Web server with built-in support for QUIC, HTTP/2, Lua, Markdown, Pongo2, HyperApp, Amber, Sass(SCSS), GCSS, JSX, BoltDB (built-in, stores the database in a file, like SQLite), Redis, PostgreSQL, MariaDB/MySQL, rate limiting, graceful shutdown, plugins, users and permissions.
All in one small self-contained executable.
Clone algernon outside of GOPATH:
git clone https://github.com/xyproto/algernon
cd algernon
go build -mod=vendor
See README.md in the go111 branch.
- algernon (statically compiled ELF)
See the release page for releases for other platforms and architectures.
The docker image is a total of 9MB.
Written in Go. Uses Bolt (built-in), MySQL, PostgreSQL or Redis (recommended) for the database backend, permissions2 for handling users and permissions, gopher-lua for interpreting and running Lua, http2 for serving HTTP/2, QUIC for serving over QUIC, blackfriday for Markdown rendering, amber for Amber templates, Pongo2 for Pongo2 templates, Sass(SCSS) and GCSS for CSS preprocessing. logrus is used for logging, goja-babel for converting from JSX to JavaScript, tollbooth for rate limiting, pie for plugins and graceful for graceful shutdowns.
- HTTP/2 over SSL/TLS (https) is used by default, if a certificate and key is given.
- If not, regular HTTP is used.
- QUIC ("HTTP over UDP", supported by Chromium) can be enabled with a flag.
- /data and /repos have user permissions, /admin has admin permissions and / is public, by default. This is configurable.
- The following filenames are special, in prioritized order:
- index.lua is Lua code that is interpreted as a handler function for the current directory.
- index.html is HTML that is outputted with the correct Content-Type.
- index.md is Markdown code that is rendered as HTML.
- index.txt is plain text that is outputted with the correct Content-Type.
- index.pongo2, index.po2 or index.tmpl is Pongo2 code that is rendered as HTML.
- index.amber is Amber code that is rendered as HTML.
- index.hyper.js or index.hyper.jsx is JSX+HyperApp code that is rendered as HTML
- data.lua is Lua code, where the functions and variables are made available for Pongo2, Amber and Markdown pages in the same directory.
- If a single Lua script is given as a commandline argument, it will be used as a standalone server. It can be used for setting up handlers or serving files and directories for specific URL prefixes.
- style.gcss is GCSS code that is used as the style for all Pongo2, Amber and Markdown pages in the same directory.
- The following filename extensions are handled by Algernon:
- Markdown: .md (rendered as HTML)
- Pongo2: .po2, .pongo2 or .tpl (rendered as any text, typically HTML)
- Amber: .amber (rendered as HTML)
- Sass: .scss (rendered as CSS)
- GCSS: .gcss (rendered as CSS)
- JSX: .jsx (rendered as JavaScript/ECMAScript)
- Lua: .lua (a script that provides its own output and content type)
- HyperApp: .hyper.js or .hyper.jsx (rendered as HTML)
- Other files are given a mimetype based on the extension.
- Directories without an index file are shown as a directory listing, where the design is hardcoded.
- UTF-8 is used whenever possible.
- The server can be configured by commandline flags or with a lua script, but no configuration should be needed for getting started.
- Supports HTTP/2, with or without HTTPS (browsers may require HTTPS when using HTTP/2).
- Also supports regular HTTP.
- Can use Lua scripts as handlers for HTTP requests.
- The Algernon executable is compiled to native and is reasonably fast.
- Works on Linux, OS X and 64-bit Windows.
- The Lua interpreter is compiled into the executable.
- Live editing/preview when using the auto-refresh feature.
- The use of Lua allows for short development cycles, where code is interpreted when the page is refreshed (or when the Lua file is modified, if using auto-refresh).
- Self-contained Algernon applications can be zipped into an archive (ending with
.zipor.alg) and be loaded at start. - Built-in support for Markdown, Pongo2, Amber, Sass(SCSS), GCSS and JSX.
- Redis is used for the database backend, by default.
- Algernon will fall back to the built-in Bolt database if no Redis server is available.
