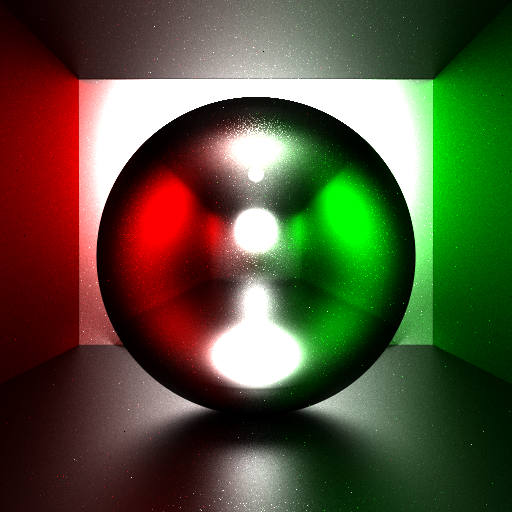
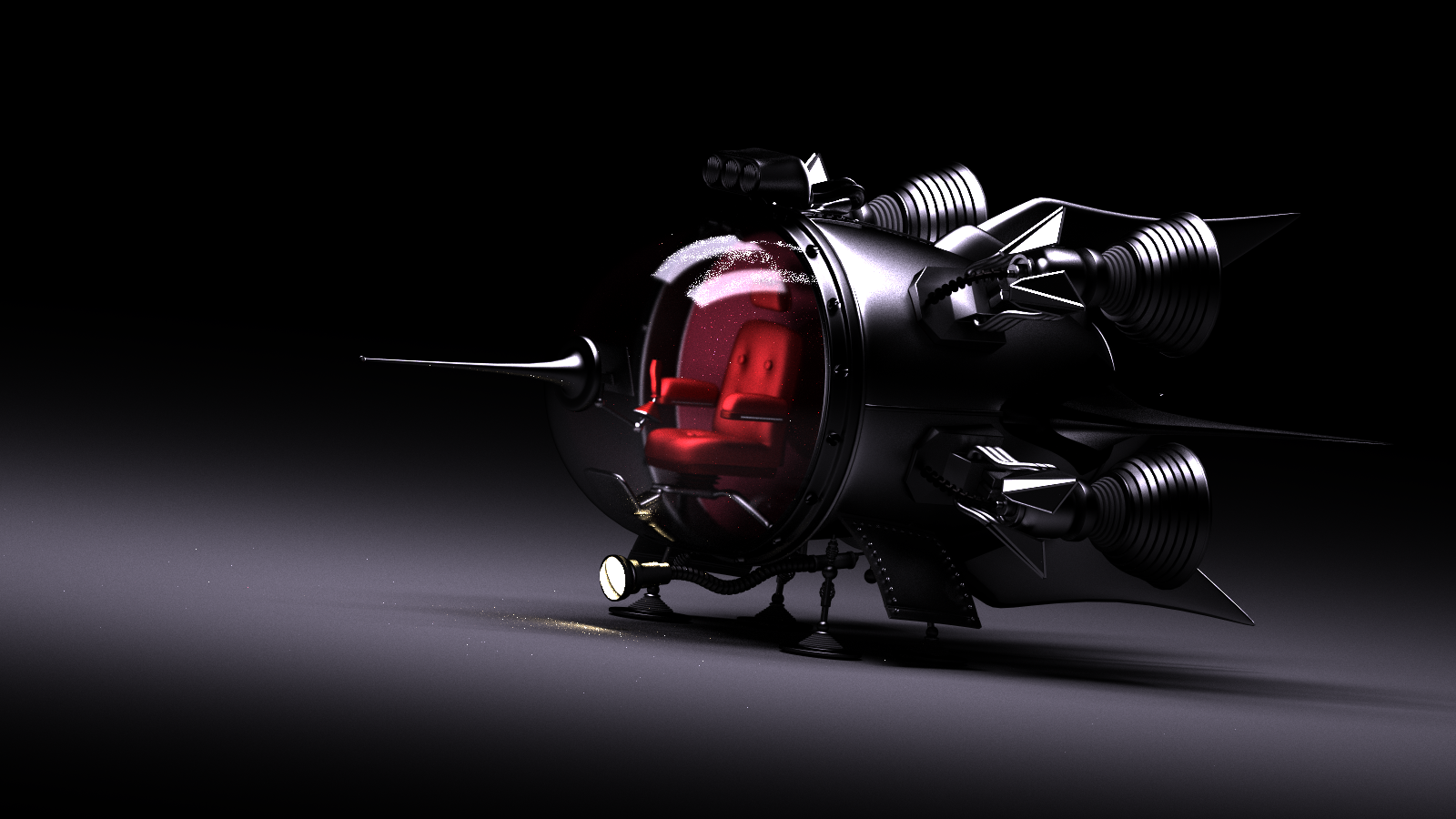
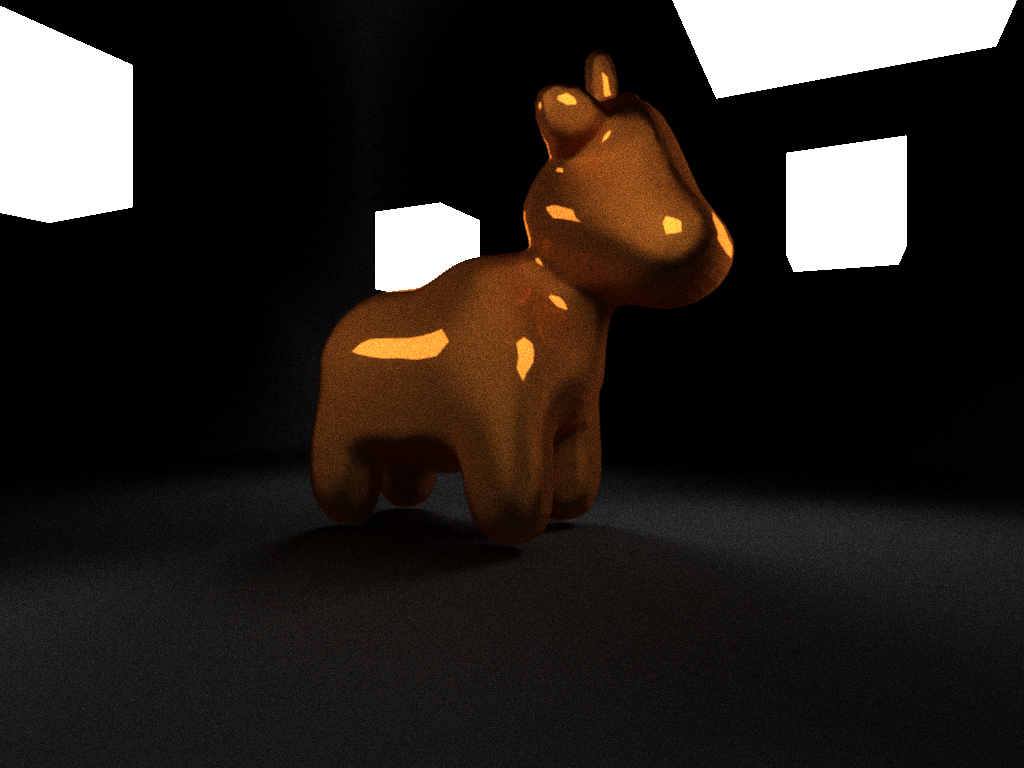
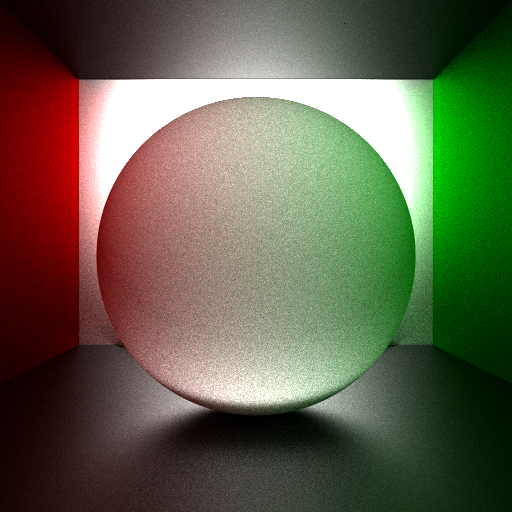
- Basic cuda raytracing framework was successfully built, tested and profiled.
- Nvidia Tesla K40m
- Compatible CPU multicore version was built and tested.
- Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-8550U CPU @ 1.80GHz, 8 Logic Cores
- Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670 v3 @ 2.30GHz, 48 Logic Cores
- Visualization module is currently broken because I modified the data structure of mesh. It is to be repaired soon.
- Material and BSDF system are being built, currently the raytracing kernel does not integrate radiance.
