Multi-Touch Attribution. Find out which channels contribute most to user conversion.
This package contains implementations the following Multi-Touch Attribution models:
- Shapley
- Markov
- So-called Simple Probabilistic Model by Shao and Li
- Bagged Logistic Regression by Shao and Li
- Additive Hazard (Survival)
In addition, some popular heuristic “models” are included, specifically
- First Touch
- Linear
- Last Touch
- Time Decay
- Position Based
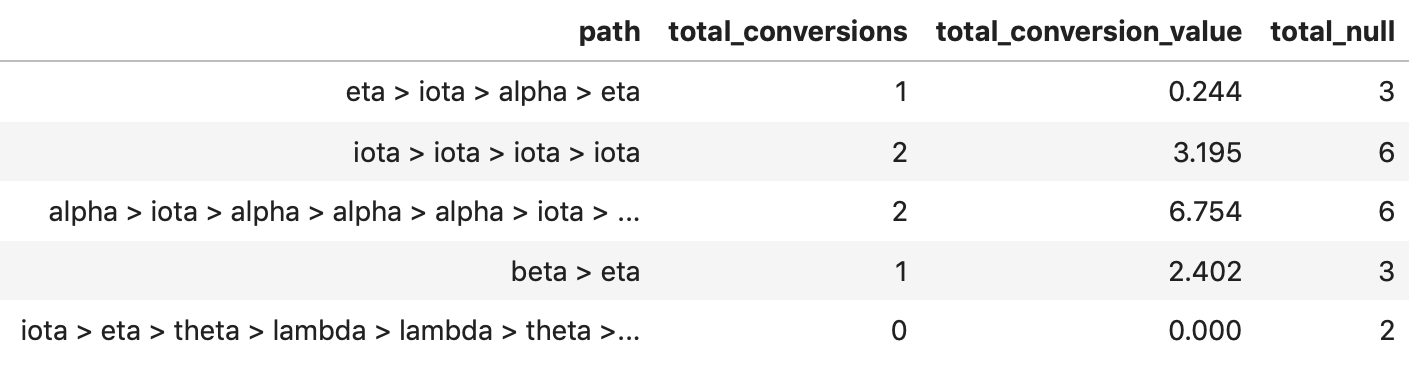
The package comes with the same test data set as an R package called ChannelAttribution - there are 10,000 rows containing customer journeys across 12 channels: alpha, beta, delta, epsilon, eta, gamma, iota, kappa, lambda, mi, theta and zeta.
These are conversion aggregations by path. Suppose there’s a path (customer journey)
a > b > c
with total_conversions equal to 2 and total_null equal to 5. This means that we recorded 2 consumer journeys
a > b > c > (conversion)
and 5 customer journeys
a > b > c > (null)
There’s an option to generate timestamp data if you want to use the Additive Hazard model (the only model that explicitly incorporates exposure times).
- Nisar and Yeung (2015) - Purchase Conversions and Attribution Modeling in Online Advertising: An Empirical Investigation pdf
- Shao and Li (2011) - Data-driven Multi-touch Attribution Models pdf
- Dalessandro et al (2012) - Causally Motivated Attribution for online Advertising pdf
- Cano-Berlanga et al (2017) - Attribution models and the Cooperative Game Theory pdf
- Ren et al (2018) - Learning Multi-touch Conversion Attribution with Dual-attention Mechanisms for Online Advertising pdf
- Zhang et al (2014) - Multi-Touch Attribution in Online Advertising with Survival Theory pdf
- Geyik et al (2014) - Multi-Touch Attribution Based Budget Allocation in Online Advertising pdf