Easily visualize a Neo4j cypher query as a graph in a Jupyter Notebook.
This packages provides an easy-to-use interface to the yFiles Graphs for Jupyter widget to directly visualize cypher queries.
Just install it from the Python Package Index
pip install yfiles_jupyter_graphs_for_neo4jor see README_DEV.md to build it yourself.
from yfiles_jupyter_graphs_for_neo4j import Neo4jGraphWidget
from neo4j import GraphDatabase
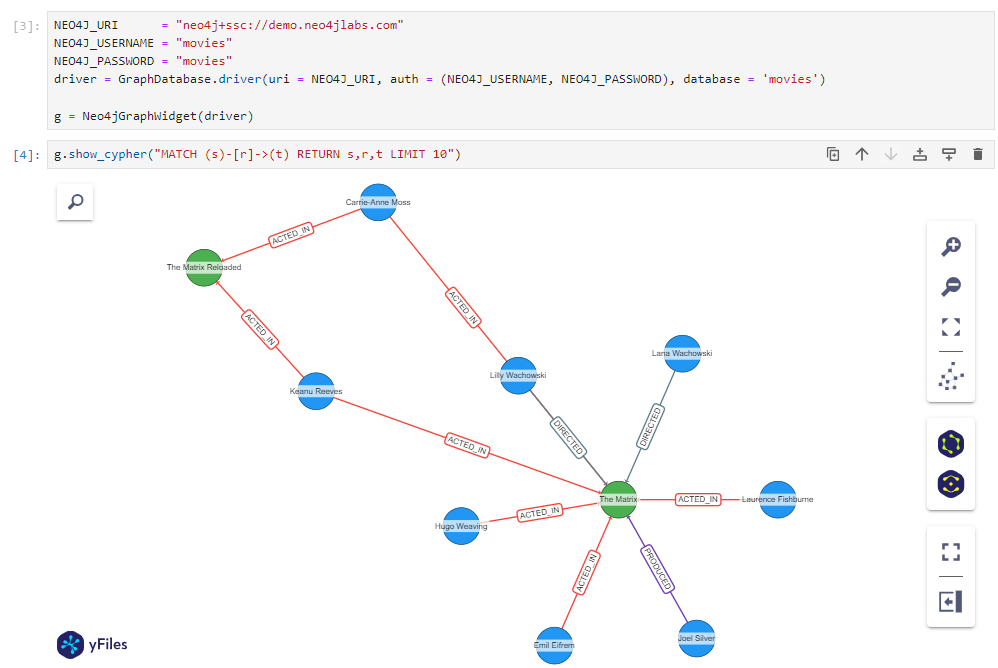
NEO4J_URI = "neo4j+ssc://demo.neo4jlabs.com"
NEO4J_USERNAME = "movies"
NEO4J_PASSWORD = "movies"
driver = GraphDatabase.driver(uri = NEO4J_URI, auth = (NEO4J_USERNAME, NEO4J_PASSWORD), database = 'movies')
g = Neo4jGraphWidget(driver)
g.show_cypher("MATCH (s)-[r]->(t) RETURN s,r,t LIMIT 20")See the basic example notebook for a running example.
The widget uses yFiles Graphs for Jupyter at its core, and therefore runs in any environment that is supported by it, see supported environments.
The main class Neo4jGraphWidget provides the following API:
Neo4jGraphWidget: Creates a new class instance with the following arguments
| Argument | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
driver |
The neo4j driver that is used to execute cypher queries. |
None |
widget_layout |
Can be used to specify general widget appearance through css attributes. See ipywidget's layout for more information. |
None |
overview_enabled |
Enable graph overview component. Default behaviour depends on cell width. | None |
show_cypher(cypher, **kwargs)cypher: The cypher query that should be visualized.**kwargs: Additional parameters that should be passed to the cypher query (e.g., see the selection example).
The default behavior is to only show the nodes and relationships returned by the cypher query. This can be changed to autocomplete relationships like in neo4j browser:
set_autocomplete_relationships(autocomplete_relationships): Sets whether to autocomplete relationships in the graph or not.
The cypher queries are executed by the provided Neo4j driver. If you have not specified a driver when instantiating the class, you can set a driver afterward:
set_driver(driver): Sets the given driver and uses this to send cypher queries to Databases.get_driver(): Returns the current driver.
The graph visualization can be adjusted by adding configurations to each node label or edge type with the following functions:
-
add_node_configuration(label, **kwargs)label: The node label for which this configuration should be used.**kwargs: Visualization configuration for the given node label. The following arguments are supported:text: The text that displayed at the node. By default, the node's label is used.color: A convenience color binding for the node (see alsostylesargument).size: The size of the node.styles: A dictionary that may contain the following attributescolor,shape(one of 'ellipse', ' hexagon', 'hexagon2', 'octagon', 'pill', 'rectangle', 'round-rectangle' or 'triangle'),image.property: Allows to specify additional properties on the node, which may be bound by other bindings.type: Defines a specific "type" for the node as described in yFiles Graphs for Jupyter which affects the automatic positioning of nodes (same "type"s are preferred to be placed next to each other).
-
add_relationship_configuration(type, **kwargs)type: The edge type for which this configuration should be used.**kwargs: Visualization configuration for the given relationship type. The following arguments are supported:text: The text that displayed at the relationship. By default, the relationship's type is used.color: The relationship's color.thickness_factor: The relationship's stroke thickness factor. By default,1.property: Allows to specify additional properties on the relationship, which may be bound by other bindings.
To remove a configuration use the following functions:
del_node_configuration(type): Deletes configuration for the given node label.del_relationship_configurations(type): Deletes configuration for the given relationship type.
You can select nodes and relationships to retrieve their ids. For example, you can use these ids in new cypher queries
by providing them as parameter to show_cypher as shown in
the selection example.
-
get_selected_node_ids(widget=None): Returns an Array of node idswidget: The widget that is used to select nodes from. IfNoneis specified, the most recently shown widget is used.
-
get_selected_relationship_ids(widget=None): Returns an Array of relationship idswidget: The widget that is used to select edges from. IfNoneis specified, the most recently shown widget is used.
The configuration bindings (see add_node_configuration or add_relationship_configuration) are resolved as follows:
If the configuration binding is a string, the package first tries to resolve it against the item's properties and uses the property value if available. If there is no property with the given key, the string value itself is used as a constant binding.
In case you want to create a constant string value as binding, which also happens to be a property key, use a binding function with a constant string as return value instead.
If the configuration binding is a function, the return value of the function is used as value for the respective configuration.
The graph visualization is provided by yFiles Graphs for Jupyter, a versatile graph visualization widget for Jupyter Notebooks.
It can import and visualize graphs from various popular Python packages (e.g. NetworkX, PyGraphviz, igraph) or just structured node and edge lists.
And provides a rich set of visualization options to bring your data to life (see the example notebooks).
 Heatmap visualization
Heatmap visualization |
 Geospatial data visualization
Geospatial data visualization |
 Data-driven item visualization
Data-driven item visualization |
For a detailed feature guide, check out the main widget example notebooks
This project and everyone participating in it is governed by the Code of Conduct. By participating, you are expected to uphold this code. Please report unacceptable behavior to contact@yworks.com.
This widget is by no means perfect. If you find something is not working as expected we are glad to receive an issue report from you. Please make sure to search for existing issues first and check if the issue is not an unsupported feature or known issue. If you did not find anything related, report a new issue with necessary information. Please also provide a clear and descriptive title and stick to the issue templates. See issues.
See LICENSE file.