A file downloader written in Rust Programming Language.
Installation | Usage | Configuration| Container
Table of contents
- Support downloading files from HTTP/HTTPs services
- Support downloading files from SFTP services
- Support downloading files from MinIO services
- Support parallel downloading to accelerate download speed
- Support broken-point continuingly-transferring
- Support daemonizing
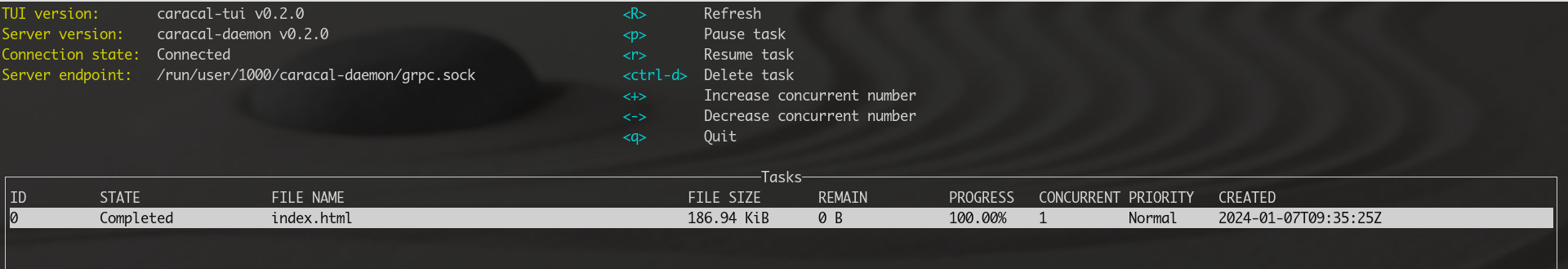
- Provide terminal user interface (TUI)
- Terminal user interface (TUI)
Install the pre-built binaries
Pre-built binaries for Linux can be found on the releases page, the latest release is available here.
For example, to install caracal to ~/bin:
# Create `~/bin`.
mkdir -p ~/bin
# Change directory to `~/bin`.
cd ~/bin
# Download and extract caracal to `~/bin/`.
# NOTE: replace the version with the version you want to install
export CARACAL_VERSION=$(basename $(curl -s -w %{redirect_url} https://github.com/xrelkd/caracal/releases/latest))
# NOTE: the architecture of your machine,
# Available values are `x86_64-unknown-linux-musl`, `x86_64-apple-darwin`, `aarch64-apple-darwin`.
export ARCH=x86_64-unknown-linux-musl
curl -s -L "https://github.com/xrelkd/caracal/releases/download/${CARACAL_VERSION}/caracal-${CARACAL_VERSION}-${ARCH}.tar.gz" | tar xzf -
# Add `~/bin` to the paths that your shell searches for executables
# this line should be added to your shells initialization file,
# e.g. `~/.bashrc` or `~/.zshrc`
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/bin"
# Show version.
caracal version
# Show version.
caracal-daemon version
# Show version.
caracal-tui versionBuild from source
caracal requires the following tools and packages to build:
rustccargopkg-configlibgit2
With the above tools and packages already installed, you can simply run:
git clone --branch=main https://github.com/xrelkd/caracal.git
cd caracal
cargo install --path caracal
cargo install --path caracal-daemon
cargo install --path caracal-tuiRun caracal without caracal-daemon
# Show usage.
caracal help
# Download a file from HTTP server.
caracal https://www.rust-lang.org/
# Download multiple files from HTTP server.
caracal https://example.com/a.tar.gz https://example.com/b.zip
# Copy a file from local file system.
caracal /etc/os-release
# Download a file from SFTP server.
caracal sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release
# Copy a file from MinIO server.
caracal minio://myminio/path/to/file
# Download multiple files from different services.
caracal \
/etc/os-release \
https://example.com/a.tar.gz \
sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release \
minio://myminio/path/to/file
# Download multiple files from different services and put them in directory `/tmp/downloads`.
mkdir -p /tmp/downloads && \
caracal -D /tmp/downloads \
/etc/os-release \
sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release \
minio://myminio/path/to/file \
https://example.com/a.tar.gz
# Specify an alternative number of connections.
caracal -n 3 https://www.rust-lang.org/
# Set the connection timeout in second.
caracal -T 3 https://www.rust-lang.org/
Run caracal-daemon and use caracal to interact with caracal-daemon.
# Show usage.
caracal-daemon help
# Start daemon, caracal-daemon runs as a daemon.
# It provides gRPC endpoint, waiting for new commands.
caracal-daemon &
# Show usage of `add-uri`.
caracal help add-uri
# Use the subcommand `add-uri` to create new task.
# Add a new task for downloading a file from HTTP server.
caracal add-uri https://www.rust-lang.org/
# Show status of tasks.
caracal status
# Add a new task for downloading multiple files from HTTP server.
caracal add-uri https://example.com/a.tar.gz https://example.com/b.zip
# Add a new task for copying a file from local file system.
caracal add-uri /etc/os-release
# Add a new task for downloading a file from SFTP server.
caracal add-uri sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release
# Add a new task for copying a file from MinIO server.
caracal add-uri minio://myminio/path/to/file
# Add a new task for downloading multiple files from different services.
caracal add-uri \
/etc/os-release \
https://example.com/a.tar.gz \
sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release \
minio://myminio/path/to/file
# Download multiple files from different services and put them in directory `/tmp/downloads`.
mkdir -p /tmp/downloads && \
caracal add-uri -D /tmp/downloads \
/etc/os-release \
sftp://my-ssh-server/etc/os-release \
minio://myminio/path/to/file \
https://example.com/a.tar.gz
# Pause tasks.
caracal pause 1 2 3
# Resume tasks.
caracal resume 1 2 3
# Pause all tasks.
caracal pause --all
# Resume all tasks.
caracal resume --all
# Remove tasks.
caracal remove 1 2 3- NOTE: Remember to start
caracal-daemon. Terminal user interface does not provide standalone mode, it provides user interface for user to interact withcaracal-daemon.
# Start `caracal-daemon` and put it in the background.
caracal-daemon &
# Show version.
caracal-tui version
# Start terminal user interface.
caracal-tuiThe configuration file of caracal is placed on $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal.toml.
The configuration file of caracal-daemon is placed on $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml.
The configuration file of caracal-tui is placed on $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-tui.toml.
# Create directory to store configuration files.
mkdir -p $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/
# Generate default configuration and place it on `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal.toml`.
caracal default-config > $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal.toml
# Generate default configuration and place it on `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml`.
caracal-daemon default-config > $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml
# Generate default configuration and place it on `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-tui.toml`.
caracal-tui default-config > $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-tui.tomlExample of $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal.toml
NOTE: ~ in a file path will be resolved to $HOME.
# File paths to profiles, see profile file configuration
profile_files = ["/path/to/profile/file", "/path/to/profile/file2", "~/path/to/my/profile"]
[daemon]
# Endpoint of gRPC server
# Caracal connect to gRPC server via local socket with file path like "/path/to/caracal-daemon/grpc.sock"
# Caracal connect to gRPC server via HTTP with URI like "http://www.my.server.com/"
server_endpoint = "/path/to/caracal-daemon/grpc.sock"
# Access token, remove this line to disable authentication
access_token = "my-access-token"
# File path of access token, remove this line to disable authentication
# `access_token_file_path` is preferred if both `access_token` and `access_token_file_path` are provided.
access_token_file_path = "/path/to/access-token"
[log]
# Emit log to systemd-journald
emit_journald = true
# Emit log to stdout
emit_stdout = false
# Emit log to stderr
emit_stderr = false
# Set the log level, available values are "ERROR", "WARN", "INFO", "DEBUG", "TRACE"
level = "INFO"
[downloader]
# Path of default output directory
default_output_directory = "/path/to/default/output/directory"
[downloader.http]
# The user-agent which will be passed to HTTP server
user_agent = "Caracal/0.2.0"
# The number of concurrent number of HTTP connection per task
concurrent_connections = 5Example of $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml
# File paths to profiles, see profile file configuration
profile_files = ["/path/to/profile/file", "/path/to/profile/file2"]
[log]
# Emit log to systemd-journald
emit_journald = true
# Emit log to stdout
emit_stdout = false
# Emit log to stderr
emit_stderr = false
# Set the log level, available values are "ERROR", "WARN", "INFO", "DEBUG", "TRACE"
level = "INFO"
[task_scheduler]
# The number of tasks to execute concurrently
concurrent_number = 10
[downloader.http]
# The user-agent which will be passed to HTTP server
user_agent = "Caracal/0.2.0"
# The number of concurrent number of HTTP connection per task
concurrent_connections = 5
[grpc]
# Provide gRPC via HTTP
enable_http = true
# Host address of gRPC, ignored while `enable_http` is `false`
host = "127.0.0.1"
# Port of gRPC server, ignored while `enable_http` is `false`
port = 37000
# Provide gRPC service via local socket (UNIX domain socket)
enable_local_socket = true
# Path of local socket
local_socket = "/path/to/caracal-daemon/grpc.sock"
# Access token, remove this line to disable authentication
access_token = "my-access-token"
# File path of access token, remove this line to disable authentication
# `access_token_file_path` is preferred if both `access_token` and `access_token_file_path` are provided.
access_token_file_path = "/path/to/access-token"
[metrics]
# Enable Prometheus metrics
enable = true
# Host address of metrics
host = "127.0.0.1"
# Port of metrics
port = 37002Example of $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/caracal/caracal-tui.toml
NOTE: ~ in a file path will be resolved to $HOME.
