Forked from abetusk/gbr2ngc
- Fixed Issue: Which can't parse G02 and G03 correctly in the Gerber file that generated by Kicad 5.1.2-2
- Add Laser Mode.
=======
Open source no frills Gerber to gcode converter, using (a slightly modified) Clipper Lib. Produces an isolation routing gcode file for the given Gerber file.
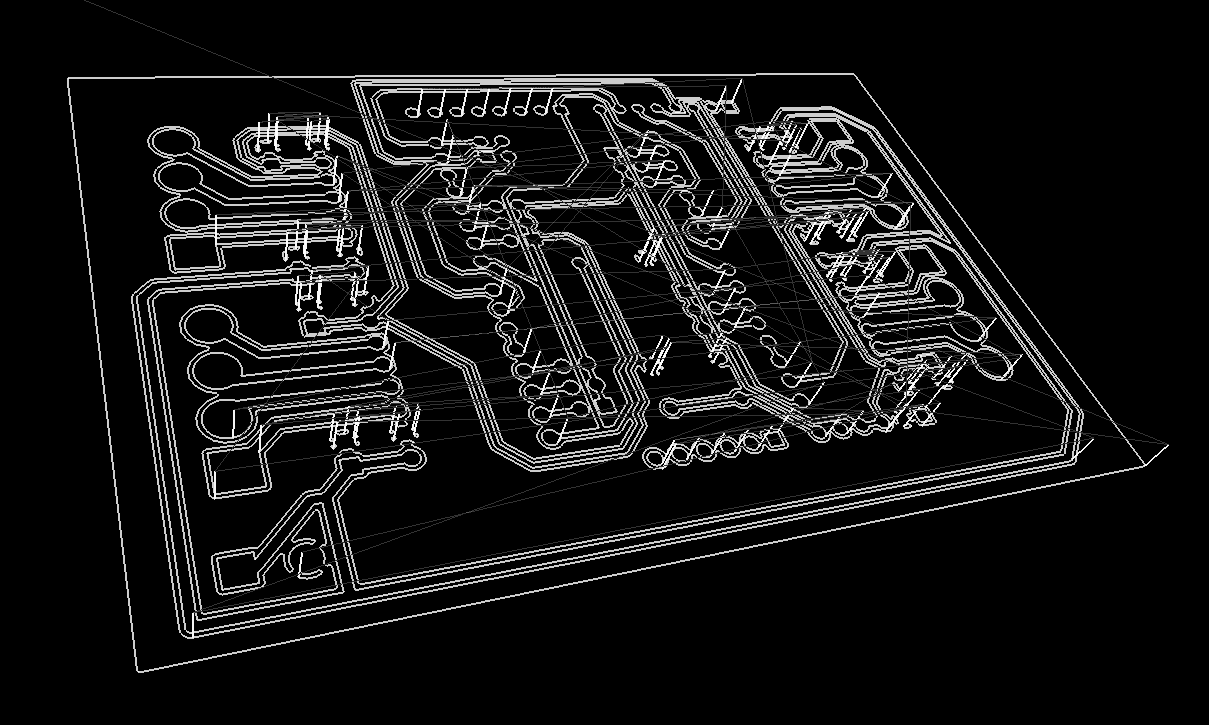
gbr2ngc will produce a GCode file like this:
from a Gerber file like this:
cd src
make
gbr2ngc --input example/example.gbr --radius 0.0025 --output example.ngc
Current version is in an alpha state, so use at your own risk.
$ gbr2ngc -h
gbr2ngc: A gerber to gcode converter
version 0.8.3
usage: gbr2ngc [<options>] [<input_Gerber>] [-o <output_GCode_file>]
-r, --radius radius radius (default 0) (units in inches)
-F, --fillradius fillradius radius to be used for fill pattern (default to radius above)
-i, --input input input file
-o, --output output output file (default stdout)
-c, --config-file config-file configuration file (default ./gbr2ngc.ini)
-f, --feed feed feed rate (default 10)
-s, --seek seek seek rate (default 100)
-z, --zsafe zsafe z safe height (default 0.1 inches)
-Z, --zcut zcut z cut height (default -0.05 inches)
-2, --gcode-header gcode-header prepend custom G-code to the beginning of the program
-3, --gcode-footer gcode-footer append custom G-code to the end of the program
-l, --segment-length segment-length minimum segment length
-M, --metric output units in metric
-I, --inches output units in inches (default)
-C, --no-comment do not show comments
-R, --machine-readable machine readable (uppercase, no spaces in gcode)
-H, --horizontal route out blank areas with a horizontal scan line technique
-V, --vertical route out blank areas with a vertical scan line technique
-G, --zengarden route out blank areas with a 'zen garden' technique
-P, --print-polygon print polygon regions only (for debugging)
--invertfill invert the fill pattern (experimental)
--simple-infill infill copper polygons with pattern (currently only -H and -V supported)
--no-outline do not route out outline when doing infill
--height-file height-file height file to use for height offseting
--height-algorithm height-algorithm height algorithm to use (default Catmull-Rom) (options: catmull-rom, inverse-square)
-v, --verbose verbose
-N, --version display version information
-h, --help help (this screen)
See the documentation for a more detailed description of each of the options.
RS-274Xcompliant- Polyginal underlying models
- Tool offsetting
- Fill pattern options
Many Gerber converters fail with RS-274X compliance and have trouble with, say, Aperture Macros (AM), Aperture Blocks (AB) and other newer definitions from RS-274D.
gbr2ngc handles all these cases.
Providing automated tests is on the roadmap but see the examples directory for Gerber files that can be successfully converted with gbr2ngc.
Using an underlying polyginal model allows for tool paths that are smoother for non axis-aligned lines. In some Gerber to Gcode converters I've used in the past, the rasterization caused a tool path to be 'jagged' when the slope of the line was not aligned to the major axies.
Angus Johnson's clipperlib is used as the fundamental building block to do polygon boolean operations. clipperlib is also used for polygon offsetting for the tool offsetting and fill pattern features.
GPLv3