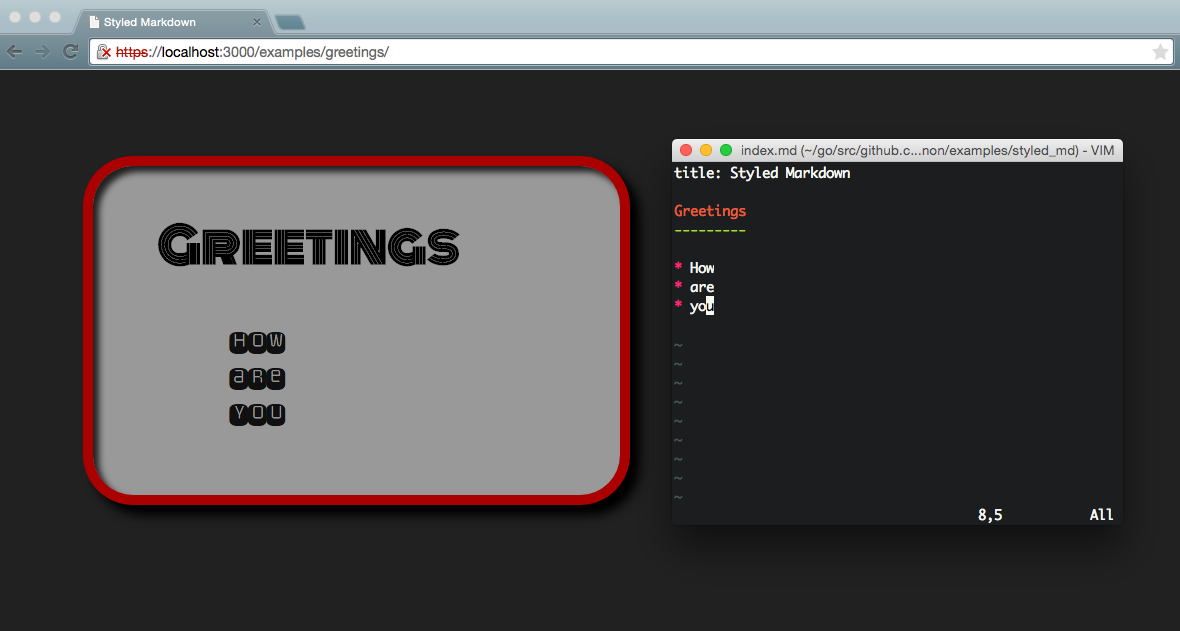
- The HTML title for a rendered Markdown page can be provided by the first line specifying the title, like this:
title: Title goes here. This is a subset of MultiMarkdown. - No file converters needs to run in the background (like for SASS). Files are converted on the fly.
- If
-autorefreshis enabled, the browser will automatically refresh pages when the source files are changed. Works for Markdown, Lua error pages and Amber (including Sass, GCSS and data.lua). This only works on Linux and OS X, for now. If listening for changes on too many files, the OS limit for the number of open files may be reached. - Includes an interactive REPL.
- If only given a Markdown filename as the first argument, it will be served on port 3000, without using any database, as regular HTTP. Handy for viewing
README.mdfiles locally. - Full multithreading. All available CPUs will be used.
- Supports rate limiting, by using tollbooth.
- The
helpcommand is available at the Lua REPL, for a quick overview of the available Lua functions. - Can load plugins written in any language. Plugins must offer the
Lua.CodeandLua.Helpfunctions and talk JSON-RPC over stderr+stdin. See pie for more information. Sample plugins for Go and Python are in thepluginsdirectory. - Thread-safe file caching is built-in, with several available cache modes (for only caching images, for example).
- Can read from and save to JSON documents. Supports simple JSON path expressions (like a simple version of XPath, but for JSON).
- If cache compression is enabled, files that are stored in the cache can be sent directly from the cache to the client, without decompressing.
- Files that are sent to the client are compressed with gzip, unless they are under 4096 bytes.
- When using PostgreSQL, the HSTORE key/value type is used (available in PostgreSQL version 9.1 or later).
- No external dependencies, only pure Go.
- Requires Go 1.12 or later. Also, the package used for QUIC support fails to build with
gccgo(GCC).
- Comes with the
alg2dockerutility, for creating Docker images from Algernon web applications (.algfiles). - http2check can be used for checking if a web server is offering HTTP/2.
brew install algernon- Install Homebrew, if needed.
- Install
algernonfrom AUR, using your favorite AUR helper.
This method is using the latest commit from the master branch:
go get -u github.com/xyproto/algernon
If needed, first:
- Set the GOPATH. For example:
export GOPATH=~/go - Add $GOPATH/bin to the path. For example:
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
Running Algernon:
Screenshot of an erlier version:
The idea is that web pages can be written in Markdown, Pongo2, Amber, HTML or JSX (+React), depending on the need, and styled with CSS, Sass(SCSS) or GCSS, while data can be provided by a Lua script that talks to Redis, BoltDB, PostgreSQL or MariaDB/MySQL.
Amber and GCSS is a good combination for static pages, that allows for more clarity and less repetition than HTML and CSS. It˙s also easy to use Lua for providing data for the Amber templates, which helps separate model, controller and view.
Pongo2, Sass and Lua also combines well. Pongo2 is more flexible than Amber.
The auto-refresh feature is supported when using Markdown, Pongo2 or Amber, and is useful to get an instant preview when developing.
The JSX to JavaScript (ECMAscript) transpiler is built-in.
Redis is fast, scalable and offers good data persistence. This should be the preferred backend.