[daemon]
# Endpoint of gRPC server
# Caracal connect to gRPC server via local socket with file path like "/path/to/caracal-daemon/grpc.sock"
# Caracal connect to gRPC server via HTTP with URI like "http://www.my.server.com/"
server_endpoint = "/path/to/caracal-daemon/grpc.sock"
# Access token, remove this line to disable authentication
access_token = "my-access-token"
# File path of access token, remove this line to disable authentication
# `access_token_file_path` is preferred if both `access_token` and `access_token_file_path` are provided.
access_token_file_path = "/path/to/access-token"
[log]
# Emit log to systemd-journald
emit_journald = true
# Emit log to stdout
emit_stdout = false
# Emit log to stderr
emit_stderr = false
# Set the log level, available values are "ERROR", "WARN", "INFO", "DEBUG", "TRACE"
level = "INFO"Example of Profile file
[[profiles]]
[profiles.MinIO]
# Name of profile
name = "my-minio"
# Endpoint of MinIO server
endpoint_url = "https://my.minio.server.com"
# Access key of MinIO server
access_key = "access_key"
# Secret key of MinIO server
secret_key = "secret_key"
[[profiles]]
[profiles.MinIO]
name = "my-minio2"
endpoint_url = "https://my.minio2.server.com"
access_key = "access_key"
secret_key = "secret_key"
[[profiles]]
[profiles.SSH]
# Name of profile
name = "my-ssh-server"
# SSH host to connect
# It may be specified as either [user@]hostname or a URI of the form ssh://[user@]hostname[:port].
endpoint = "my-ssh-server"
# Set the SSH user
user = "user"
# Set the key file to use
identity_file = "/path/to/ssh/key"
[[profiles]]
[profiles.SSH]
name = "my-ssh-server2"
endpoint = "my-ssh-server2"
user = "user"
identity_file = "/path/to/ssh/key2"Container images are available on GitHub Packages.
- Run
caracal-daemonwithDocker
docker pull ghcr.io/xrelkd/caracal:latest
docker run -d ghcr.io/xrelkd/caracal:latestRun with Docker Compose
We use Docker Compose to configure caracal-daemon service.
- Create
docker-compose.yamlandcaracal-daemon.tomlwith the following contents.
docker-compose.yaml
services:
caracal:
image: ghcr.io/xrelkd/caracal:latest
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:37000:37000"
- "127.0.0.1:37002:37002"
volumes:
- ${PWD}/caracal-daemon.toml:/etc/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml
- downloads:/downloads
entrypoint: ["caracal-daemon", "--config=/etc/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml"]
volumes:
downloads:caracal-daemon.toml
profile_files = []
[log]
# systemd-journald is not available in container, disable it
emit_journald = false
# Emit log message to stdout.
emit_stdout = true
emit_stderr = false
level = "INFO"
[task_scheduler]
concurrent_number = 10
[downloader]
# Set default output directory to `/downloads`.
default_output_directory = "/downloads"
[downloader.http]
user_agent = "Caracal/0.2.0"
concurrent_connections = 5
[grpc]
enable_http = true
# Disable local socket because we only interact with the daemon via HTTP.
enable_local_socket = false
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 37000
[metrics]
enable = true
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 37002NOTE: In order to connect the caracal-daemon in container, daemon.server_endpoint in caracal.toml should be set as http://127.0.0.1:37000.
- Run
docker compose upto start the container. - Run
caracal add-uri https://www.rust-lang.org/to create a new task, the downloaded file is placed on/downloadsin the container. - Run
caracal statusto display the status of tasks. - Run
docker compose downto stop the container.
Deploy on Kubernetes
Save the following contents to caracal.yaml and execute kubectl apply -f caracal.yaml to deploy caracal-daemon on Kubernetes cluster:
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/configmap/
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: caracal
data:
caracal-daemon.toml: |
profile_files = []
[log]
emit_journald = false
emit_stdout = true
emit_stderr = false
level = "INFO"
[task_scheduler]
concurrent_number = 10
[downloader]
default_output_directory = "/tmp"
[downloader.http]
user_agent = "Caracal/0.2.0"
concurrent_connections = 5
[grpc]
enable_http = true
enable_local_socket = false
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 37000
[metrics]
enable = true
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 37002
---
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/deployment/
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: caracal
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: caracal
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: caracal
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: caracal
spec:
restartPolicy: Always
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: caracal
items:
- key: caracal-daemon.toml
path: caracal-daemon.toml
containers:
- name: caracal
image: ghcr.io/xrelkd/caracal:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- "caracal-daemon"
- "--config=/etc/caracal/caracal-daemon.toml"
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/caracal/
ports:
- containerPort: 37000
name: grpc
- containerPort: 37002
name: metrics
---
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: caracal
spec:
selector:
app: caracal
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: grpc
protocol: TCP
port: 37000
targetPort: 37000
---Caracal is licensed under the GNU General Public License version 3. See LICENSE for more information.