This project demonstrates how to use Terraform to manage AWS resources needed to create Hugo static website using AWS Lambda service. See the excellent blog hugo-awslambda-static-website/ about how does it work. In this project we use Terraform to automate the AWS resource creation. This gives you a repeatable process so you can build and tear down as you wish.
Resources managed are:
- Source, destination and log buckets on AWS, buckets's policies, static website configuration
- Lambda function, IAM role and policies
- Lambda S3 trigger
- Route53 record for static website pointing to the S3 bucket
This tutorial uses content and ideas from a number of open source projects. See Acknowledgements for details.
Install the awscli, jq, terraform, and optionally vagrant as described on https://github.com/xuwang/install-tools page.
When setting up AWS credentials in the above steps, use IAM user assumptions for this project:
- Create a group
myhugowithAWSLambdaFullAccess,IAMFullAccess,AmazonS3FullAccess, andAmazonRoute53FullAccesspolicy. - Create a user
myhugoand Download the user credentials. - Add user
myhugoto groupmyhugo.
$ git clone git@github.com:xuwang/aws-hugo
$ cd aws-hugo
If you use Vagrant, instead of install tools on your host machine, there is Vagranetfile for a Ubuntu box with all the necessary tools installed:
$ vagrant up
$ vagrant ssh
$ cd aws-hugo
First setup parameters for your site. There is only one file you need to customize.
$ cd terraforms
$ cp provider.tf.tmpl provider.tf
Edit terraforms/provider.tf to set up AWS region, profile and root domain for your hugo site, for example:
# Customize this to your account configuration.
provider "aws" {
profile = "myhugo"
region = "us-west-2"
}
variable "hugo_site" {
# your static site FQDN
default = {
root_domain = "example.com"
}
}
Polices for buckets and lambda function role are located under terraform/artifacts/policies directory. The lambda code will be downloaded under terraform/artifacts directory.
Run plan first to see what resources will be created. Still under terraform directory:
$ terraform get
$ terraform plan
Verify all the resoucre to be created. These are example resouces:
+ module.hugo.aws_iam_policy_attachment.hugo_lambda_attach
+ module.hugo.aws_iam_role.lambda_role
+ module.hugo.aws_iam_role_policy.lambda_policy
+ module.hugo.aws_lambda_function.hugo_lambda
+ module.hugo.aws_route53_record.root_domain
+ module.hugo.aws_route53_zone.main
+ module.hugo.aws_s3_bucket.html
+ module.hugo.aws_s3_bucket.input
+ module.hugo.aws_s3_bucket.log
+ module.hugo.null_resource.lambda_download
+ module.hugo.template_file.lambda_policy
$ terraform apply
...
You may see the following errors:
1 error(s) occurred:
aws_lambda_function.hugo_lambda: Error creating Lambda function: timeout while waiting for state to become '[success]'
This is caused by [terraform issue 4926](issue hashicorp/terraform#4926), but the function actually is created alright. You can ignore this error.
To verify Terraform output created:
$ terraform output -module=hugo
aws_route53_record_fqdn = example.com
html_bucket_id = example.com
html_domain = s3-website-us-west-2.amazonaws.com
html_endpoint = example.com.s3-website-us-west-2.amazonaws.com
hugo_lambda_name = hugo-lambda
input_bucket_id = input.example.com
There are some bugs arouond Terraform lambda resource management. To workaround the issues, let's use awc cli to create lambda event trigger and s3 bucket invoke policy:
$ ./set-s3-trigger.sh
- Upload Hugo page content to S3 bucket
There is a hugo-example diretory in this repo, which has a simple "Hello World" website:
$ cd hugo-example
Edit config.toml so the baseurl matches your root_domain:
baseurl = "http://example.com"
Then upload hugo-example directory to the input bucket we created previously:
$ cd ..
$ aws --profile myhugo s3 sync hugo-example/ s3://input.example.com/
-
You should be able to go to http://example.com to see the page,like this:
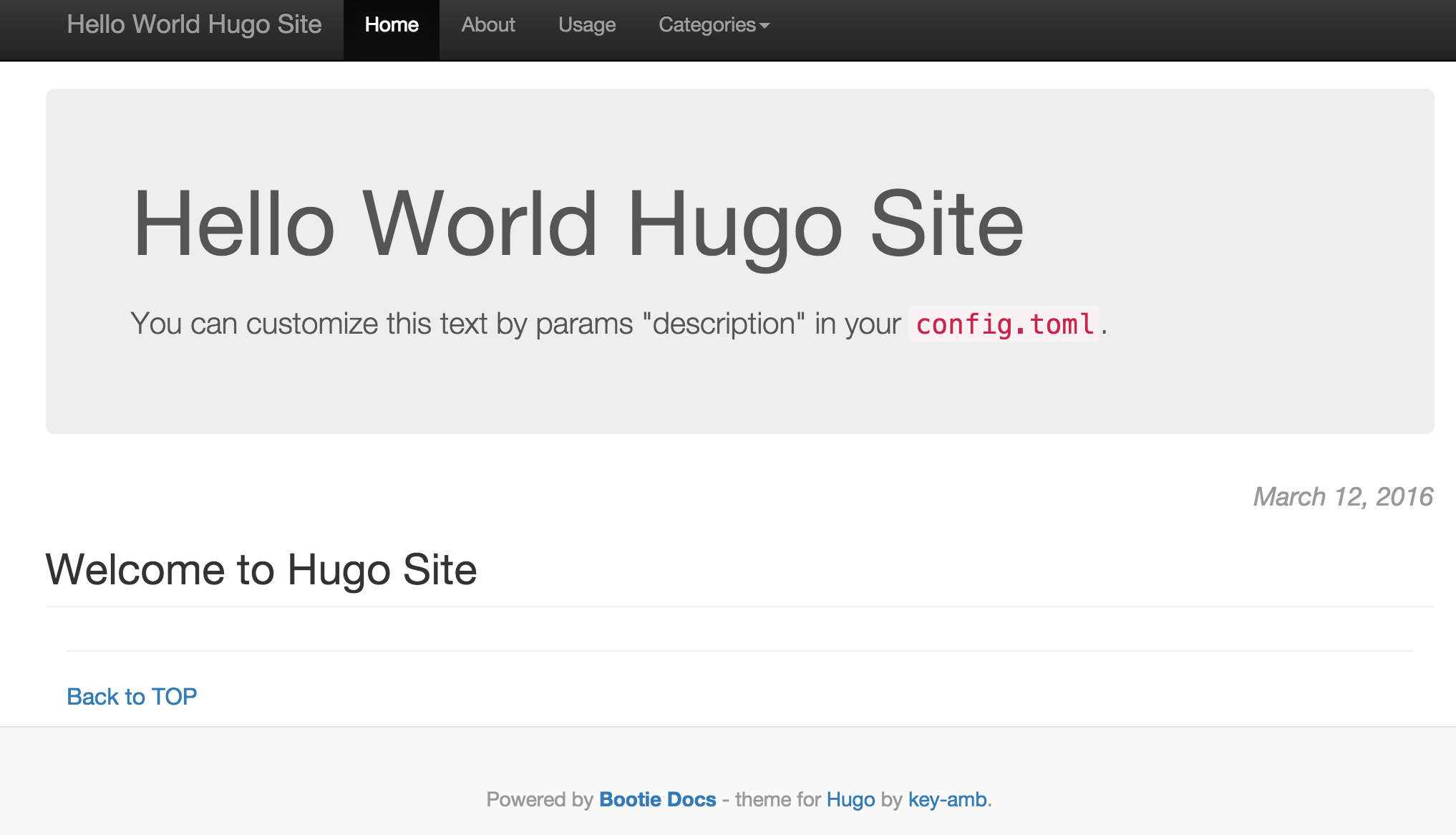
Use your favoriate editor to update files under hugo content directory, upload to S3 input bucket, lambda function will be invoked to re-generate your websites. You can view Lambda function logs as instructed [here] (http://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/monitoring-functions-logs.html)
You can use the setup for production implementation. If you no longer need the resources, you can easily wipe out everything you created, including the buckets and contents:
$ cd terraform
$ ./delete-s3-trigger.sh
$ terraform destroy
Do you really want to destroy?
Terraform will delete all your managed infrastructure.
There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
If you are in Vagrant my-hugo-box:
$ logout
$ vagrant destroy