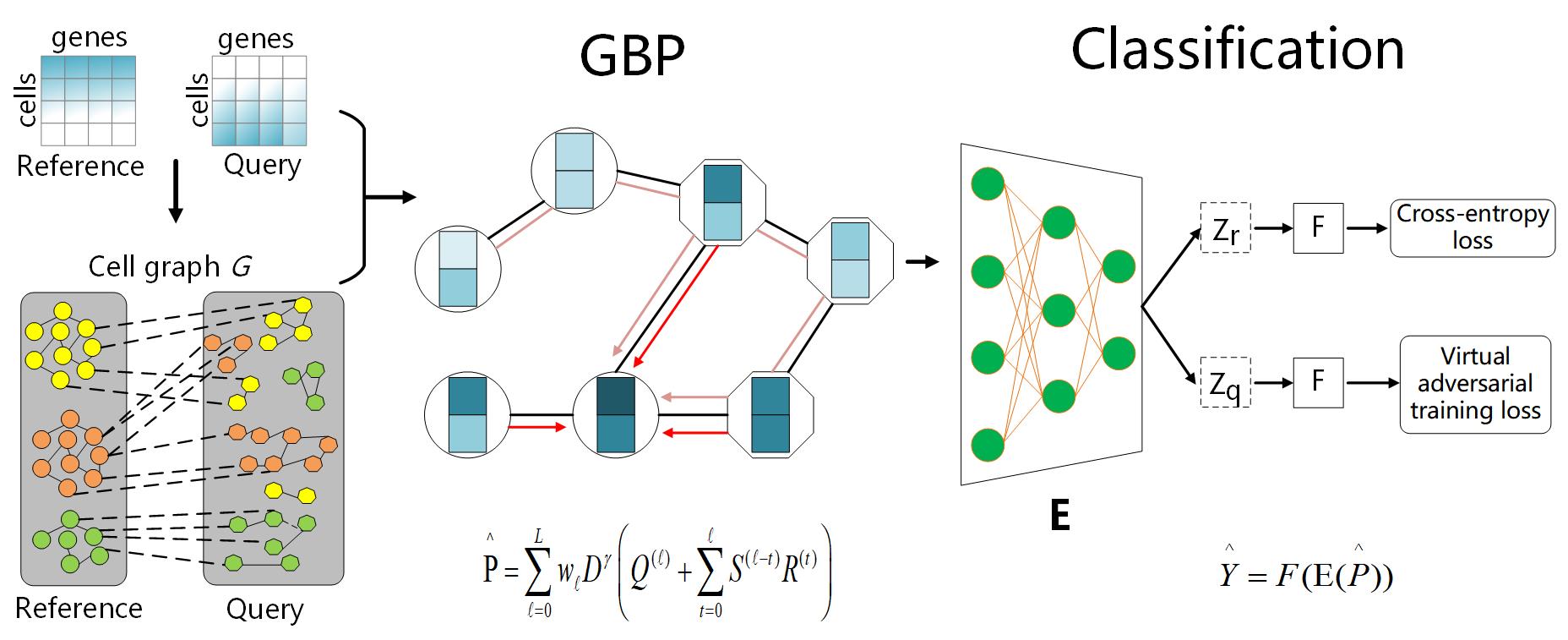
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) techniques provide high-resolution data on cellular heterogeneity in diverse tissues, and a critical step for the data analysis is cell type identification. Tradi-tional methods usually cluster the cells and manually identify cell clusters through marker genes, which is time-consuming and subjective. With the launch of several large-scale single-cell projects, millions of sequenced cells have been annotated and it is promising to transfer labels from the annotated datasets to newly generated datasets. One powerful way for the transferring is to learn cell relations through the graph neural network (GNN), while vanilla GNN is difficult to process millions of cells due to the expensive costs of the message-passing procedure at each training epoch. Here, we have developed a robust and scalable GNN-based meth-od for accurate single cell classification (GraphCS), where the graph is constructed to connect similar cells within and between labelled and unlabelled scRNA-seq datasets for propagation of shared information. To overcome the slow information propaga-tion of GNN at each training epoch, the diffused information is pre-calculated via the approximate Generalized PageRank algorithm, enabling sublinear complexity for a high speed and scalability on millions of cells. Compared with existing methods, GraphCS demonstrates better performance on simulated, cross-platform, and cross-species scRNA-seq datasets. More importantly, our model can achieve superior performance on a large dataset with one million cells within 50 minutes. GraphCS is implemented as an integrated workflow and provided here.
Note: We provide an easy-to-install docker version of GraphCS, please follow instructions in the folder docker_image to use the docker version.
Please ensure that all the libraries below are successfully installed.
-
Operating system
Ubuntu 16.04.7 LTS
Kernel version4.4.0-189-generic
-
BBKNN 1.4.0
-
GCC 5.4.0
-
Scanpy 1.8.1
-
leidenalg 0.8.3
-
CUDA 10.2.89
-
Python 3.7.9
-
Pytorch 1.7.0
-
scrattch.io 0.1.0
-
Seurat 3.1.5
Note: All results have been obtained under Ubuntu 16.04.7 LTS. We have also noticed that the BBKNN 1.4.0 used in our method has constructed approximate nearest neighbors based on the Annoy algorithm, which slightly changes under different operating environments. To obtain the same results with us, we recommend installing GCC 5.4.0 firstly before installing BBKNN 1.4.0.
Execute the following command in the folder GraphCS (same dir with Makefile)
makeThe example_data folder includes the raw data.
The data folder includes the preprocessed data.
All datasets used in this manuscript could be downloaded at here
we provide the preprocessed datasets, which had been normalized by Seurat and the corresponding cell graphs had been constructed by BBKNN. Thus, you can run the following command to get the predicted results directly.
python -u train.py --data Baron_segerstolpe_example.ref
You can download the other Preprocessed example data from the website, and put them into the data folder. Then you can follow the above command to train GraphCS and predict cell types directly.
- pre_process raw data: cd data_preprocess; Rscript data_preprocess.R example
- construct graph: cd graph_construction; python graph.py --name example
- python -u train.py --data example
we save mouse brain in h5 format due to huge storage space are needed.
- pre_process raw data: cd data_preprocess; Rscript normalized_big_data.R
- construct graph: cd graph_construction; python graph.py --name example --large_data T
- python -u train.py --data mouse_brain
- pre_process raw data: cd data_preprocess; Rscript data_preprocess.R siumlated_data_name TRUE
- construct graph: cd graph_construction; python graph_for_simulated_data.py --name siumlated_data_name
- python -u train.py --data mouse_brain
You can reproduce all results reported in this study following the README stored in folder reproducibility.
Note: All raw datasets (RData format) used in this paper were saved on here website. You can download them and put them into the folder example_data to reproduce the results reported in this paper. On the other hand, For Python-based competing methods, you can use the function convert_between_scanpy_seurat.R in the folder reproducibility/competing_methods/ to convert RData type into h5ad type.
The predicted cell labels will be stored in the dataname_pred.csv.
you can follow the format of the dataset example stored in the folder example_data to prepare your own dataset and put it into the folder example_data. Then, Execute the following commands.
- pre_process raw data: cd data_preprocess; Rscript data_preprocess.R your_data_name
- construct graph: cd graph_construction; python graph.py --name your_data_name
- python -u train.py --data your_data_name
Please cite our paper if you use this code in your own work:
@article{zengys,
title={A Robust and Scalable Graph Neural Networkfor Accurate Single Cell Classification},
author={Yuansong Zeng, Xiang Zhou, Zixiang Pan, Yutong Lu1, Yuedong Yang},
journal={xxx},
year={2021}
}