaled structures under strict and coarse setting.
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_MP-21-40/matchcheck3
python 1_ini.py
#After running python 1_ini.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_grid_new.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_grid_new.py to get results.Reproduction of Table S1: the table below illustrates the correspondence between the data in "results_collection_matchcheck3.csv" and the match rates of SLI2Cry for the filtered MP-21-40 dataset (23,560 crystals) presented in Table S1.
| Setting | Filtered MP-21-40 |
|---|---|
| Strict | opt2_match_sum |
| Loose | opt2_match2_sum |
Extract MOFs with 21-40 atoms per unit cells in QMOF database to build the QMOF-21-40 dataset ( Figshare: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/QMOF_Database/13147324 Version 14)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_QMOF-21-40/get_json/0_get_mof_json
python get_json.pyRule out unsupported elements
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_QMOF-21-40/get_json/1_element_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Convert to primitive cell
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_QMOF-21-40/get_json/2_primitive_cell_conversion
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Rule out crystals with low-dimensional units (e.g. molecular crystals or layered crystals)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_QMOF-21-40/get_json/3_3d_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Calculate reconstruction rate of IAP-refined structures, ZL*-optimized structures, rescaled structures under strict and coarse setting.
cd /crystal/benchmark/Match_rate_QMOF-21-40/matchcheck3
python 1_ini.py
#After running python 1_ini.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_grid_new.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_grid_new.py to get results.Reproduction of Table S1: the table below illustrates the correspondence between the data in "results_collection_matchcheck3.csv" and the match rates of SLI2Cry for the filtered QMOF-21-40 dataset (339 MOFs) presented in Table S1.
| Setting | Filtered QMOF-21-40 |
|---|---|
| Strict | opt2_match_sum |
| Loose | opt2_match2_sum |
Convert MP-20 dataset to json (cdvae/data/mp_20 at main · txie-93/cdvae. GitHub. https://github.com/txie-93/cdvae (accessed 2023-03-12))
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/0_get_json/0_get_mp20_json
python 0_mp20.pyRule out unsupported elements
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/0_get_json/1_element_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Convert to primitive cell
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/0_get_json/2_primitive_cell_conversion
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Rule out crystals with low-dimensional units (e.g. molecular crystals or layered crystals)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/0_get_json/3_3d_filter
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Convert crystal structures in datasets to SLICES strings and conduct data augmentation
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/1_augmentation
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect.py to get results.Train unconditional RNN; sample 10000 SLICES strings
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/2_train_sample
sh 0_train_prior_model.shModify ./workflow/2_sample_HTL_model_100x.py to define the number of SLICES to be sampled
sh 1_sample_in_parallel.sh
#After running sh 1_sample_in_parallel.sh, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py to get results.Removing duplicate edges in SLICES strings to fix the syntax error
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/3_fix_syntax_check
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py to get results.Reconstruct crystal structures from SLICES strings and calculate the number of reconstructed crystals (num_reconstructed)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/4_inverse
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py to get results.
!!! In order to address the potential memory leaks associated with M3GNet, we implemented a strategy of
restarting the Python script at regular intervals, with a batch size of 30.
python count.py #calculate the number of reconstructed crystals (num_reconstructed)Evaluate the compositional validity of the reconstructed crystals and calculate the number of compositionally valid reconstructed crystals (num_comp_valid)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/5_check_comp_valid
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py to get results.
python count.py # calculate the number of compositionally valid reconstructed crystals (num_comp_valid)Evaluate the structural validity of the reconstructed crystals and calculate the number of structurally valid reconstructed crystals (num_struc_valid)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/1_unconditioned_RNN/6_check_struc_validity
python 1_splitRun.py
#After running python 1_splitRun.py, the computation is only submitted to the queue,
# not completed. To monitor the progress of the computation, use the qstat command.
#If all tasks are marked with a status of "C", it indicates that the computation has finished.
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
#After the computation are finished, running python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py to get results.
python count.py # calculate the number of compositionally valid reconstructed crystals (num_struc_valid)Reproduction of Table 3: Structural validity (%) = num_struc_valid/num_reconstructed*100 Compositional validity (%) = num_comp_valid/num_reconstructed*100
(1) Convert crystal structures in datasets to SLICES strings and conduct data augmentation
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/1_augmentation
python 1_splitRun.py # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect.py(2) Train conditional RNN
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/2_train_sample
sh 0_train_prior_model.sh(3) Sample 1000 SLICES strings with
sh 1_sample_in_parallel.sh # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py(4) Removing duplicate edges in SLICES strings to fix the syntax error
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/3_fix_syntax_check
python 1_splitRun.py # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py(5) Reconstruct crystal structures from SLICES strings and calculate the number of reconstructed crystals (num_reconstructed)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/4_inverse
python 1_splitRun.py # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
!!! In order to address the potential memory leaks associated with M3GNet, we implemented a strategy of
restarting the Python script at regular intervals, with a batch size of 30.
python count.py #calculate the number of reconstructed crystals (num_reconstructed)(6) Evaluate the formation energy distribution of the reconstructed crystals with the M3GNet model
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/5_eform_m3gnet
python 1_splitRun.py # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
python 3_normal_distri_plot.py # plot the formation energy distribution (M3GNet) of the reconstructed crystals (7) Evaluate the formation energy distribution of the reconstructed crystals at PBE level (took less than 1 day to finish with 36*26 cores HPC; need to tweak the ./workflow/0_EnthalpyOfFormation*.py to deal with some tricky cases of VASP cell optimization)
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/6_eform_PBE
python 1_splitRun.py # wait for jobs to finish (using qstat to check)
python 2_collect_clean_glob_details.py
python 3_normal_distri_plot.py # plot the formation energy distribution (PBE) of the reconstructed crystals (8) Reproduction of Table 3: Calculate SR5, SR10, SR15 in Table S1 using formation energies (at PBE level) of crystals generated with a target of -4.5 eV/atom
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/7_calculate_FigureS2c
python calculate_SR5-10-15_TableS1.py # SR5, SR10, SR15 are printed in the terminal(9) Reproduction of Fig. S2c: Repeat step (3-6) with
cd /crystal/benchmark/Validity_rate_ucRNN__Success_rate_cRNN/2_conditioned_RNN/7_calculate_FigureS2c
python plot_FigureS1c.py # get Fig. S2c as test3.svgThe formation energy distributions with
Please consider citing the following paper if you find our code & data useful.
@article{xiao2023invertible,
title={An invertible, invariant crystal representation for inverse design of solid-state materials using generative deep learning},
author={Xiao, Hang and Li, Rong and Shi, Xiaoyang and Chen, Yan and Zhu, Liangliang and Chen, Xi and Wang, Lei},
journal={Nature Communications},
volume={14},
number={1},
pages={7027},
year={2023},
publisher={Nature Publishing Group UK London}
}
@misc{chen2024mattergptgenerativetransformermultiproperty,
title={MatterGPT: A Generative Transformer for Multi-Property Inverse Design of Solid-State Materials},
author={Yan Chen and Xueru Wang and Xiaobin Deng and Yilun Liu and Xi Chen and Yunwei Zhang and Lei Wang and Hang Xiao},
year={2024},
eprint={2408.07608},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cond-mat.mtrl-sci},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.07608},
}
During the development process, I referenced and drew inspiration from several excellent open source projects and related resources. I would like to express special thanks to the developers of these projects and the contributions of the open source community. The main projects we referenced are:
Start a new discussion thread in [Discussion], or reach out to Hang Xiao (https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hang-Xiao-8) xiaohang07@live.cn if you have any questions.