Bolt is a pure key/value store, written in Go. It makes it easy to run Algernon without having to set up a database host first. MariaDB/MySQL support is included because of its widespread availability.
PostgreSQL is a solid and fast database that is also supported.
Markdown can easily be styled with Sass or GCSS.
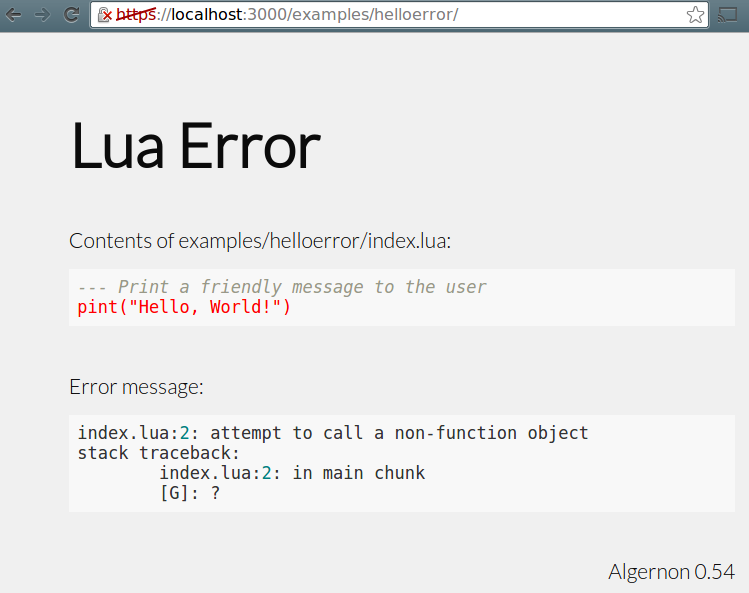
This is how errors in Lua scripts are handled, when Debug mode is enabled.
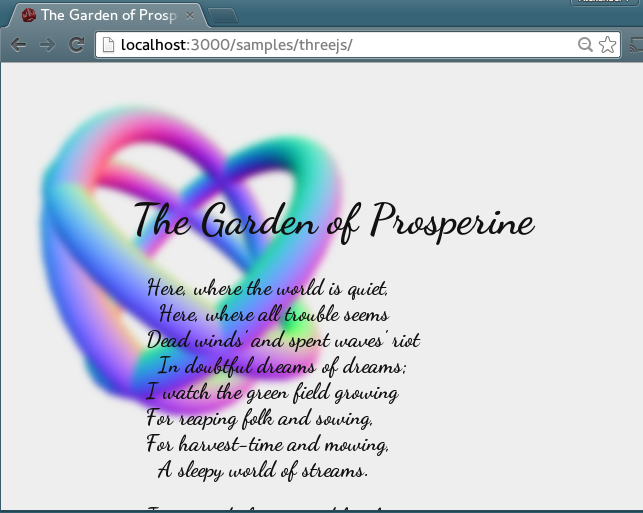
One of the poems of Algernon Charles Swinburne, with three rotating tori in the background. Uses CSS3 for the Gaussian blur and three.js for the 3D graphics.
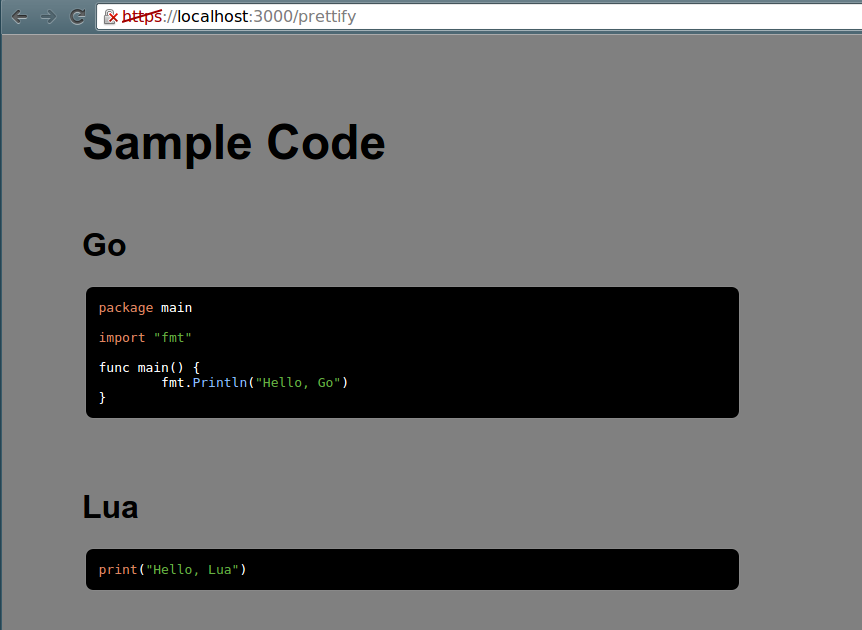
Screenshot of the prettify sample. Served from a single Lua script.
JSX transforms are built-in. Using React together with Algernon is easy.
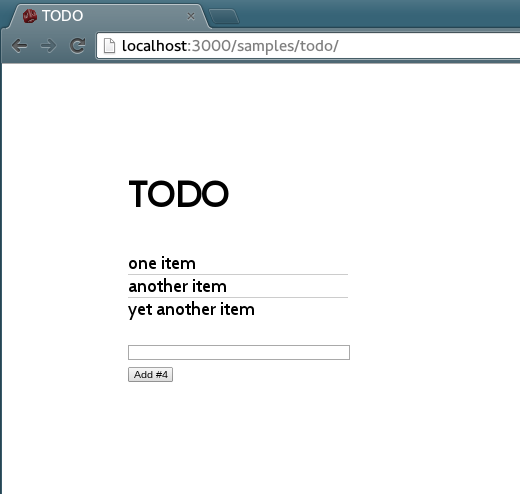
The sample collection can be downloaded from the samples directory in this repository, or here: samplepack.zip.
This enables debug mode, uses the internal Bolt database, uses regular HTTP instead of HTTPS+HTTP/2 and enables caching for all files except: Pongo2, Amber, Lua, Sass, GCSS, Markdown and JSX.
algernon -e
Then try creating an index.lua file with print("Hello, World!") and visit the served web page in a browser.
- Chrome: go to
chrome://flags/#enable-spdy4, enable, save and restart the browser. - Firefox: go to
about:config, setnetwork.http.spdy.enabled.http2drafttotrue. You might need the nightly version of Firefox.
- You may need to change the firewall settings for port 3000, if you wish to use the default port for exploring the samples.
- For the auto-refresh feature to work, port 5553 must be available (or another host/port of your choosing, if configured otherwise).
Go 1.12 or later:
git clone https://github.com/xyproto/algernon
cd algernon
go build -mod=vendor
Go 1.11:
See `README.md` in the `go111` branch.
- Run
./welcome.shto start serving the "welcome" sample. - Visit
http://localhost:3000/
mkdir mypagecd mypage- Create a file named
index.lua, with the following contents:print("Hello, Algernon") - Start
algernon --httponly --autorefresh. - Visit
http://localhost:3000/. - Edit
index.luaand refresh the browser to see the new result. - If there were errors, the page will automatically refresh when
index.luais changed. - Markdown, Pongo2 and Amber pages will also refresh automatically, as long as
-autorefreshis used.
mkdir mypagecd mypage- Create a file named
index.lua, with the following contents:print("Hello, Algernon") - Create a self-signed certificate, just for testing:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 3000 -nodes- Press return at all the prompts, but enter
localhostat Common Name. - For production, store the keys in a directory with as strict permissions as possible, then specify them with the
--certand--keyflags. - Start
algernon. - Visit
https://localhost:3000/. - If you have not imported the certificates into the browser, nor used certificates that are signed by trusted certificate authorities, perform the necessary clicks to confirm that you wish to visit this page.
- Edit
index.luaand refresh the browser to see the result (or a Lua error message, if the script had a problem).
// Return the version string for the server.
version() -> string
// Sleep the given number of seconds (can be a float).
sleep(number)
// Log the given strings as information. Takes a variable number of strings.
log(...)
// Log the given strings as a warning. Takes a variable number of strings.
warn(...)
// Log the given strings as an error. Takes a variable number of strings.
err(...)
// Return the number of nanoseconds from 1970 ("Unix time")
unixnano() -> number
// Convert Markdown to HTML
markdown(string) -> string
// Return the directory where the REPL or script is running. If a filename (optional) is given, then the path to where the script is running, joined with a path separator and the given filename, is returned.
scriptdir([string]) -> string
// Return the directory where the server is running. If a filename (optional) is given, then the path to where the server is running, joined with a path separator and the given filename, is returned.
serverdir([string]) -> string// Set the Content-Type for a page.
content(string)
// Return the requested HTTP method (GET, POST etc).
method() -> string
// Output text to the browser/client. Takes a variable number of strings.
print(...)
// Return the requested URL path.
urlpath() -> string
// Return the HTTP header in the request, for a given key, or an empty string.
header(string) -> string
// Set an HTTP header given a key and a value.
setheader(string, string)
// Return the HTTP headers, as a table.
headers() -> table
// Return the HTTP body in the request (will only read the body once, since it's streamed).
body() -> string
// Set a HTTP status code (like 200 or 404). Must be used before other functions that writes to the client!
status(number)
// Set a HTTP status code and output a message (optional).
error(number[, string])
// Serve a file that exists in the same directory as the script. Takes a filename.
serve(string)
// Serve a Pongo2 template file, with an optional table with template key/values.
serve2(string[, table)
// Return the rendered contents of a file that exists in the same directory as the script. Takes a filename.
render(string) -> string
// Return a table with keys and values as given in a posted form, or as given in the URL.
formdata() -> table
// Return a table with keys and values as given in the request URL, or in the given URL (`/some/page?x=7` makes the key `x` with the value `7` available).
urldata([string]) -> table
// Redirect to an absolute or relative URL. May take an HTTP status code that will be used when redirecting.
redirect(string[, number])
// Permanent redirect to an absolute or relative URL. Uses status code 302.
permanent_redirect(string)
// Transmit what has been outputted so far, to the client.
flush()// Output rendered Markdown to the browser/client. The given text is converted from Markdown to HTML. Takes a variable number of strings.
mprint(...)
// Output rendered Amber to the browser/client. The given text is converted from Amber to HTML. Takes a variable number of strings.
aprint(...)
// Output rendered GCSS to the browser/client. The given text is converted from GCSS to CSS. Takes a variable number of strings.
gprint(...)
// Output rendered HyperApp JSX to the browser/client. The given text is converted from JSX to JavaScript. Takes a variable number of strings.
hprint(...)
// Output rendered React JSX to the browser/client. The given text is converted from JSX to JavaScript. Takes a variable number of strings.
jprint(...)
// Output rendered HTML to the browser/client. The given text is converted from Pongo2 to HTML. The first argument is the Pongo2 template and the second argument is a table. The keys in the table can be referred to in the template.
poprint(string[, table])
// Output a simple HTML page with a message, title and theme.
// The title and theme are optional.
msgpage(string[, string][, string])Tips:
- Use
JFile(filename)to use or store a JSON document in the same directory as the Lua script. - A JSON path is on the form
x.mapkey.listname[2].mapkey, where[,]and.have special meaning. It can be used for pinpointing a specific place within a JSON document. It's a bit like a simple version of XPath, but for JSON. - Use
tostring(userdata)to fetch the JSON string from the JFile object.
// Use, or create, a JSON document/file.
JFile(filename) -> userdata
// Takes a JSON path. Returns a string value, or an empty string.
jfile:getstring(string) -> string
// Takes a JSON path. Returns a JNode or nil.
jfile:getnode(string) -> userdata
// Takes a JSON path. Returns a value or nil.
jfile:get(string) -> value
// Takes a JSON path (optional) and JSON data to be added to the list.
// The JSON path must point to a list, if given, unless the JSON file is empty.
// "x" is the default JSON path. Returns true on success.
jfile:add([string, ]string) -> bool
// Take a JSON path and a string value. Changes the entry. Returns true on success.
jfile:set(string, string) -> bool
// Remove a key in a map. Takes a JSON path, returns true on success.
jfile:delkey(string) -> bool
// Convert a Lua table, where keys are strings and values are strings or numbers, to JSON.
// Takes an optional number of spaces to indent the JSON data.
// (Note that keys in JSON maps are always strings, ref. the JSON standard).
json(table[, number]) -> string
// Create a JSON document node.
JNode() -> userdata
// Add JSON data to a node. The first argument is an optional JSON path.
// The second argument is a JSON data string. Returns true on success.
// "x" is the default JSON path.
jnode:add([string, ]string) ->
// Given a JSON path, retrieves a JSON node.
jnode:get(string) -> userdata
// Given a JSON path, retrieves a JSON string.
jnode:getstring(string) -> string
// Given a JSON path and a JSON string, set the value.
jnode:set(string, string)
// Given a JSON path, remove a key from a map.
jnode:delkey(string) -> bool
// Return the JSON data, nicely formatted.
jnode:pretty() -> string
// Return the JSON data, as a compact string.
jnode:compact() -> string
// Sends JSON data to the given URL. Returns the HTTP status code as a string.
// The content type is set to "application/json; charset=utf-8".
// The second argument is an optional authentication token that is used for the
// Authorization header field.
jnode:POST(string[, string]) -> string
// Alias for jnode:POST
jnode:send(string[, string]) -> string
// Same as jnode:POST, but sends HTTP PUT instead.
jnode:PUT(string[, string]) -> string
// Fetches JSON over HTTP given an URL that starts with http or https.
