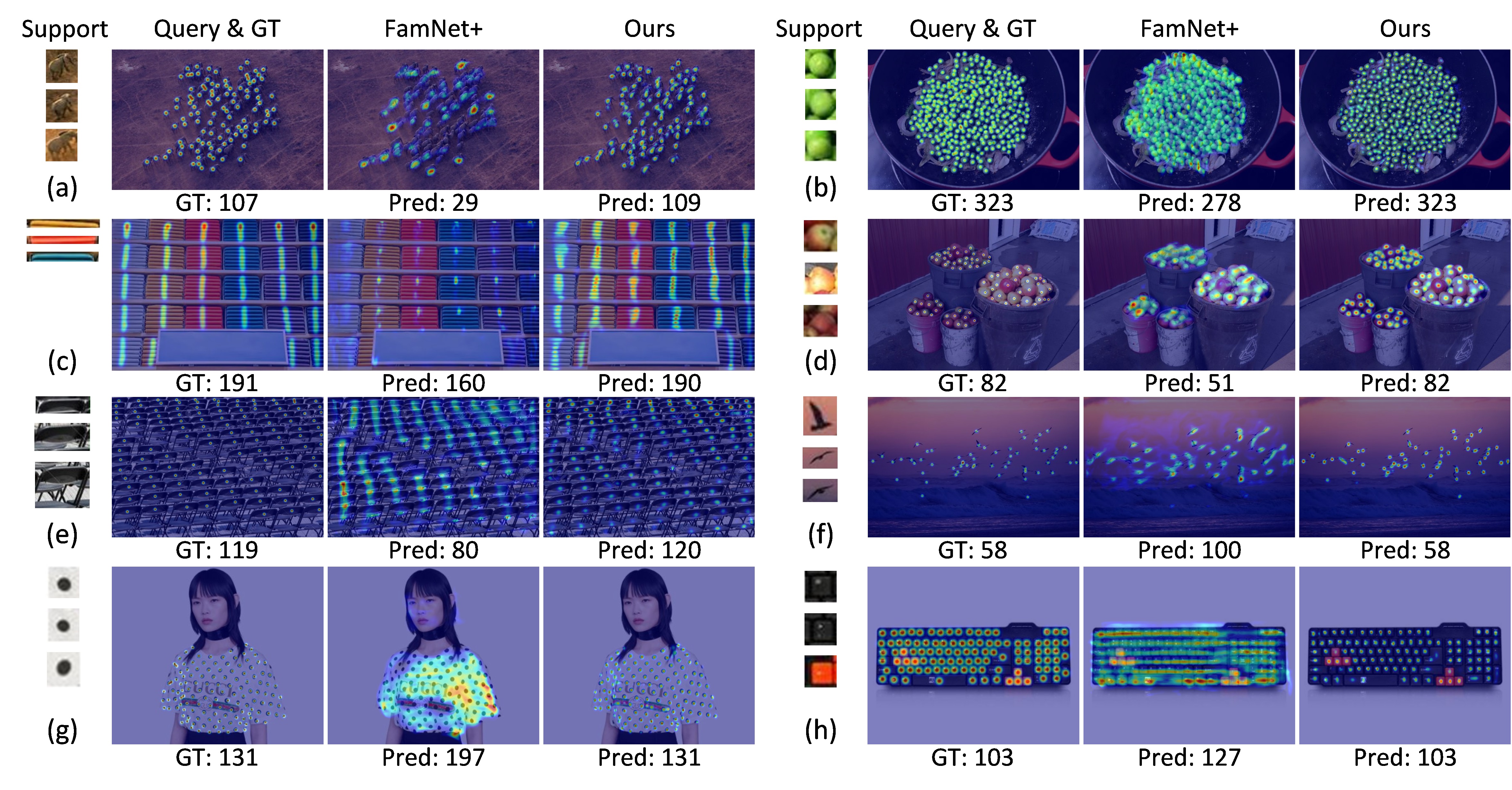
Official PyTorch Implementation of Few-shot Object Counting with Similarity-Aware Feature Enhancement, Accepted by WACV 2023.
- Create the FSC147 dataset directory. Download the FSC147 dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/FSC147_384_V2/. The FSC147 dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- FSC147_384_V2
|-- images_384_VarV2
|-- gt_density_map_adaptive_384_VarV2
|-- train.json
|-- val.json
|-- test.json
|-- fold0.json
|-- fold1.json
|-- fold2.json
|-- fold3.json
-
cd the experiment directory by running
cd ./experiments/FSC147/. -
Train, eval, or test by running:
(1) For slurm group:
sh train.sh #NUM_GPUS #PARTITION,sh eval.sh #NUM_GPUS #PARTITION, orsh test.sh #NUM_GPUS #PARTITION.(2) For torch.distributed.launch:
sh train_torch.sh #NUM_GPUS #GPU_IDS,sh eval_torch.sh #NUM_GPUS #GPU_IDS, orsh test_torch.sh #NUM_GPUS #GPU_IDS, e.g., train with GPU 1,3,4,6 (4 GPU in total):sh train_torch.sh 4 1,3,4,6.Note: During eval or test, please set config.saver.load_path to load the checkpoints.
-
Results and checkpoints.
| Platform | Val MAE | Val RMSE | Test MAE | Test RMSE | Checkpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 GPUs (NVIDIA Tesla V100 16GB) | 14.42 | 51.72 | 13.56 | 91.30 | here |
Here we provide one example (3 shot, fold0 as val set), and others are similar.
-
Create the FSC147 dataset directory, the same as in 1.1.
-
cd the experiment directory by running
cd experiments/FSC147_fold/3shot/fold0/. -
Train or eval by running:
(1) For slurm group:
sh train.sh #NUM_GPUS #PARTITIONorsh eval.sh #NUM_GPUS #PARTITION.(2) For torch.distributed.launch:
sh train_torch.sh #NUM_GPUS #GPU_IDSorsh eval_torch.sh #NUM_GPUS #GPU_IDS.Note: During eval or test, please set config.saver.load_path to load the checkpoints.
-
Results. Training on 8 GPUs (NVIDIA Tesla V100 16GB) results in following performance.
| Shot | Val Fold | Val MAE | Val RMSE | Shot | Val Fold | Val MAE | Val RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 15.62 | 51.20 | 3 | 0 | 13.84 | 43.99 | |
| 1 | 1 | 7.14 | 15.77 | 3 | 1 | 6.29 | 13.89 | |
| 1 | 2 | 14.05 | 92.48 | 3 | 2 | 11.19 | 86.81 | |
| 1 | 3 | 13.88 | 38.38 | 3 | 3 | 11.73 | 33.85 |
-
Create the FSC147 & CARPK dataset directory, the same as in 1.1 & 1.4.
-
cd the experiment directory by running
cd experiments/FSC147_to_CARPK/. -
Pretrain, finetune, or eval. The pretrain, finetune, or eval are similar to FSC147.
-
Results. Training on 8 GPUs (NVIDIA Tesla V100 16GB) results in following performance.
| MAE (pretrain on FSC147) | RMSE (pretrain on FSC147) | MAE (finetune on CARPK) | RMSE (finetune on CARPK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17.78 | 20.95 | 4.91 | 6.32 |
The train and eval of class-specific counting are similar to FSC147. Here we only provide the construction of the dataset directory. The checkpoints (trained on 8 NVIDIA Tesla V100 16GB GPUs) and the corresponding results are given.
| CARPK | PUCPR+ | UCSD | Mall | ShanghaiTech PartA | ShanghaiTech PartB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 4.91 | 2.24 | 1.01 | 1.77 | 74.36 | 9.75 |
| RMSE | 6.32 | 3.44 | 1.34 | 2.24 | 121.15 | 15.87 |
| checkpoints | here | here | here | here | here | here |
1) CARPK
- Download the CARPK dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/CARPK_devkit/. The CARPK dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- CARPK_devkit
|-- Images
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
- run
python gen_gt_density.pyto generate ground-truth density map. The ground-truth density map will be saved to./data/CARPK_devkit/gt_density_map/.
2) PUCPR+
- Download the PUCPR+ dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/PUCPR+_devkit/. The PUCPR+ dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- PUCPR+_devkit
|-- Images
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
- run
python gen_gt_density.pyto generate ground-truth density map. The ground-truth density map will be saved to./data/PUCPR+_devkit/gt_density_map/.
3) UCSD
- Download the UCSD dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/UCSD/. The UCSD dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- UCSD
|-- ucsdpeds_vidf
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
|-- mask.png
-
We use the annotations in
vidf-cvpr.zip, which corresponds to 10 directories (fromucsdpeds_vidf/video/vidf/vidf1_33_000.y/toucsdpeds_vidf/video/vidf/vidf1_33_009.y/). Merge all images under these 10 directories toucsdpeds_vidf/video/vidf/. Other directories could be removed. -
run
python gen_gt_density.pyto generate ground-truth density map. The ground-truth density map will be saved to./data/UCSD/gt_density_map/.
4) Mall
- Download the Mall dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/Mall/. The Mall dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- Mall
|-- frames
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
|-- mask.png
- run
python gen_gt_density.pyto generate ground-truth density map. The ground-truth density map will be saved to./data/Mall/gt_density_map/.
5) ShanghaiTech
- Download the ShanghaiTech dataset from here. Unzip the file and move some to
./data/ShanghaiTech/. The ShanghaiTech dataset directory should be as follows.
|-- data
|-- ShanghaiTech
|-- part_A
|-- train_data
|-- images
|-- test_data
|-- images
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
|-- part_B
|-- train_data
|-- images
|-- test_data
|-- images
|-- gen_gt_density.py
|-- train.json
|-- test.json
|-- exemplar.json
- run
python gen_gt_density.pyto generate ground-truth density map. Note that you should run this twice for both part_A and part_B. The ground-truth density map will be saved to (1)./data/ShanghaiTech/part_A/train_data/gt_density_map/, (2)./data/ShanghaiTech/part_A/test_data/gt_density_map/, (3)./data/ShanghaiTech/part_B/train_data/gt_density_map/, (4)./data/ShanghaiTech/part_B/test_data/gt_density_map/.
- We provide two datasets: custom_dataset.py & custom_exemplar_dataset.py, and three models: safecount.py, safecount_exemplar.py, & safecount_crossdataset.py. They should be cooperated and used as follows.
| dataset | model | circumstance |
|---|---|---|
| custom_dataset.py | safecount.py | The support images are parts of the query image, and annotated by bounding boxes, e.g., FSC147. |
| custom_exemplar_dataset.py | safecount_exemplar.py | The support images are sampled then fixed, and not parts of the query image, e.g., CARPK, PUCPR+, UCSD, Mall, and ShanghaiTech. |
| custom_dataset.py | safecount_crossdataset.py | In cross-dataset generalization, pretraining a model on FSC147 and finetuning on class-specific counting. |
-
CUDA Out of Memory.
(1). Choose a smaller image size (config.dataset.input_size).
(2). Set a smaller exemplar number (config.dataset.shot for FSC147, config.dataset.exemplar.num_exemplar for class-specific counting).
(3). Set a larger out_stride (config.net.kwargs.backbone.out_stride), but you also need to revise the Regressor (in models.utils.py) to upsample the feature to the original image size.