地址:https://github.com/zhanghecn/luckzh_fnative_monitor
吾爱破解: https://www.52pojie.cn/thread-1798143-1-1.html
写这个项目 本意是想 监控native 下的 svc 调用来协助我分析 anti_frida。
但发现写完并不怎么好用 哎~
看来还是得看 elf结构和so修复才能有帮助。 所以这个项目 由于逆向经验少,和技术 代码质量问题,我并没能写好。
但是弃之可惜,所以我发在github上各位看一下,也希望大佬希望可以协助完善下
不过目前来说功能还是可以用的,各位可以尝试用用看
个人测试 android 10. 理论上 android9~ 以上都行。 现在只支持 arm64
当然我觉得肯定大家会遇到问题,因为我有点寒酸 只有一台手机可以测,其他不敢保证
观察我只观察重要区域,默认全部都是 "user" 范围 也就是
//只观察 应用目录
//系统目录不观察 避免观察数据太多
user = /data/app/**
对于 python 仅支持 spawn 启动
//进入到 main 目录
cd main
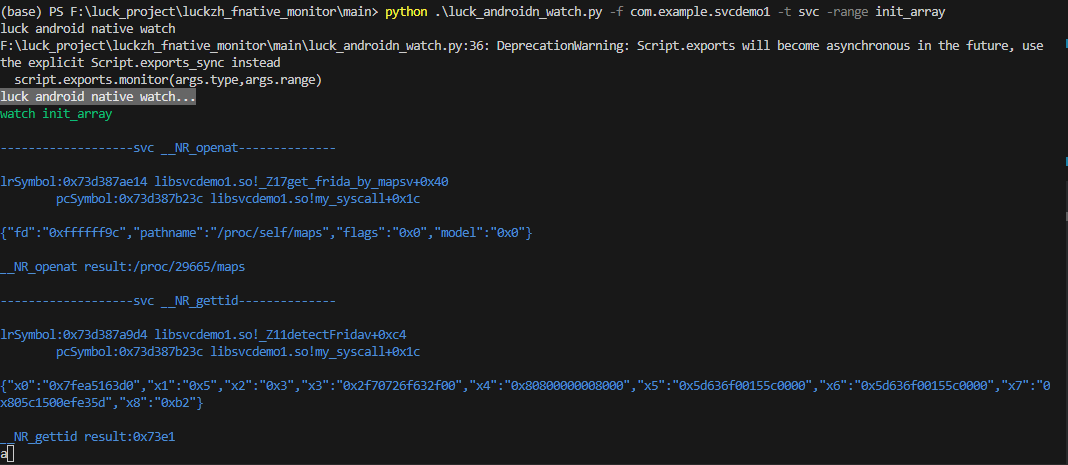
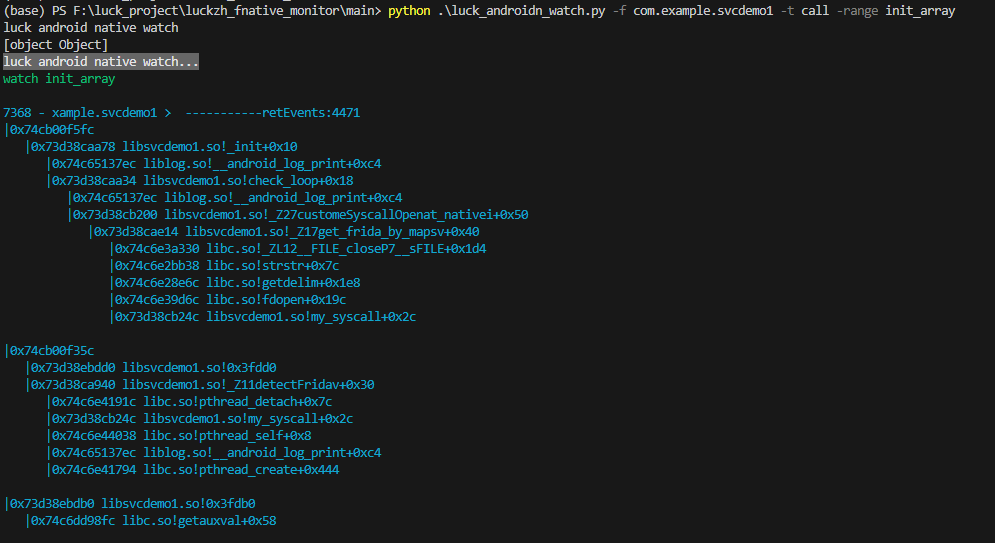
//默认观察方法调用 范围路径是 so 中的 init_array。
python luck_androidn_watch.py -f packname
//当然您也可以更详细一点
// -t 观察类型 svc 调用 还是 普通方法调用
// -range 观察范围 jni init_array pthread_create
python luck_androidn_watch.py -f packname [-t (svc|call)] [-range ("jni"|"init_array"|"pthread_create")]下面是一些浏览图
当然这是我自己写的demo ,所以肯定没有说服力
如果您想附加使用,那么直接用
cd agent
frida -U -l _agent.js [应用名称]
然后再控制台输入下面任意一项
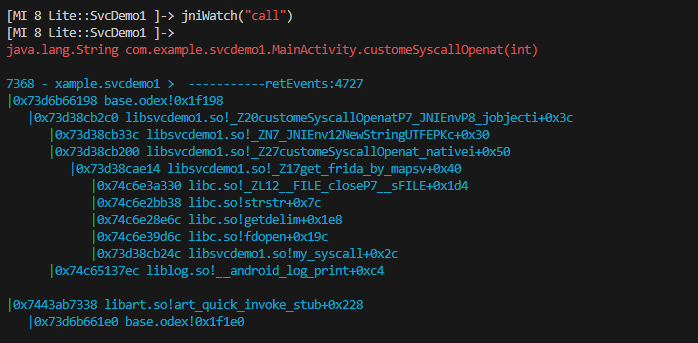
jniWatch("svc")
jniWatch("call")
pthreadCreateWatch("svc")
pthreadCreateWatch("call")
目前观察范围有 3个
关于 jni 观察实际原理我不确定是否都通用 目前我所搜索的资料和测试效果来说,所有的 android 方法都走 libart.so 中的 ArtMethod::Invoke
void ArtMethod::Invoke(Thread* self, uint32_t* args, uint32_t args_size, JValue* result,
const char* shorty) {
if (UNLIKELY(!runtime->IsStarted() ||
(self->IsForceInterpreter() && !IsNative() && !IsProxyMethod() && IsInvokable()))) {
//... 非静态方法
}else{
//如果 native 是非静态调用 art_quick_invoke_stub
if (!IsStatic()) {
(*art_quick_invoke_stub)(this, args, args_size, self, result, shorty);
} else {
// 静态方法调用 art_quick_invoke_static_stub
(*art_quick_invoke_static_stub)(this, args, args_size, self, result, shorty);
}
}
}虽然通过 art_quick_invoke_stub 和 art_quick_invoke_static_stub 能够监控到 native 方法调用,但是我发现了两个问题。
- 部分情况会对 .dex 文件 被 jit 编译成 oat 二进制文件,导致第一次观察堆栈情况不完整,但是调用第二次 又可以成功观察到 jni 调用。
下面是观察 oat文件的堆栈
|0x7443ab7338 libart.so!art_quick_invoke_stub+0x228
|0x74386a51e0 base.odex!0x1f1e0
- jni 的native 静态注册 和 动态注册 有些许差别 我们先从动态注册开始看。 一般使用动态注册 会使用到 jni.h 中的 RegisterNatives。 其最终会通过 class_linker将我们传入的 native 方法指针 对应上 artMethod的 data_ 属性
// 1.jni.h
jint (*RegisterNatives)(JNIEnv*, jclass, const JNINativeMethod*,
jint);
// 2.runtime/jni/jni_internal.cc
static jint RegisterNatives(JNIEnv* env,
jclass java_class,
const JNINativeMethod* methods,
jint method_count) {
.....