- Build environments:
- Windows 10 Education Insider Preview 18290.rs_prerelease
- MinGW-w64 8.1.0 (test CPU multicore)
- CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core)
- CUDA 9.0 (test cuda)
- gcc (GCC) 6.3.1 20170216 (Red Hat 6.3.1-3)
- Windows 10 Education Insider Preview 18290.rs_prerelease
- Polymorphism
- Spheres
- Other
- Bidirectional Path Tracer
- Point Lights
- Spot Lights
- Area Lights
- Heuristic Light Estimation
- Acceleration
- Hybrid Renderer
- Reduce GPU Divergency
- Refactor
- Several Classes
- DSL
- Material
- Mat Sphere
- Mixed Shader(Blender)
- BTDF
- Microfacet Distribution
- Cosine
- Beckmann
- GGX
- Other
Bidirectional Path Tracing, beckmann microfacet brdf, 1024spp
lambert, 512spp
area light demo, 4096spp
Microfacet BRDF with Beckmann Distribution of different roughness
{
"assets": [
["import", {
"path": "./x6.blend"
}]
],
"camera": [],
"material": {
"Material": ["Microfacet", {
"distribution": ["Beckmann", {
"alpha": 0.5
}],
"color": [0.608, 0.522, 0.333]
}],
"luz": ["Luz", {
"emission": [50, 50, 50]
}],
"cafe": ["Microfacet", {
"distribution": ["Beckmann", {
"alpha": 0.1
}],
"color": [0.275, 0.25, 0.23]
}],
"Material.001": ["Microfacet", {
"distribution": ["Beckmann", {
"alpha": 0.6
}]
}],
"porcelana": ["Microfacet", {
"distribution": ["Beckmann", {
"alpha": 0.3
}],
"color": [0.545, 0.463, 0.427]
}],
"DefaultMaterial": ["Lambert"]
}
}Perfect mirror reflection.
The ray emitter of this version is somehow buggy, and raytracing process is not completely correct.
- gcc 4.8+
- assimp
- cuda [ optional ]
- gl & glfw3 [ optional ]
The tracer aimed at working on heterogeneous systems.
-
Use
-DCUDA=ONto enable cuda toolkits. If so, macroKOISHI_USE_CUDAwill be defined. -
Use
-DGL=ONto enable bvh visualization. If so, macroKOISHI_USE_GLwill be defined, allvis/*source code will we included.
Use vis::Renderer.
#include <vis/renderer.hpp>
using namespace koishi;
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
vis::Renderer r{ 1024, 768 };
r.render( "./cow.json" );
}
Tracing functions are defined using PolyFunction macro:
// template <typename T> // optional
PolyFunction( name, requirements ) (
( parameters ) -> value_type {
// do sth
}
);nameis the name of that poly-function.requirementsis one or more class defination which the function requires to work, using template Require<>.- the function body lies in the second bracket.
e.g.
PolyFunction( DRand48, Require<Host> )(
()->double {
static unsigned long long seed = ( ( (long long int)time( nullptr ) ) << 16 ) | ::rand();
constexpr auto m = 0x100000000LL;
constexpr auto c = 0xB16;
constexpr auto a = 0x5DEECE66DLL;
seed = ( a * seed + c ) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFLL;
unsigned int x = seed >> 16;
return ( (double)x / (double)m );
} );poly-function DRand48 works only on host machine (Require<Host>).
PolyFunction( F, Require<Host>, Require<Device> )(
(...)->double3 {
// poly-function F works on both host(cpu) and device(gpu).
} );
PolyFunction( G, Require<F> )(
()->double3 {
// poly-function G works on all platforms that F supports.
} );
PolyFunction( H, Require<F, G> )(
()->double3 {
// poly-function H works on all platforms that F, G both supports.
// use `call<>()` function in poly-function to call other poly-functions
auto res = call<F>(...); // if the function H is executed on host, that's a host call, otherwise a device call.
} );
PolyFunction( J, Require<F, G, Device> )(
()->double3 {
// poly-function J works only on device(gpu) and F, G must both support gpu, or it leads to a compile error.
} );- PolyFunction is incompatible with
openmp, but you u can usestd::threadinstead of it. - use regular
__global__call to emit jobs to gpu.
cmake . -Bbuild -DGL=ON/OFF -DCUDA=ON/OFF
cmake --build build --target cr./cr ./spaceship.json -o a.png --resolution=1024x512 -k Radiance -s 64