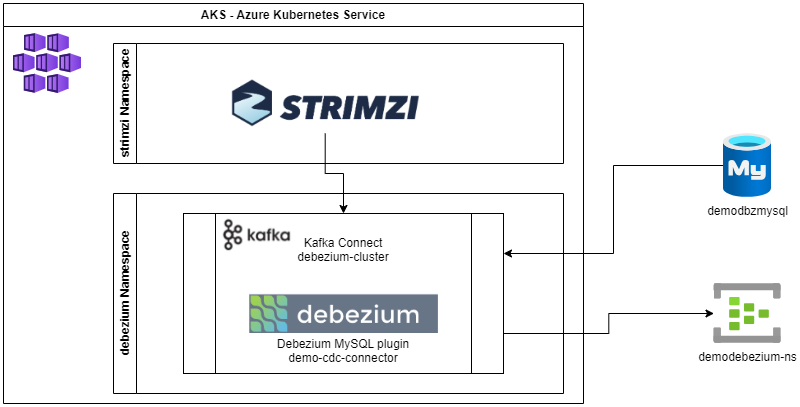
This was originally created as a demo to present at TDC Connections 2021, MVPConf2021 and TDC Future 2021 conferences, on sessions which I spoke about Event Driven Architectures and CDC and showed how to deploy Debezium on AKS, configure it to capture changes from a MySQL database and send those events to Azure Event Hub
It was updated on October/2023, to use newer versions of Debezium, Kafka, Strimzi, and new features of Azure Event Hub (like Compaction on topics). Those changes allowed me to simplify the solution removing the Kafka Broker cluster and the Kafka MirrorMaker2, since now it is possible to deploy the Kafka Connect connected to directly to Azure Event Hub.
-
Pre-reqs => For running this demo you will need to:
- An Azure Subscription where you have administrative permissions
- A Cloud Shell configured to use Bash on that subscription
-
Start by creating the required infrastructure you will need:
-
Use the Bash environment on Azure Cloud Shell.
-
Select your Subscription, if you have more than one, and create the resource group:
az account set --subscription '<your-subscription-name-or-id>' az group create --location eastus --resource-group demodebezium-rg
-
Register some of the required resource providers:
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.OperationalInsights az provider register --namespace microsoft.insights az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerRegistry az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Kubernetes az provider register --namespace Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration az provider register --namespace Microsoft.EventHub
-
Then create:
- A Log Analytics Workspace;
- An AKS (Azure Kubernetes Service) cluster;
- An Azure Database for MySQL server;
- An ACR (Azure Container Registry) repository, and;
- An Azure Event Hub namespace
az monitor log-analytics workspace create --resource-group demodebezium-rg --workspace-name demodebezium-laws lawsId=`az monitor log-analytics workspace show --resource-group demodebezium-rg --workspace-name demodebezium-laws | jq '.id' -r` az aks create --resource-group demodebezium-rg --name demodbzakscluster --node-count 2 --enable-addons monitoring --generate-ssh-keys --workspace-resource-id $lawsId az mysql flexible-server create --resource-group demodebezium-rg --name demodbzmysql --location eastus --admin-user debezium --admin-password P@ssw0rd2023 --sku-name Standard_B1s --storage-size 20 --version 8.0.21 az acr create --resource-group demodebezium-rg --name demodbzacr --sku Basic az eventhubs namespace create --name demodebezium-ns --resource-group demodebezium-rg -l eastus
-
You may need to change the names used here for the MySQL server, the ACR repository and the Event Hub namespace because those names need to be unique. If you do that, you will need to remember to change those names on subsequent commands and, also, inside the provided files. Following is a list of files and the references they have inside:
Provided File References inside debezium-mysql-connector.yaml MySQL server, Azure Event Hub namespace kafka-connect.yaml ACR repository, Azure Event Hub namespace
-
-
Configure some basic things on your MySQL database:
-
Connect to your recently created MySQL (using MySQL Workbench or any other client tool of your preference), and execute the following commands or use the provided SQL Script file demo_debezium_grant_privileges.sql:
SET SQL_SAFE_UPDATES=0; CALL mysql.az_load_timezone(); GRANT SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'debezium'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
-
On Azure Portal, go to your newly created MySQL server, called
demodbzmysql, select "Server parameters" on left menu, and:- set
binlog_row_imagetoFULL - set
binlog_expire_logs_secondsto7200 - set
time_zoneto- mine is
America/Chicago, but you can find the available time zones by querying the database:
SELECT name FROM mysql.time_zone_name;
- mine is
- set
-
You can find more information about MySQL required configurations, here, on Debezium documentation.
-
After deploying and configuring the MySQL server, you can use the provided SQL script demo_debezium_create_database.sql to create the simple schema used on this demo. Just open this script on MySQL Workbench and run it.
-
-
Download from GitHub and unzip the 0.38.0 version of Strimzi:
curl -L https://github.com/strimzi/strimzi-kafka-operator/releases/download/0.38.0/strimzi-0.38.0.tar.gz --output strimzi-0.38.0.tar.gz tar -xvzf strimzi-0.38.0.tar.gz rm strimzi-0.38.0.tar.gz
-
Download from Maven and unzip the 2.4.0 version of Debezium Kafka Connector for MySQL:
curl https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/io/debezium/debezium-connector-mysql/2.4.0.Final/debezium-connector-mysql-2.4.0.Final-plugin.tar.gz --output debezium-connector-mysql-2.4.0.Final-plugin.tar.gz tar -xvzf debezium-connector-mysql-2.4.0.Final-plugin.tar.gz rm debezium-connector-mysql-2.4.0.Final-plugin.tar.gz
-
Connect to AKS and prepare to install Strimzi:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group demodebezium-rg --name demodbzakscluster kubectl create ns strimzi kubectl create ns debezium
-
Change Strimzi installation files to use your created namespaces
- Change all files named as
strimzi-0.38.0/install/cluster-operator/\*RoleBinding\*.yamlreplacingnamespace: myProjectwithnamespace: strimzi. You can use the Linux sed utility for that:
cd strimzi-0.38.0 sed -i 's/namespace: .*/namespace: strimzi/' install/cluster-operator/*RoleBinding*.yaml
- Then edit
strimzi-0.38.0/install/cluster-operator/060-Deployment-strimzi-cluster-operator.yamlfile to change theSTRIMZI_NAMESPACEenvironment variable setting:- You can use the Linux nano editor for that:
nano install/cluster-operator/060-Deployment-strimzi-cluster-operator.yaml
- The resultant section on file should like that:
# ... env: - name: STRIMZI_NAMESPACE value: debezium # ...
- Change all files named as
-
Deploy Strimzi to your AKS cluster on "strimzi" namespace and, then, give it permissions to operate on "debezium" namespace where you will deploy the Kafka Connect and Debezium components
kubectl create -f install/cluster-operator/ -n strimzi kubectl create -f install/cluster-operator/020-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator.yaml -n debezium kubectl create -f install/cluster-operator/023-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator.yaml -n debezium kubectl create -f install/cluster-operator/031-RoleBinding-strimzi-cluster-operator-entity-operator-delegation.yaml -n debezium cd .. -
Prepare to create a Kafka Connect docker image with Debezium and MySQL plugins:
- Create a
Dockerfilewith the following lines (or use the provided one):
FROM quay.io/strimzi/kafka:latest-kafka-3.6.0 USER root:root RUN mkdir -p /opt/kafka/plugins/debezium COPY ./debezium-connector-mysql/ /opt/kafka/plugins/debezium/ USER 1001
- Create a
-
Build the image, push it to Azure Container Registry and attach ACR to your AKS cluster:
az acr build --image debezium/mysql-plugin:v1 --image debezium/mysql-plugin:latest --registry demodbzacr --file Dockerfile . az aks update -n demodbzakscluster -g demodebezium-rg --attach-acr demodbzacr -
Edit the provided demodebezium-secrets.yaml to include your Azure Event Hub connection string, which you can find on Azure Portal under the "Shared access policies" menu. If you have changed the MySQL credentials during its creation, update this file with the new credentials too.
- Replace
<your-azure-eventhub-connection-string>with your Azure Event Hub connection string - Update "mysql-username" and "mysql-password" values, if needed
- Create a Secret on AKS
kubectl apply -f demodebezium-secrets.yaml -n debezium
- Then give the Strimzi operator permissions to access the secret using the two provided files: connector-configuration-role.yaml and connector-configuration-role-binding.yaml
kubectl apply -f connector-configuration-role.yaml -n debezium kubectl apply -f connector-configuration-role-binding.yaml -n debezium
- Replace
-
Deploy the Kafka Connect to your AKS cluster using your custom image that includes Debezium and MySQL plugins. Use the provided kafka-connect.yaml.
kubectl apply -f kafka-connect.yaml -n debezium
-
The Debezium/MySQL connector will need an internal topic that it uses to control the Snapshot strategy and the schema changes. It usually creates this topic automatically but, since we are not using a real Kafka broker but an Azure Event Hub namespace instead, we need to create this topic manually.
az eventhubs eventhub create --resource-group demodebezium-rg --namespace-name demodebezium-ns --name schema-history-internal.demodbz-aks-eh --cleanup-policy Delete --retention-time-in-hours 168 --partition-count 1
- WARNING: When using Kafka, this is a "permanent" topic where messages won't expire and get deleted. Azure Event Hub does not support that type of topic, so messages will expire and deleted. In that case, a new Snapshot will probably occur. Since Debezium uses this topic to decide when a new database snapshot is needed, in your scenario you should evaluate carefully what will be your Snapshot strategy. Refer to Debezium documentation about this
-
Configure the Debezium/MySQL connector to start capturing data changes on MySQL database. Use the provided debezium-mysql-connector.yaml.
kubectl apply -f debezium-mysql-connector.yaml -n debezium
And voilà... Now all changes happening on your MySQL database are being monitored by Debezium, and all CDC events are being posted on Azure Event Hub...
kubectl get kctr demo-cdc-connector -o yaml -n debeziumkubectl get pods -n debeziumkubectl get strimzi -n debeziumkubectl delete kafkaconnect.kafka.strimzi.io/debezium-cluster -n debeziumkubectl delete kafkaconnector.kafka.strimzi.io/demo-cdc-connector -n debezium