EGADS (Extensible Generic Anomaly Detection System) is an open-source Java package to automatically detect anomalies in large scale time-series data. EGADS is meant to be a library that contains a number of anomaly detection techniques applicable to many use-cases in a single package with the only dependency being Java. EGADS works by first building a time-series model which is used to compute the expected value at time t. Then a number of errors E are computed by comparing the expected value with the actual value at time t. EGADS automatically determines thresholds on E and outputs the most probable anomalies. EGADS library can be used in a wide variety of contexts to detect outliers and change points in time-series that can have a various seasonal, trend and noise components.
EGADS was designed as a self contained library that has a collection of time-series and anomaly detection models that are applicable to a wide-range of use cases. To compile the library into a single jar, clone the repo and type the following:
mvn clean compile assembly:singleYou may have to set your JAVA_HOME variable to the appropriate JVM. To do this run:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/{JVM directory for desired version}To run a simple example type:
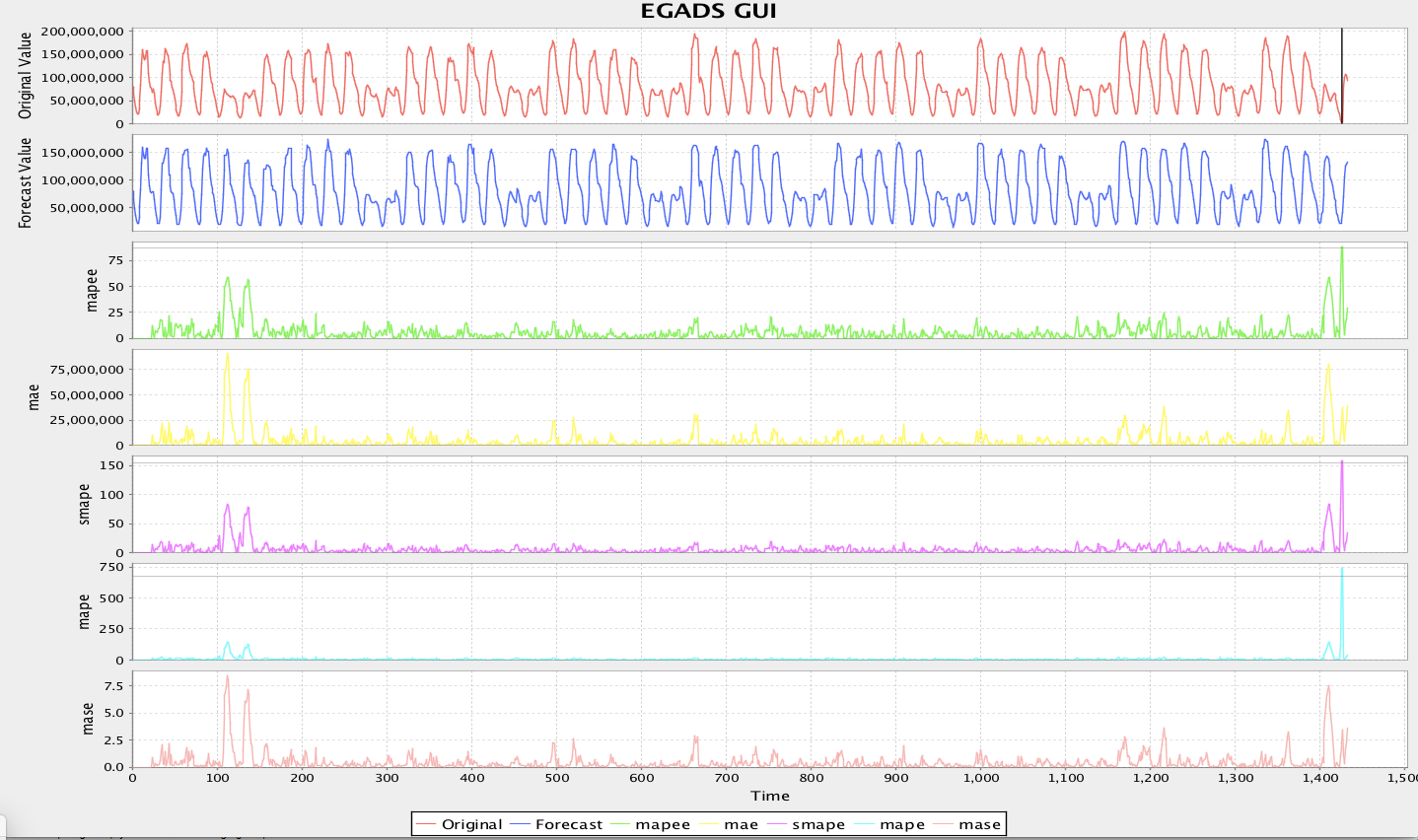
java -Dlog4j.configurationFile=src/test/resources/log4j2.xml -cp target/egads-*-jar-with-dependencies.jar com.yahoo.egads.Egads src/test/resources/sample_config.ini src/test/resources/sample_input.csvwhich produces the following picture (Note that you can enable this UI by setting OUTPUT config key to GUI in sample_config.ini).
One can also specify config parameters on a command line. For example to do anomaly detection using Olympic Scoring as a time-series model and a density based method as an anomaly detection model use the following.
java -Dlog4j.configurationFile=src/test/resources/log4j2.xml -cp target/egads-*-jar-with-dependencies.jar com.yahoo.egads.Egads "MAX_ANOMALY_TIME_AGO:999999999;AGGREGATION:1;OP_TYPE:DETECT_ANOMALY;TS_MODEL:OlympicModel;AD_MODEL:ExtremeLowDensityModel;INPUT:CSV;OUTPUT:STD_OUT;BASE_WINDOWS:168;PERIOD:-1;NUM_WEEKS:3;NUM_TO_DROP:0;DYNAMIC_PARAMETERS:0;TIME_SHIFTS:0" src/test/resources/sample_input.csvTo run anomaly detection using no time-series model with an auto static threshold for anomaly detection, use the following:
java -Dlog4j.configurationFile=src/test/resources/log4j2.xml -cp target/egads-*-jar-with-dependencies.jar com.yahoo.egads.Egads "MAX_ANOMALY_TIME_AGO:999999999;AGGREGATION:1;OP_TYPE:DETECT_ANOMALY;TS_MODEL:NullModel;AD_MODEL:SimpleThresholdModel;SIMPLE_THRESHOLD_TYPE:AdaptiveMaxMinSigmaSensitivity;INPUT:CSV;OUTPUT:STD_OUT;AUTO_SENSITIVITY_ANOMALY_PCNT:0.2;AUTO_SENSITIVITY_SD:2.0" src/test/resources/sample_input.csvWhile rapid advances in computing hardware and software have led to powerful applications, still hundreds of software bugs and hardware failures continue to happen in a large cluster compromising user experience and subsequently revenue. Non-stop systems have a strict uptime requirement and continuous monitoring of these systems is critical. From the data analysis point of view, this means non-stop monitoring of large volume of time-series data in order to detect potential faults or anomalies. Due to the large scale of the problem, human monitoring of this data is practically infeasible which leads us to automated anomaly detection. An anomaly, or an outlier, is a data point which is significantly different from the rest of the data. Generally, the data in most applications is created by one or more generating processes that reflect the functionality of a system.
When the underlying generating process behaves in an unusual way, it creates outliers. Fast and efficient identification of these outliers is useful for many applications including: intrusion detection, credit card fraud, sensor events, medical diagnoses, law enforcement and others. Current approaches in automated anomaly detection suffer from a large number of false positives which prohibit the usefulness of these systems in practice. Use-case, or category specific, anomaly detection models may enjoy a low false positive rate for a specific application, but when the characteristics of the time-series change, these techniques perform poorly without proper retraining.