for (jint i = 0; i < method_count; ++i) {
const char* name = methods[i].name;
const char* sig = methods[i].signature;
//注意 native 方法指针
const void* fnPtr = methods[i].fnPtr;
//根据 类信息和方法签名 查找 art methodId
ArtMethod* m = nullptr;
for (ObjPtr<mirror::Class> current_class = c.Get();
current_class != nullptr;
current_class = current_class->GetSuperClass()) {
m = FindMethod<true>(current_class, name, sig);
}
//通过 class_linker 绑定到 art_method
const void* final_function_ptr = class_linker->RegisterNative(soa.Self(), m, fnPtr);
}
return JNI_OK;
}
//3. runtime/class_linker.cc
const void* ClassLinker::RegisterNative(
Thread* self, ArtMethod* method, const void* native_method) {
void* new_native_method = nullptr;
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
runtime->GetRuntimeCallbacks()->RegisterNativeMethod(method,
native_method,
/*out*/&new_native_method);
if (method->IsCriticalNative()) {
....
if (method->GetDeclaringClass()->IsVisiblyInitialized()) {
//设置 artMethod的EntryPointFromJni
method->SetEntryPointFromJni(new_native_method);
} else {
critical_native_code_with_clinit_check_.emplace(method, new_native_method);
}
} else {
//设置 artMethod的EntryPointFromJni
method->SetEntryPointFromJni(new_native_method);
}
return new_native_method;
} 动态注册是没问题的。我们只需要监控 ArtMethod方法中的**_data字段即可 麻烦的是静态注册 静态注册一般通过我们写好的方法名格式寻找,在此之前, ArtMethod方法中的_data**储存的是一个寻找 symbol的方法。 这种我们需要看看 art 加载类时候的过程
void ClassLinker::LoadClass(Thread* self,
const DexFile& dex_file,
const dex::ClassDef& dex_class_def,
Handle<mirror::Class> klass) {
size_t class_def_method_index = 0;
uint32_t last_dex_method_index = dex::kDexNoIndex;
size_t last_class_def_method_index = 0;
ClassAccessor accessor(dex_file,
dex_class_def,
/* parse_hiddenapi_class_data= */ klass->IsBootStrapClassLoaded());
....
//通过 类访问器 遍历 字段和方法
accessor.VisitFieldsAndMethods([&](
const ClassAccessor::Field& field){
...
},[&](const ClassAccessor::Field& field) REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
...
}, [&](const ClassAccessor::Method& method) REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
//获取 artMethod
ArtMethod* art_method = klass->GetDirectMethodUnchecked(class_def_method_index,
image_pointer_size_);
// 从 dex_file 中读取信息 加载到 artMethod
LoadMethod(dex_file, method, klass.Get(), art_method);
// 链接执行代码
LinkCode(this, art_method, oat_class_ptr, class_def_method_index);
....
});
...
}
static void LinkCode(ClassLinker* class_linker,
ArtMethod* method,
const OatFile::OatClass* oat_class,
uint32_t class_def_method_index) REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
....
if (method->IsNative()) {
// Set up the dlsym lookup stub. Do not go through `UnregisterNative()`
// as the extra processing for @CriticalNative is not needed yet.
method->SetEntryPointFromJni(
method->IsCriticalNative() ? GetJniDlsymLookupCriticalStub() : GetJniDlsymLookupStub());
}
} 对于静态注册而说,通过 class_linker 加载类的过程会遍历方法通过 LinkCode 设置 GetJniDlsymLookupStub 方法指针 这就通过 ArtMethod 的 _data 属性 动态监控 jni调用照成了阻力。 不过好在 除了第一次调用是通过 GetJniDlsymLookupStub()。后续又会被设置成 实际的 jni native 指针
ENTRY art_jni_dlsym_lookup_stub
...
//调用 artFindNativeMethodRunnable
bl artFindNativeMethod
b .Llookup_stub_continue
.Llookup_stub_fast_or_critical_native:
bl artFindNativeMethodRunnable
END art_jni_dlsym_lookup_stubextern "C" const void* artFindNativeMethodRunnable(Thread* self)
REQUIRES_SHARED(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
uint32_t dex_pc;
ArtMethod* method = self->GetCurrentMethod(&dex_pc);
ClassLinker* class_linker = Runtime::Current()->GetClassLinker();
if (!method->IsNative()) {
.....
}
//判断是不是 IsJniDlsymLookupStub
// 不是的话代表寻找到 jni 的 native 方法指针
const void* native_code = class_linker->GetRegisteredNative(self, method);
if (native_code != nullptr) {
return native_code;
}
...
//没有的话就根据查找 通过 class——linker 注册 native
native_code = vm->FindCodeForNativeMethod(method, &error_msg, /*can_suspend=*/true);
return class_linker->RegisterNative(self, method, native_code);
} 当 so 通过 linker 加载的时候,会调用初始化段的方法。 如 .init 和 .init_array 在 bionic 的 linker 中可以看到这个地方
//linker.cpp
void* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags,
const android_dlextinfo* extinfo,
const void* caller_addr) {
....
//查找 library
soinfo* si = find_library(ns, translated_name, flags, extinfo, caller);
loading_trace.End();
if (si != nullptr) {
void* handle = si->to_handle();
//调用 .init_array
si->call_constructors();
failure_guard.Disable();
LD_LOG(kLogDlopen,
"... dlopen successful: realpath=\"%s\", soname=\"%s\", handle=%p",
si->get_realpath(), si->get_soname(), handle);
return handle;
}
return nullptr;
}
void soinfo::call_constructors() {
....
get_children().for_each([] (soinfo* si) {
si->call_constructors();
});
if (!is_linker()) {
bionic_trace_begin((std::string("calling constructors: ") + get_realpath()).c_str());
}
//调用 INIT 和 INIT_ARRAY
// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.
call_function("DT_INIT", init_func_, get_realpath());
call_array("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array_, init_array_count_, false, get_realpath());
if (!is_linker()) {
bionic_trace_end();
}
} 所以我们监控 soinfo::call_constructors 跟踪其堆栈即可。
在 bionic 的 libc 中 pthread_create 用与创建线程
#include "pthread.h"
int pthread_create(pthread_t* __pthread_ptr, pthread_attr_t const* __attr, void* (*__start_routine)(void*), void*);其中 void* (*__start_routine)(void*) 是线程调用的方法。
也就是说我们可以 通过拦截 pthread_create 获取到调用方法的指针 。完成方法的跟踪
不过也不能全部都拦截。对于 android 线程来说,跟踪的代码太多。所以我们得屏蔽 art 中的方法的
下面是 android 创建线程的过程
new Thread(run).start()
class Thread {
public synchronized void start() {
...
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
...
}
}
//runtime/native/java_lang_Thread.cc
static void Thread_nativeCreate(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jobject java_thread, jlong stack_size,
jboolean daemon) {
// There are sections in the zygote that forbid thread creation.
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
....
Thread::CreateNativeThread(env, java_thread, stack_size, daemon == JNI_TRUE);
}
void Thread::CreateNativeThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject java_peer, size_t stack_size, bool is_daemon) {
....
int pthread_create_result = 0;
if (child_jni_env_ext.get() != nullptr) {
pthread_t new_pthread;
pthread_attr_t attr;
pthread_create_result = pthread_create(&new_pthread,
&attr,
gUseUserfaultfd ? Thread::CreateCallbackWithUffdGc
: Thread::CreateCallback,
child_thread);
}
...
}
void* Thread::CreateCallback(void* arg) {
...
//调用 run 方法
// Invoke the 'run' method of our java.lang.Thread.
ObjPtr<mirror::Object> receiver = self->tlsPtr_.opeer;
WellKnownClasses::java_lang_Thread_run->InvokeVirtual<'V'>(self, receiver);
...
}
https://github.com/zhanghecn/sktrace https://github.com/zhanghecn/frida-trace https://github.com/frida/frida-java-bridge