// The JSON data is placed in the JNode. Returns the HTTP status code as a string.
jnode:GET(string) -> string
// Alias for jnode:GET
jnode:receive(string) -> string
// Convert from a simple Lua table to a JSON string
JSON(table) -> stringQuick example: GET("http://ix.io/1FTw")
// Create a new HTTP Client object
HTTPClient() -> userdata
// Select Accept-Language (ie. "en-us")
hc:SetLanguage(string)
// Set the request timeout (in milliseconds)
hc:SetTimeout(number)
// Set a cookie (name and value)
hc:SetCookie(string, string)
// Set the user agent (ie. "curl")
hc:SetUserAgent(string)
// Perform a HTTP GET request. First comes the URL, then an optional table with
// URL paramets, then an optional table with HTTP headers.
hc:Get(string, [table], [table]) -> string
// Perform a HTTP POST request. It's the same arguments as for hc:Get, except
// the fourth optional argument is the POST body.
hc:Post(string, [table], [table], [string]) -> string
// Like hc:Get, except the first argument is the HTTP method (like "PUT")
hc:Do(string, string, [table], [table]) -> string
// Shorthand for HTTPClient():Get()
GET(string, [table], [table]) -> string
// Shorthand for HTTPClient():Post()
POST(string, [table], [table], [string]) -> string
// Shorthand for HTTPClient():Do()
DO(string, string, [table], [table]) -> string// Load a plugin given the path to an executable. Returns true on success. Will return the plugin help text if called on the Lua prompt.
Plugin(string)
// Returns the Lua code as returned by the Lua.Code function in the plugin, given a plugin path. May return an empty string.
PluginCode(string) -> string
// Takes a plugin path, function name and arguments. Returns an empty string if the function call fails, or the results as a JSON string if successful.
CallPlugin(string, string, ...) -> stringThese functions can be used in combination with the plugin functions for storing Lua code returned by plugins when serverconf.lua is loaded, then retrieve the Lua code later, when handling requests. The code is stored in the database.
// Create or uses a code library object. Optionally takes a data structure name as the first parameter.
CodeLib([string]) -> userdata
// Given a namespace and Lua code, add the given code to the namespace. Returns true on success.
codelib:add(string, string) -> bool
// Given a namespace and Lua code, set the given code as the only code in the namespace. Returns true on success.
codelib:set(string, string) -> bool
// Given a namespace, return Lua code, or an empty string.
codelib:get(string) -> string
// Import (eval) code from the given namespace into the current Lua state. Returns true on success.
codelib:import(string) -> bool
// Completely clear the code library. Returns true on success.
codelib:clear() -> bool// Creates a file upload object. Takes a form ID (from a POST request) as the first parameter.
// Takes an optional maximum upload size (in MiB) as the second parameter.
// Returns nil and an error string on failure, or userdata and an empty string on success.
UploadedFile(string[, number]) -> userdata, string
// Return the uploaded filename, as specified by the client
uploadedfile:filename() -> string
// Return the size of the data that has been received
uploadedfile:size() -> number
// Return the mime type of the uploaded file, as specified by the client
uploadedfile:mimetype() -> string
// Save the uploaded data locally. Takes an optional filename. Returns true on success.
uploadedfile:save([string]) -> bool
// Save the uploaded data as the client-provided filename, in the specified directory.
// Takes a relative or absolute path. Returns true on success.
uploadedfile:savein(string) -> bool// Return information about the file cache.
CacheInfo() -> string
// Clear the file cache.
ClearCache()
// Load a file into the cache, returns true on success.
preload(string) -> bool// Get or create a database-backed Set (takes a name, returns a set object)
Set(string) -> userdata
// Add an element to the set
set:add(string)
// Remove an element from the set
set:del(string)
// Check if a set contains a value
// Returns true only if the value exists and there were no errors.
set:has(string) -> bool
// Get all members of the set
set:getall() -> table
// Remove the set itself. Returns true on success.
set:remove() -> bool
// Clear the set
set:clear() -> bool// Get or create a database-backed List (takes a name, returns a list object)
List(string) -> userdata
// Add an element to the list
list:add(string)
// Get all members of the list
list:getall() -> table
// Get the last element of the list
// The returned value can be empty
list:getlast() -> string
// Get the N last elements of the list
list:getlastn(number) -> table
// Remove the list itself. Returns true on success.
list:remove() -> bool
// Clear the list. Returns true on success.
list:clear() -> bool
// Return all list elements (expected to be JSON strings) as a JSON list
list:json() -> string// Get or create a database-backed HashMap (takes a name, returns a hash map object)
HashMap(string) -> userdata
// For a given element id (for instance a user id), set a key
// (for instance "password") and a value.
// Returns true on success.
hash:set(string, string, string) -> bool
// For a given element id (for instance a user id), and a key
// (for instance "password"), return a value.
// Returns a value only if they key was found and if there were no errors.
hash:get(string, string) -> string
// For a given element id (for instance a user id), and a key
// (for instance "password"), check if the key exists in the hash map.
// Returns true only if it exists and there were no errors.
hash:has(string, string) -> bool
// For a given element id (for instance a user id), check if it exists.
// Returns true only if it exists and there were no errors.
hash:exists(string) -> bool
// Get all keys of the hash map
hash:getall() -> table
// Remove a key for an entry in a hash map
// (for instance the email field for a user)
// Returns true on success
hash:delkey(string, string) -> bool
// Remove an element (for instance a user)
// Returns true on success
hash:del(string) -> bool
// Remove the hash map itself. Returns true on success.
hash:remove() -> bool
// Clear the hash map. Returns true on success.
hash:clear() -> bool// Get or create a database-backed KeyValue collection (takes a name, returns a key/value object)
KeyValue(string) -> userdata
// Set a key and value. Returns true on success.
kv:set(string, string) -> bool
// Takes a key, returns a value.