EGADS (Extensible Generic Anomaly Detection System) enables the accurate and scalable detection of time-series anomalies. EGADS separates forecasting and anomaly detection two separate components which allows the person to add her own models into any of the components.
The EGADS framework consists of two main components: the time-series modeling module (TMM), the anomaly detection module (ADM). Given a time-series the TMM component models the time-series producing an expected value later consumed by the ADM that computes anomaly scores. EGADS was built as a framework to be easily integrated into an existing monitoring infrastructure. At Yahoo, our internal Yahoo Monitoring Service (YMS) processes millions of data-points every second. Therefore, having a scalable, accurate and automated anomaly detection for YMS is critical. For this reason, EGADS can be compiled into a single light-weight jar and deployed easily at scale.
The TMM and ADM can be found under main/java/com/yahoo/egads/models.
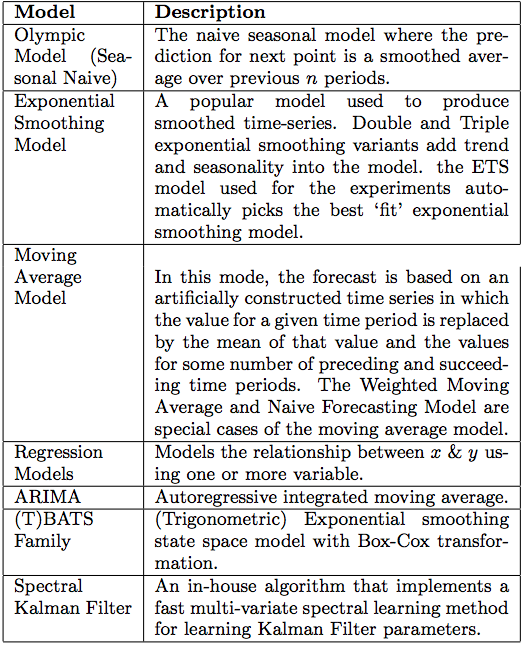
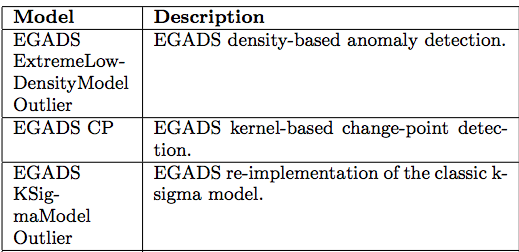
The example of the models supported by TMM and ADM can be found in in the two table below. We expect this collection of models to grow as more contribution is put forward by the community.
Below are the various configuration parameters supported by EGADS.
# Only show anomalies no older than this.
# If this is set to 0, then only output an anomaly
# if it occurs on the last time-stamp.
MAX_ANOMALY_TIME_AGO 99999
# Denotes how much should the time-series be aggregated by.
# If set to 1 or less, this setting is ignored.
AGGREGATION 1
# OP_TYPE specifies the operation type.
# Options: DETECT_ANOMALY,
# UPDATE_MODEL,
# TRANSFORM_INPUT
OP_TYPE DETECT_ANOMALY
# TS_MODEL specifies the time-series
# model type.
# Options: AutoForecastModel
# DoubleExponentialSmoothingModel
# MovingAverageModel
# MultipleLinearRegressionModel
# NaiveForecastingModel
# OlympicModel
# PolynomialRegressionModel
# RegressionModel
# SimpleExponentialSmoothingModel
# TripleExponentialSmoothingModel
# WeightedMovingAverageModel
# SpectralSmoother
# NullModel
TS_MODEL OlympicModel
# AD_MODEL specifies the anomaly-detection
# model type.
# Options: ExtremeLowDensityModel
# AdaptiveKernelDensityChangePointDetector
# KSigmaModel
# NaiveModel
# DBScanModel
# SimpleThresholdModel
AD_MODEL ExtremeLowDensityModel
# Type of the simple threshold model.
# Options: AdaptiveMaxMinSigmaSensitivity
# AdaptiveKSigmaSensitivity
# SIMPLE_THRESHOLD_TYPE
# Specifies the input src.
# Options: STDIN
# CSV
INPUT CSV
# Specifies the output src.
# Options: STD_OUT,
# ANOMALY_DB
# GUI
# PLOT
OUTPUT STD_OUT
# THRESHOLD specifies the threshold for the
# anomaly detection model.
# Comment to auto-detect all thresholds.
# Options: mapee,mae,smape,mape,mase.
# THRESHOLD mape#10,mase#15
#####################################
### Olympic Forecast Model Config ###
#####################################
# The possible time-shifts for Olympic Scoring.
TIME_SHIFTS 0,1
# The possible base windows for Olympic Scoring.
BASE_WINDOWS 24,168
# Period specifies the periodicity of the
# time-series (e.g., the difference between successive time-stamps).
# Options: (numeric)
# 0 - auto detect.
# -1 - disable.
PERIOD -1
# NUM_WEEKS specifies the number of weeks
# to use in OlympicScoring.
NUM_WEEKS 8
# NUM_TO_DROP specifies the number of
# highest and lowest points to drop.
NUM_TO_DROP 0
# If dynamic parameters is set to 1, then
# EGADS will dynamically vary parameters (NUM_WEEKS)
# to produce the best fit.
DYNAMIC_PARAMETERS 0
###################################################
### ExtremeLowDensityModel & DBScanModel Config ###
###################################################
# Denotes the expected % of anomalies
# in your data.
AUTO_SENSITIVITY_ANOMALY_PCNT 0.01
# Refers to the cluster standard deviation.
AUTO_SENSITIVITY_SD 3.0
############################
### NaiveModel Config ###
############################
# Window size where the spike is to be found.
WINDOW_SIZE 0.1
#######################################################
### AdaptiveKernelDensityChangePointDetector Config ###
#######################################################
# Change point detection parameters
PRE_WINDOW_SIZE 48
POST_WINDOW_SIZE 48
CONFIDENCE 0.8
###############################
### SpectralSmoother Config ###
###############################
# WINDOW_SIZE should be greater than the size of longest important seasonality.
# By default it is set to 192 = 8 * 24 which is worth of 8 days (> 1 week) for hourly time-series.
WINDOW_SIZE 192
# FILTERING_METHOD specifies the filtering method for Spectral Smoothing
# Options: GAP_RATIO (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 0.01)
# EIGEN_RATIO (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 0.1)
# EXPLICIT (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 10)
# K_GAP (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 8)
# VARIANCE (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 0.99)
# SMOOTHNESS (Recommended: FILTERING_PARAM = 0.97)
FILTERING_METHOD GAP_RATIO
FILTERING_PARAM 0.01
- Clone your fork
- Hack away
- If you are adding new functionality, document it in the README
- Verify your code by running
mvn packageand adding additional tests. - Push the branch up to GitHub
- Send a pull request to the yahoo/egads project.
We actively welcome contributions. If you don't know where to start, try checking out the issue list and fixing up the place. Or, you can add a model - a goal of this project is to have a robust, lightweight and dependency-free set of models to choose from that are ready to be deployed in production.
Generic and Scalable Framework for Automated Time-series Anomaly Detection by Nikolay Laptev, Saeed Amizadeh, Ian Flint , KDD 2015 (August 10, 2015)
If you use EGADS in your projects, please cite: Generic and Scalable Framework for Automated Time-series Anomaly Detection by Nikolay Laptev, Saeed Amizadeh, Ian Flint , KDD 2015
BibTeX:
@inproceedings{laptev2015generic,
title={Generic and Scalable Framework for Automated Time-series Anomaly Detection},
author={Laptev, Nikolay and Amizadeh, Saeed and Flint, Ian},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
pages={1939--1947},
year={2015},
organization={ACM}
}Code licensed under the GPL License. See LICENSE file for terms.