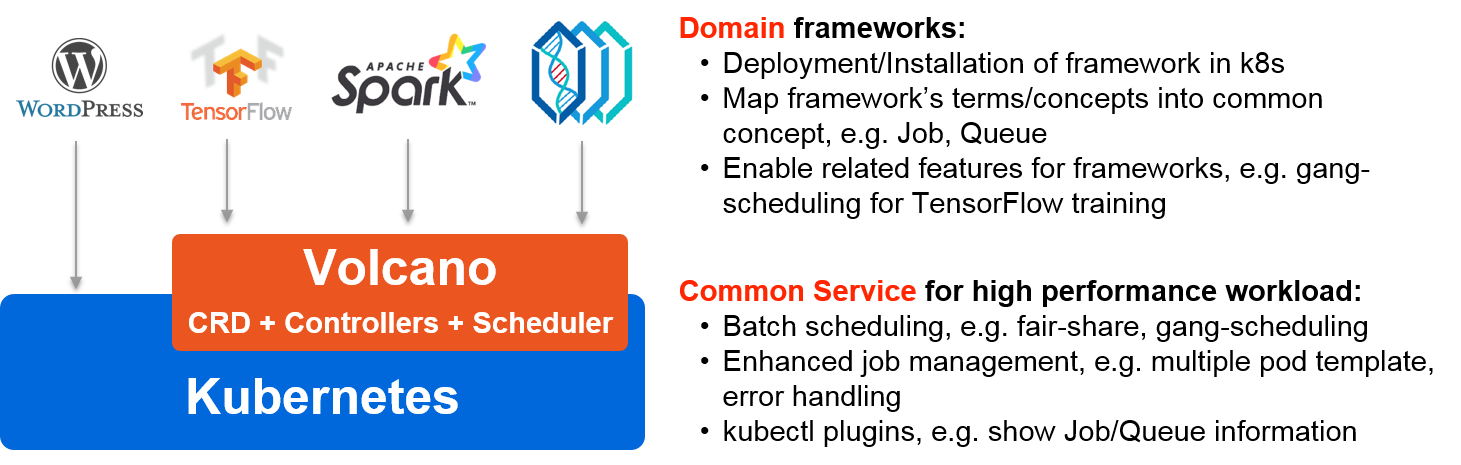
Volcano is a batch system built on Kubernetes. It provides a suite of mechanisms currently missing from Kubernetes that are commonly required by many classes of batch & elastic workload including:
- machine learning/deep learning,
- bioinformatics/genomics
- other "big data" applications.
These types of applications typically run on generalized domain frameworks like Tensorflow, Spark, PyTorch, MPI, etc, which Volcano integrates with.
Some examples of the mechanisms and features that Volcano adds to Kubernetes are:
- Job management extensions and improvements, e.g:
- Multi-pod jobs
- Lifecycle management extensions including suspend/resume and restart.
- Improved error handling
- Indexed jobs
- Task dependencies
- Scheduling extensions, e.g:
- Co-scheduling
- Fair-share scheduling
- Queue scheduling
- Preemption and reclaims
- Reservations and backfills
- Topology-based scheduling
- Runtime extensions, e.g:
- Support for specialized continer runtimes like Singularity, with GPU accelerator extensions and enhanced security features.
- Other
- Data locality awareness and intelligent scheduling
- Optimizations for data throughput, round-trip latency, etc.
Volcano builds upon a decade and a half of experience running a wide variety of high performance workloads at scale using several systems and platforms, combined with best-of-breed ideas and practices from the open source community.
NOTE: the scheduler is built based on kube-batch; refer to #241 and #288 for more detail.
You can watch industry experts talking about Volcano in different International Conferences over here.
The easiest way to deploy Volcano is to use the Helm chart. Volcano can be deployed by cloning code and also by adding helm repo.
Add helm repo using following command,
helm repo add volcano https://volcano-sh.github.io/charts
Install Volcano using following command,
helm install volcano/volcano --namespace <namespace> --name <specified-name>
e.g :
helm install volcano/volcano --namespace volcano-trial --name volcano-trial
First of all, clone the repo to your local path:
# mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/volcano.sh/
# cd $GOPATH/src/volcano.sh/
# git clone --recursive https://github.com/volcano-sh/volcano.git
Official images are available on DockerHub, however you can build them locally with the command:
cd $GOPATH/src/volcano.sh/volcano
make images
## Verify your images
# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
volcanosh/vk-admission latest a83338506638 8 seconds ago 41.4MB
volcanosh/vk-kube-batch latest faa3c2a25ac3 9 seconds ago 49.6MB
volcanosh/vk-controllers latest 7b11606ebfb8 10 seconds ago 44.2MB
NOTE:
- You need ensure the images are correctly loaded in your kubernetes cluster, for
example, if you are using kind cluster,
try command
kind load docker-image <image-name>:<tag>for each of the images. - When reinstall the volcano charts, since tiller server will not manage CRD resource,
you need to delete them manually eg:
kubectl delete crds xxxxbefore reinstalling or try command with--no-crd-hookoption.
Secondly, install helm chart.
helm install installer/helm/chart/volcano --namespace <namespace> --name <specified-name>
e.g :
helm install installer/helm/chart/volcano --namespace volcano-trial --name volcano-trial
To verify your installation run the following commands:
#1. Verify the Running Pods
# kubectl get pods --namespace <namespace>
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
<specified-name>-admission-84fd9b9dd8-9trxn 1/1 Running 0 43s
<specified-name>-controllers-75dcc8ff89-42v6r 1/1 Running 0 43s
<specified-name>-scheduler-b94cdb867-89pm2 1/1 Running 0 43s
<specified-name>--admission-init-qbtmb 0/1 Completed 0 43s
#2. Verify the Services
# kubectl get services --namespace <namespace>
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
<specified-name>-admission-service ClusterIP 10.105.78.53 <none> 443/TCP 91s
You can reach the maintainers of this project at:
Slack: #volcano-sh
Mailing List: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/volcano-sh