// Returns an empty string if the function fails.
kv:get(string) -> string
// Takes a key, returns the value+1.
// Creates a key/value and returns "1" if it did not already exist.
// Returns an empty string if the function fails.
kv:inc(string) -> string
// Remove a key. Returns true on success.
kv:del(string) -> bool
// Remove the KeyValue itself. Returns true on success.
kv:remove() -> bool
// Clear the KeyValue. Returns true on success.
kv:clear() -> bool// Check if the current user has "user" rights
UserRights() -> bool
// Check if the given username exists (does not look at the list of unconfirmed users)
HasUser(string) -> bool
// Check if the given username exists in the list of unconfirmed users
HasUnconfirmedUser(string) -> bool
// Get the value from the given boolean field
// Takes a username and field name
BooleanField(string, string) -> bool
// Save a value as a boolean field
// Takes a username, field name and boolean value
SetBooleanField(string, string, bool)
// Check if a given username is confirmed
IsConfirmed(string) -> bool
// Check if a given username is logged in
IsLoggedIn(string) -> bool
// Check if the current user has "admin rights"
AdminRights() -> bool
// Check if a given username is an admin
IsAdmin(string) -> bool
// Get the username stored in a cookie, or an empty string
UsernameCookie() -> string
// Store the username in a cookie, returns true on success
SetUsernameCookie(string) -> bool
// Clear the login cookie
ClearCookie()
// Get a table containing all usernames
AllUsernames() -> table
// Get the email for a given username, or an empty string
Email(string) -> string
// Get the password hash for a given username, or an empty string
PasswordHash(string) -> string
// Get all unconfirmed usernames
AllUnconfirmedUsernames() -> table
// Get the existing confirmation code for a given user,
// or an empty string. Takes a username.
ConfirmationCode(string) -> string
// Add a user to the list of unconfirmed users
// Takes a username and a confirmation code
// Remember to also add a user, when registering new users.
AddUnconfirmed(string, string)
// Remove a user from the list of unconfirmed users
// Takes a username
RemoveUnconfirmed(string)
// Mark a user as confirmed
// Takes a username
MarkConfirmed(string)
// Removes a user
// Takes a username
RemoveUser(string)
// Make a user an admin
// Takes a username
SetAdminStatus(string)
// Make an admin user a regular user
// Takes a username
RemoveAdminStatus(string)
// Add a user
// Takes a username, password and email
AddUser(string, string, string)
// Set a user as logged in on the server (not cookie)
// Takes a username
SetLoggedIn(string)
// Set a user as logged out on the server (not cookie)
// Takes a username
SetLoggedOut(string)
// Log in a user, both on the server and with a cookie
// Takes a username
Login(string)
// Log out a user, on the server (which is enough)
// Takes a username
Logout(string)
// Get the current username, from the cookie
Username() -> string
// Get the current cookie timeout
// Takes a username
CookieTimeout(string) -> number
// Set the current cookie timeout
// Takes a timeout number, measured in seconds
SetCookieTimeout(number)
// Get the current server-wide cookie secret. This is used when setting
// and getting browser cookies when users log in.
CookieSecret() -> string
// Set the current server-side cookie secret. This is used when setting
// and getting browser cookies when users log in. Using the same secret
// makes browser cookies usable across server restarts.
SetCookieSecret(string)
// Get the current password hashing algorithm (bcrypt, bcrypt+ or sha256)
PasswordAlgo() -> string
// Set the current password hashing algorithm (bcrypt, bcrypt+ or sha256)
// ‘bcrypt+‘ accepts bcrypt or sha256 for old passwords, but will only use
// bcrypt for new passwords.
SetPasswordAlgo(string)
// Hash the password
// Takes a username and password (username can be used for salting sha256)
HashPassword(string, string) -> string
// Change the password for a user, given a username and a new password
SetPassword(string, string)
// Check if a given username and password is correct
// Takes a username and password
CorrectPassword(string, string) -> bool
// Checks if a confirmation code is already in use
// Takes a confirmation code
AlreadyHasConfirmationCode(string) -> bool
// Find a username based on a given confirmation code,
// or returns an empty string. Takes a confirmation code
FindUserByConfirmationCode(string) -> string
// Mark a user as confirmed
// Takes a username
Confirm(string)
// Mark a user as confirmed, returns true on success
// Takes a confirmation code
ConfirmUserByConfirmationCode(string) -> bool
// Set the minimum confirmation code length
// Takes the minimum number of characters
SetMinimumConfirmationCodeLength(number)
// Generates a unique confirmation code, or an empty string
GenerateUniqueConfirmationCode() -> string// Set the default address for the server on the form [host][:port].
// May be useful in Algernon application bundles (.alg or .zip files).
SetAddr(string)
// Reset the URL prefixes and make everything *public*.
ClearPermissions()
// Add an URL prefix that will have *admin* rights.
AddAdminPrefix(string)
// Add an URL prefix that will have *user* rights.
AddUserPrefix(string)
// Provide a lua function that will be used as the permission denied handler.
DenyHandler(function)
// Return a string with various server information.
ServerInfo() -> string
// Direct the logging to the given filename. If the filename is an empty
// string, direct logging to stderr. Returns true on success.
LogTo(string) -> bool
// Returns the version string for the server.
version() -> string
// Logs the given strings as INFO. Takes a variable number of strings.
log(...)
// Logs the given strings as WARN. Takes a variable number of strings.
warn(...)
// Logs the given string as ERROR. Takes a variable number of strings.
err(...)
// Provide a lua function that will be run once, when the server is ready to start serving.
OnReady(function)
// Use a Lua file for setting up HTTP handlers instead of using the directory structure.
ServerFile(string) -> bool
// Get the cookie secret from the server configuration.
CookieSecret() -> string
// Set the cookie secret that will be used when setting and getting browser cookies.
SetCookieSecret(string)This function is only available when a Lua script is used instead of a server directory, or from Lua files that are specified with the ServerFile function in the server configuration.
// Given an URL path prefix (like "/") and a Lua function, set up an HTTP handler.
// The given Lua function should take no arguments, but can use all the Lua functions for handling requests, like `content` and `print`.
handle(string, function)
// Given an URL prefix (like "/") and a directory, serve the files and directories.
servedir(string, string)helpdisplays a syntax highlighted overview of most functions.webhelpdisplays a syntax highlighted overview of functions related to handling requests.confighelpdisplays a syntax highlighted overview of functions related to server configuration.
// Pretty print. Outputs the values in, or a description of, the given Lua value(s).
pprint(...)
// Takes a Python filename, executes the script with the `python` binary in the Path.
// Returns the output as a Lua table, where each line is an entry.
py(string) -> table
// Takes one or more system commands (possibly separated by `;`) and runs them.
// Returns the output lines as a table.
run(string) -> table
// Lists the keys and values of a Lua table. Returns a string.
// Lists the contents of the global namespace `_G` if no arguments are given.
dir([table]) -> stringAlgernon can be used as a quick Markdown viewer with the -m flag.
Try algernon -m README.md to view README.md in the browser, serving the file once on a port >3000.
In addition to the regular Markdown syntax, Algernon supports setting the page title and syntax highlight style with a header comment like this at the top of a Markdown file:
<!--
title: Page title
theme: dark
code_style: lovelace
replace_with_theme: default_theme
-->
Code is highlighted with highlight.js and several styles are available.
The string that follows replace_with_theme will be used for replacing the current theme string (like dark) with the given string. This makes it possible to use one image (like logo_default_theme.png) for one theme and another image (logo_dark.png) for the dark theme.
The theme can be light, dark, redbox, bw, github, wing, material, neon, default, werc or a path to a CSS file. Or style.gcss can exist in the same directory.
An overview of available syntax highlighting styles can be found at the Chroma Style Gallery.
Follow the guide at certbot.eff.org for the "None of the above" web server, then start algernon with --cert=/etc/letsencrypt/live/mydomain.space/cert.pem --key=/etc/letsencrypt/live/mydomain.space/privkey.pem where mydomain.space is replaced with your own domain name.
First make Algernon serve a directory for the domain, like /srv/mydomain.space, then use that as the webroot when configuring certbot with the certbot certonly command.
Remember to set up a cron-job or something similar to run certbot renew every once in a while (every 12 hours is suggested by certbot.eff.org). Also remember to restart the algernon service after updating the certificates. A way to refresh the certificates without restarting Algernon will be implemented in the future.
- Arch Linux package in the AUR.
- Windows executable.
- OS X homebrew package
- Algernon Tray Launcher for OS X, in App Store
- Source releases are tagged with a version number at release.
- go >= 1.12
Can log to a Combined Log Format access log with the --accesslog flag. This works nicely together with goaccess.
Serve files in one directory:
algernon --accesslog=access.log -x
Then visit the webpage once, to create one entry in the access.log.
The wonderful goaccess utility can then be used to view the access log, while it is being filled:
goaccess --no-global-config --log-format=COMBINED access.log
If you have goaccess setup correctly, running goaccess without any flags should work too:
goaccess access.log
Thanks to Egon Elbre for the two SVG drawings that I remixed into the current logo (CC0 licensed).
- Version: 1.12.4
- License: MIT
- Alexander F. Rødseth <xyproto@archlinux.org>