A command-line tool to quickly analyze all IPs in a file and see which ones have open ports/ vulnerabilities. Can also be fed data from stdin to be used in a data pipeline.
nrich fetches information via the InternetDB API and the vulnerability assessment technique is documented in the help center.
Grab the latest release for your operating system. For example, to install the nrich command in Ubuntu:
$ wget https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/33695681/packages/generic/nrich/latest/nrich_latest_x86_64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i nrich_latest_x86_64.debFor MacOS, install from tap repository with homebrew
$ brew tap shodan-public/homebrew-shodan https://gitlab.com/shodan-public/homebrew-shodan
$ brew install nrichTo confirm that it's working you can pipe an IP to the command. For example:
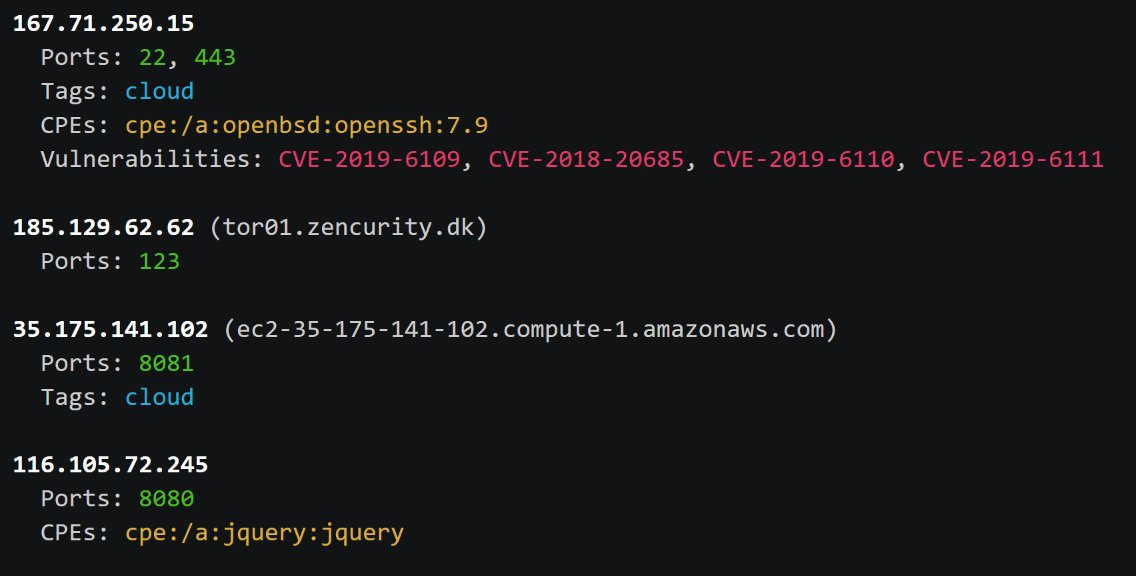
$ echo 149.202.182.140 | nrich -
149.202.182.140 (ftptech1.pcsoft.fr)
Ports: 21, 80, 111, 443
CPEs: cpe:/a:proftpd:proftpd:1.3.5b, cpe:/a:apache:http_server:2.4.25
Vulnerabilities: CVE-2018-11763, CVE-2019-0220, CVE-2017-15710, CVE-2018-1312, CVE-2019-0197, CVE-2017-9798, CVE-2018-1283, CVE-2017-7668, CVE-2017-3169, CVE-2017-15715, CVE-2017-7659, CVE-2018-1333, CVE-2019-0211, CVE-2019-12815, CVE-2017-3167, CVE-2017-9788, CVE-2019-0196, CVE-2017-7679, CVE-2018-17199
The nrich command only requires a single argument: the filename that contains the IPs:
$ nrich --help
nrich 0.1.0
Add network information to IPs
USAGE:
nrich [OPTIONS] <filename>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-o, --output <output> Output format (shell or json) [default: shell]
ARGS:
<filename> File containing an IP per line. Non-IPs are ignoredHere is a short video that shows how to install nrich and then run it against a list of emerging threats: