Named Entity Recognition for Scientific Paper(PDF)
BERT + BiLSTM + CRF
BERT is based on SCIBERT
Dataset is SCIERC which is taken from 12 AI conference/workshop proceedings in four AI communities, from the semantic scholar corpus.
- main.py: Users input pdf file path then it will generate NER outputs.
- toolkit
- pdf_parser: pdf2xml
- save: BERT model for NER(User should add their own model file to here such as .h5 files.)
- Python 3.6+
- tensorflow<2.0
- kashgari
Versions need to be compatible with each other.
pip install tensorflow<2.0
pip install kashgari>=1.0.0,<2.0.0paperNERapi.py
- fastapi
- uvicorn
- pydantic
"C:\Program Files\Python36\python.exe" C:/Users/xy644/Desktop/scibert-project/paperNER/main.py
input file path: ELG.pdf
--------------------------------
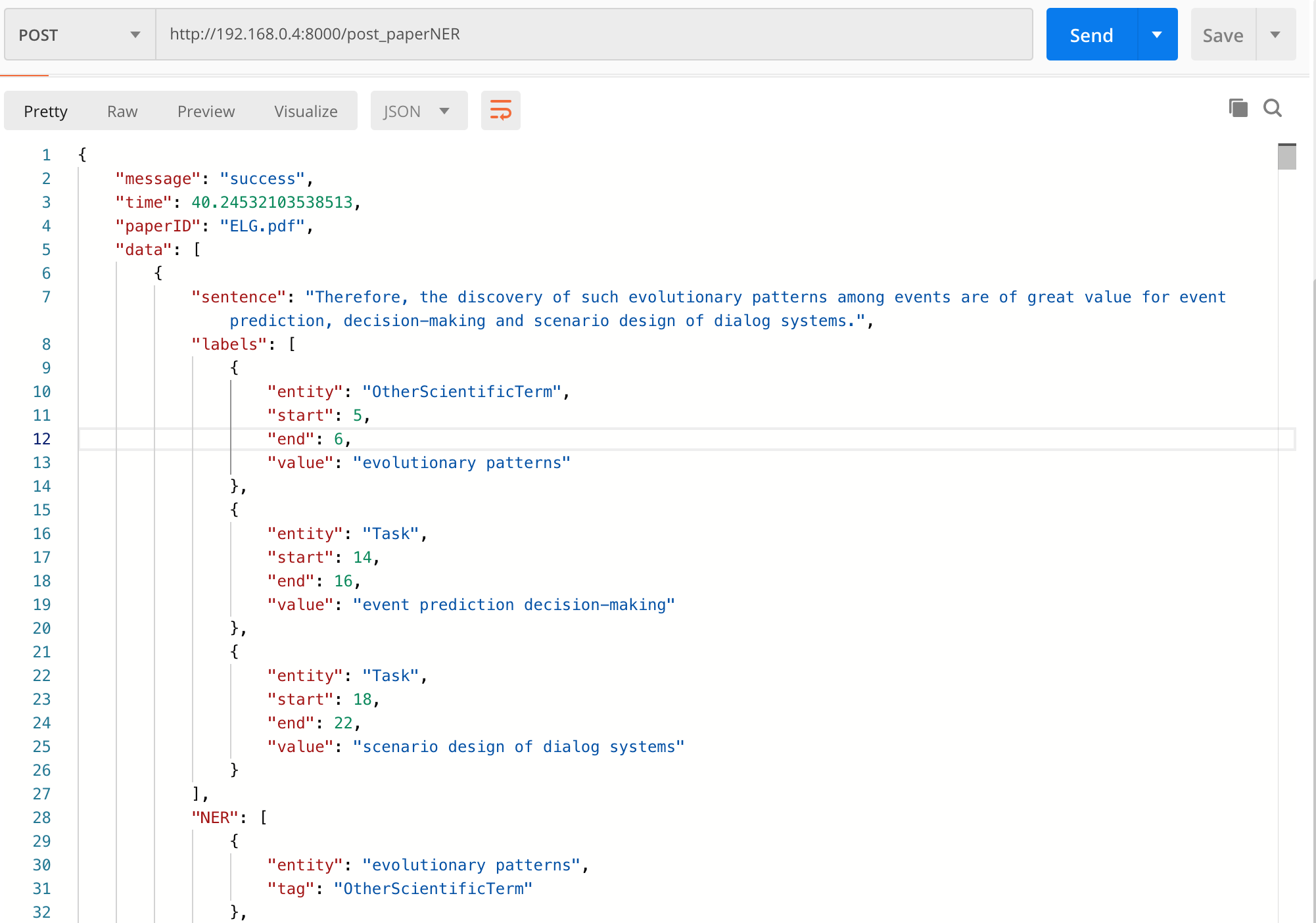
text: In order to discover the evolutionary patterns and logics of events, we propose an eventcentric knowledge graph — Event Logic Graph (ELG) and the framework to construct ELG.
labels [{'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 5, 'end': 6, 'value': 'evolutionary patterns'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 8, 'end': 8, 'value': 'logics'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 10, 'end': 10, 'value': 'events,'}, {'entity': 'Method', 'start': 14, 'end': 16, 'value': 'eventcentric knowledge graph'}, {'entity': 'Method', 'start': 18, 'end': 18, 'value': 'Event'}]
value: evolutionary patterns OtherScientificTerm
value: logics OtherScientificTerm
value: events, OtherScientificTerm
value: eventcentric knowledge graph Method
value: Event Method
--------------------------------
text: ELG is a directed cyclic graph, whose nodes are events, and edges stand for the sequential (the same meaning with “temporal”), causal, conditional or hypernym-hyponym (“is-a”) relations between events.
labels [{'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 3, 'end': 3, 'value': 'directed'}, {'entity': 'Method', 'start': 4, 'end': 5, 'value': 'cyclic graph,'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 7, 'end': 7, 'value': 'nodes'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 9, 'end': 9, 'value': 'events,'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 15, 'end': 15, 'value': 'sequential'}]
value: directed OtherScientificTerm
value: cyclic graph, Method
value: nodes OtherScientificTerm
value: events, OtherScientificTerm
value: sequential OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
text: Essentially, ELG is an event logic knowledge base, which can reveal evolutionary patterns and development logics of real world events.
labels [{'entity': 'Method', 'start': 1, 'end': 1, 'value': 'ELG'}, {'entity': 'Method', 'start': 4, 'end': 7, 'value': 'event logic knowledge base,'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 11, 'end': 12, 'value': 'evolutionary patterns'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 14, 'end': 15, 'value': 'development logics'}]
value: ELG Method
value: event logic knowledge base, Method
value: evolutionary patterns OtherScientificTerm
value: development logics OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
text: ELG is a directed cyclic graph, whose nodes are events, and edges stand for the sequential, causal, conditional or hypernym-hyponym relations between events.
labels [{'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 3, 'end': 5, 'value': 'directed cyclic graph,'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 7, 'end': 7, 'value': 'nodes'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 9, 'end': 9, 'value': 'events,'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 15, 'end': 18, 'value': 'sequential, causal, conditional or'}]
value: directed cyclic graph, OtherScientificTerm
value: nodes OtherScientificTerm
value: events, OtherScientificTerm
value: sequential, causal, conditional or OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
text: While (go, somewhere), (do, the things) and (eat) are unreasonable or incomplete event representations, as their semantics are too vague to be understood.
labels [{'entity': 'Method', 'start': 1, 'end': 2, 'value': '(go, somewhere),'}, {'entity': 'Method', 'start': 5, 'end': 5, 'value': 'things)'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 6, 'end': 7, 'value': 'and (eat)'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 9, 'end': 12, 'value': 'unreasonable or incomplete event'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 16, 'end': 16, 'value': 'semantics'}]
value: (go, somewhere), Method
value: things) Method
value: and (eat) OtherScientificTerm
value: unreasonable or incomplete event OtherScientificTerm
value: semantics OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
text: ” (have, lunch), (pay, the bill) and (leave the restaurant) compose a sequential event chain.
labels [{'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 5, 'end': 5, 'value': 'bill)'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 9, 'end': 9, 'value': 'restaurant)'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 12, 'end': 13, 'value': 'sequential event'}]
value: bill) OtherScientificTerm
value: restaurant) OtherScientificTerm
value: sequential event OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
text: binations between frequency-based features may provide extra information that is useful for sequential relation and direction classification, shown in Table 2 (R1 to R11).
labels [{'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 0, 'end': 0, 'value': 'binations'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 2, 'end': 3, 'value': 'frequency-based features'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 12, 'end': 13, 'value': 'sequential relation'}, {'entity': 'OtherScientificTerm', 'start': 15, 'end': 16, 'value': 'direction classification,'}]
value: binations OtherScientificTerm
value: frequency-based features OtherScientificTerm
value: sequential relation OtherScientificTerm
value: direction classification, OtherScientificTerm
--------------------------------
input file path: