Welcome to the official GitHub repository of the HEST-Library introduced in "HEST-1k: A Dataset for Spatial Transcriptomics and Histology Image Analysis". This project was developed by the Mahmood Lab at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women's Hospital.
HEST-1k, HEST-Library, and HEST-Benchmark are released under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license.
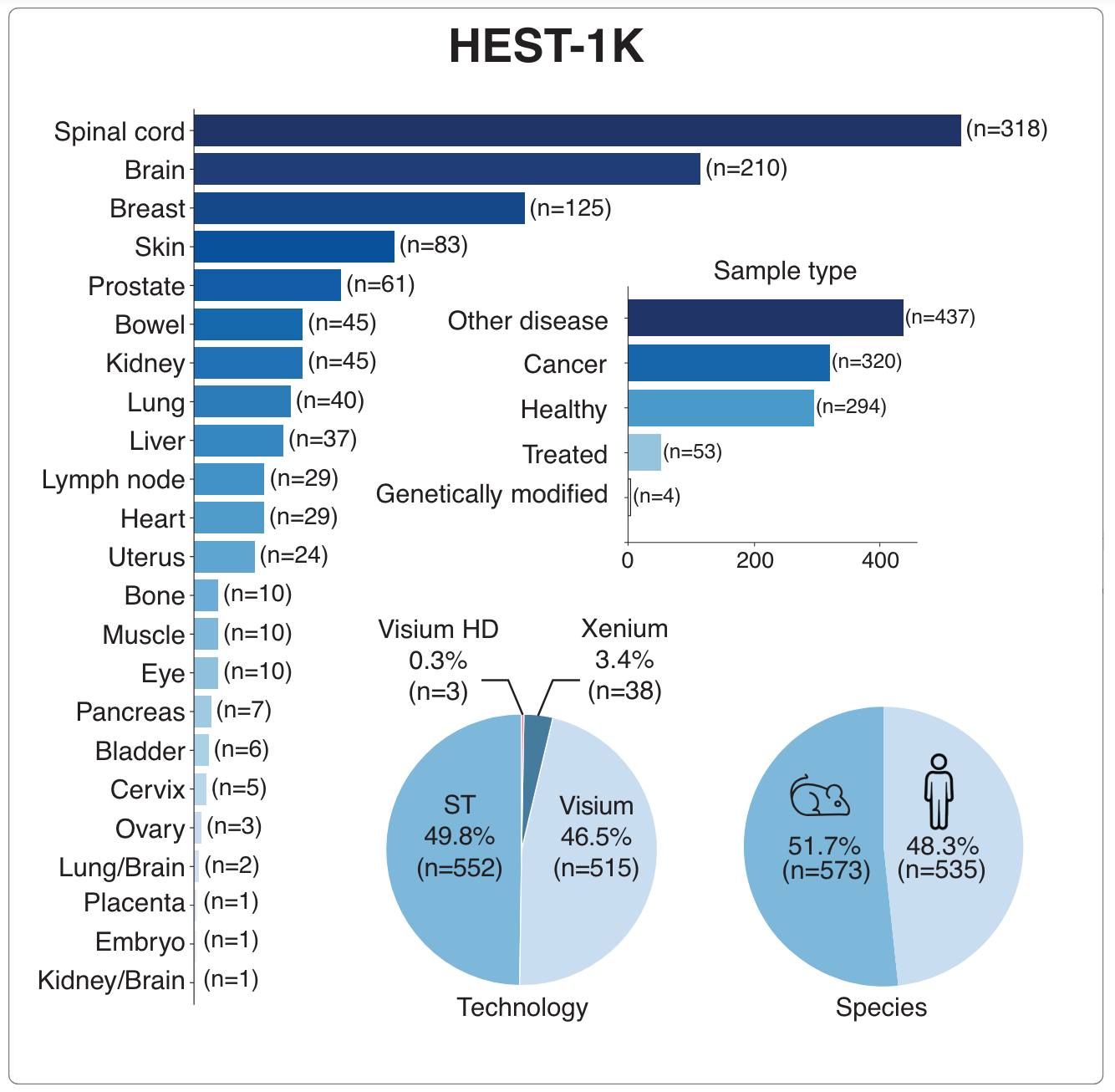
- HEST-1k: Free access to HEST-1K, a dataset of 1,108 paired Spatial Transcriptomics samples with HE-stained whole-slide images
- HEST-Library: A series of helpers to assemble new ST samples (from ST, Visium, Visium HD, or Xenium) and work with HEST-1k
- HEST-Benchmark: A new benchmark to assess the predictive performance of foundation models for histology in predicting gene expression from morphology
git clone https://github.com/mahmoodlab/hest.git
cd hest
conda create -n "hest" python=3.9
conda activate hest
pip install -e .
sudo apt install libvips libvips-dev openslide-tools
If a GPU is available on your machine, we recommend installing cucim on your conda environment. (hest was tested with cucim-cu12==24.4.0 and CUDA 12.1)
pip install \
--extra-index-url=https://pypi.nvidia.com \
cudf-cu12==24.6.* dask-cudf-cu12==24.6.* cucim-cu12==24.6.* \
raft-dask-cu12==24.6.*
NOTE: HEST-Library was only tested on Linux/macOS machines, please report any bugs in the GitHub issues.
To download/query HEST-1k, follow the tutorial 1-Downloading-HEST-1k.ipynb or follow instructions on Hugging Face.
NOTE: The entire dataset weighs 743 GB but you can easily download a subset by querying per id, organ, species...
You can then simply view the dataset as,
from hest import load_hest
print('Lazy loading of hest...')
hest_data = load_hest('hest_data') # location of the data
print('loaded hest')
for d in hest_data:
print(d)The HEST-Library allows assembling new samples using HEST format and interacting with HEST-1k. We provide two tutorials:
- 2-Interacting-with-HEST-1k.ipynb: Playing around with HEST data for loading patches, visualizing nuclear segmentation.
- 3-Assembling-HEST-Data.ipynb: Walkthrough to transform a Visum sample into HEST.
In addition, we provide complete documentation.
The HEST-Benchmark was designed to assess foundation models for pathology under a new, diverse, and challenging benchmark. HEST-Benchmark includes 10 tasks for gene expression prediction (50 highly variable genes) from morphology (112 x 112 um regions at 0.5 um/px) in 10 different organs and 9 cancer types. We provide a step-by-step tutorial to run HEST-Benchmark and reproduce our results in 4-Running-HEST-Benchmark.ipynb.
HEST-Benchmark was used to assess 10 publicly available models. Reported results are based on a Random Forest regression model (70 trees). Additional results based on Ridge regression are provided in the paper.
| ResNet50 | KimiaNet | Ciga | CTransPath | Remedis | Phikon | PLIP | UNI | CONCH | GigaPath | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDC | 0.440 | 0.420 | 0.406 | 0.454 | 0.491 | 0.430 | 0.436 | 0.502 | 0.504 | 0.492 |
| PRAD | 0.318 | 0.328 | 0.332 | 0.346 | 0.335 | 0.377 | 0.362 | 0.357 | 0.373 | 0.372 |
| PAAD | 0.389 | 0.410 | 0.397 | 0.406 | 0.451 | 0.372 | 0.392 | 0.424 | 0.431 | 0.425 |
| SKCM | 0.446 | 0.452 | 0.484 | 0.535 | 0.577 | 0.516 | 0.461 | 0.613 | 0.582 | 0.541 |
| COAD | 0.107 | 0.080 | 0.102 | 0.123 | 0.125 | 0.137 | 0.112 | 0.147 | 0.124 | 0.139 |
| READ | 0.051 | 0.038 | 0.046 | 0.083 | 0.099 | 0.138 | 0.063 | 0.162 | 0.132 | 0.156 |
| CCRCC | 0.136 | 0.136 | 0.127 | 0.171 | 0.200 | 0.178 | 0.124 | 0.186 | 0.149 | 0.182 |
| HCC | 0.034 | 0.028 | 0.045 | 0.060 | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.038 | 0.051 | 0.040 | 0.055 |
| LUAD | 0.497 | 0.507 | 0.515 | 0.531 | 0.573 | 0.541 | 0.533 | 0.511 | 0.569 | 0.547 |
| LYMPH_IDC | 0.205 | 0.206 | 0.218 | 0.238 | 0.243 | 0.243 | 0.229 | 0.234 | 0.249 | 0.248 |
| Average | 0.262 | 0.261 | 0.267 | 0.295 | 0.315 | 0.297 | 0.275 | 0.319 | 0.315 | 0.316 |
Our tutorial in 4-Running-HEST-Benchmark.ipynb will guide users interested in benchmarking their own model on HEST-Benchmark.
Note: Spontaneous contributions are encouraged if researchers from the community want to include new models. To do so, simply create a Pull Request.
- The preferred mode of communication is via GitHub issues.
- If GitHub issues are inappropriate, email
gjaume@bwh.harvard.edu(and ccpdoucet@bwh.harvard.edu). - Immediate response to minor issues may not be available.
If you find our work useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{jaume2024hest,
author = {Jaume, Guillaume and Doucet, Paul and Song, Andrew H. and Lu, Ming Y. and Almagro-Perez, Cristina and Wagner, Sophia J. and Vaidya, Anurag J. and Chen, Richard J. and Williamson, Drew F. K. and Kim, Ahrong and Mahmood, Faisal},
title = {{HEST-1k: A Dataset for Spatial Transcriptomics and Histology Image Analysis}},
journal = {arXiv},
year = {2024},
month = jun,
eprint = {2406.16192},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.16192v1}
}