Joonhyuk Seo1,✢, Jaegang Jo2,✢, Joohoon Kim3,✢, Joonho Kang2,, Haejun Chung2,📧, Junsuk Rho3,📧, Jehyung Hong2,📧,
1 Department of Artificial Intelligence, Hanyang University
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Hanyang University
3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)
(✢) Equal contribution. (📧) corresponding author.
Abstract: Recent advances in metasurface lenses (metalenses) show great potential for opening a new era of compact imaging, photography, LiDAR, and VR/AR applications. However, the reported performances of manufactured broadband metalenses are still limited due to a fundamental trade-off between broadband focusing efficiency and operating bandwidth, resulting in chromatic aberrations, angular aberrations, and relatively low efficiency. Here, we demonstrate a deep learning-based image restoration framework to overcome these limitations and to realize end-to-end metalens imaging. The proposed image restoration framework achieves aberration-free full-color imaging for one of the largest mass-produced metalens (10-mm-diameter). The metalens imaging assisted by the neural network provides competitive image qualities compared to the ground truth.
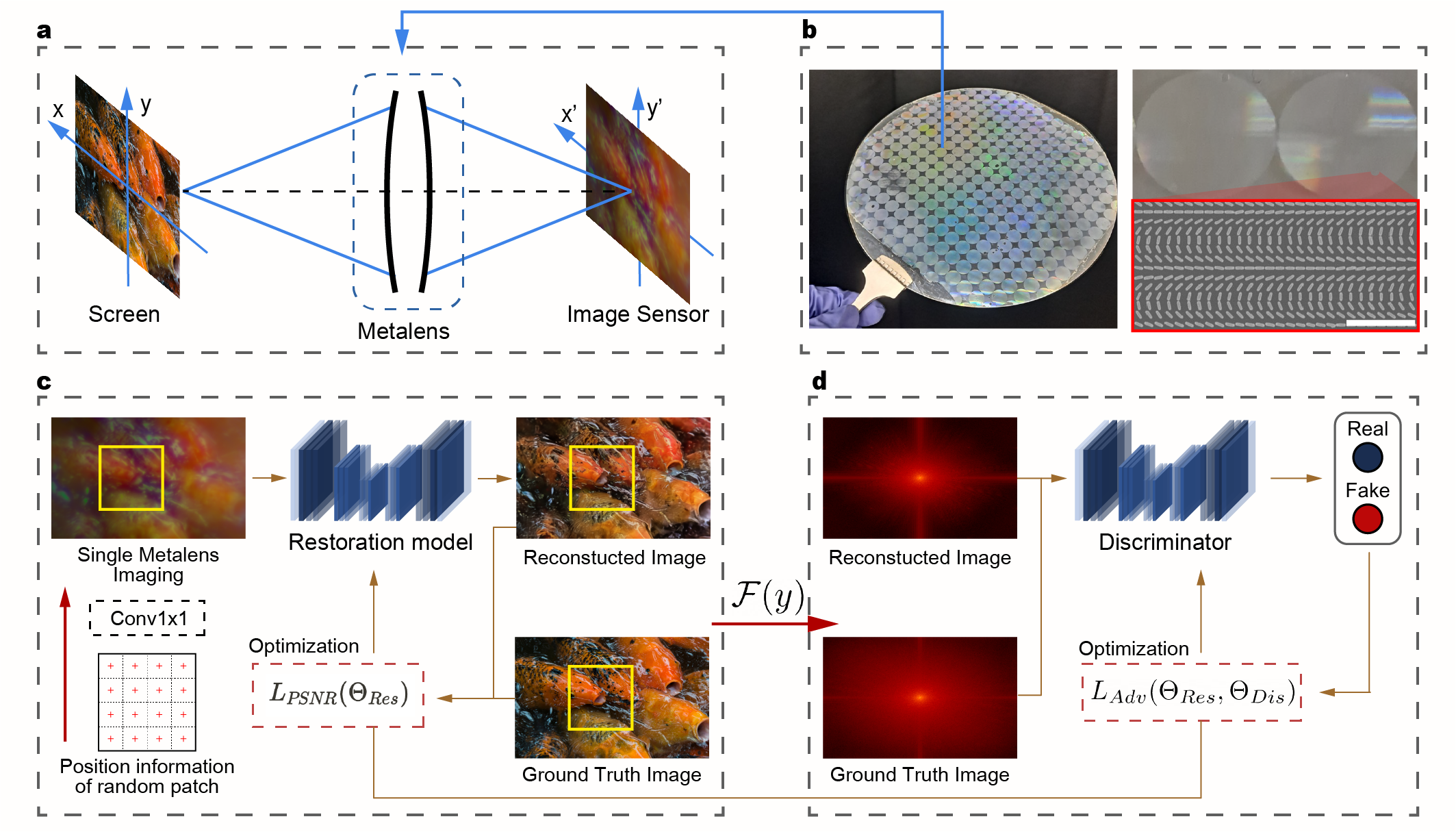
Metalenses, ultra-thin film lenses composed of subwavelength structures, have been spotlighted as a technology to overcome the limitations of conventional lenses. However, recent studies suggest that large-area broadband metalenses may suffer from a fundamental trade-off between broadband focusing efficiency and their diameter. Consequently, at present, reported broadband metalenses show chromatic aberration or low focusing efficiency over the large bandwidth, which hinders a commercialization of metalens-based compact imaging.
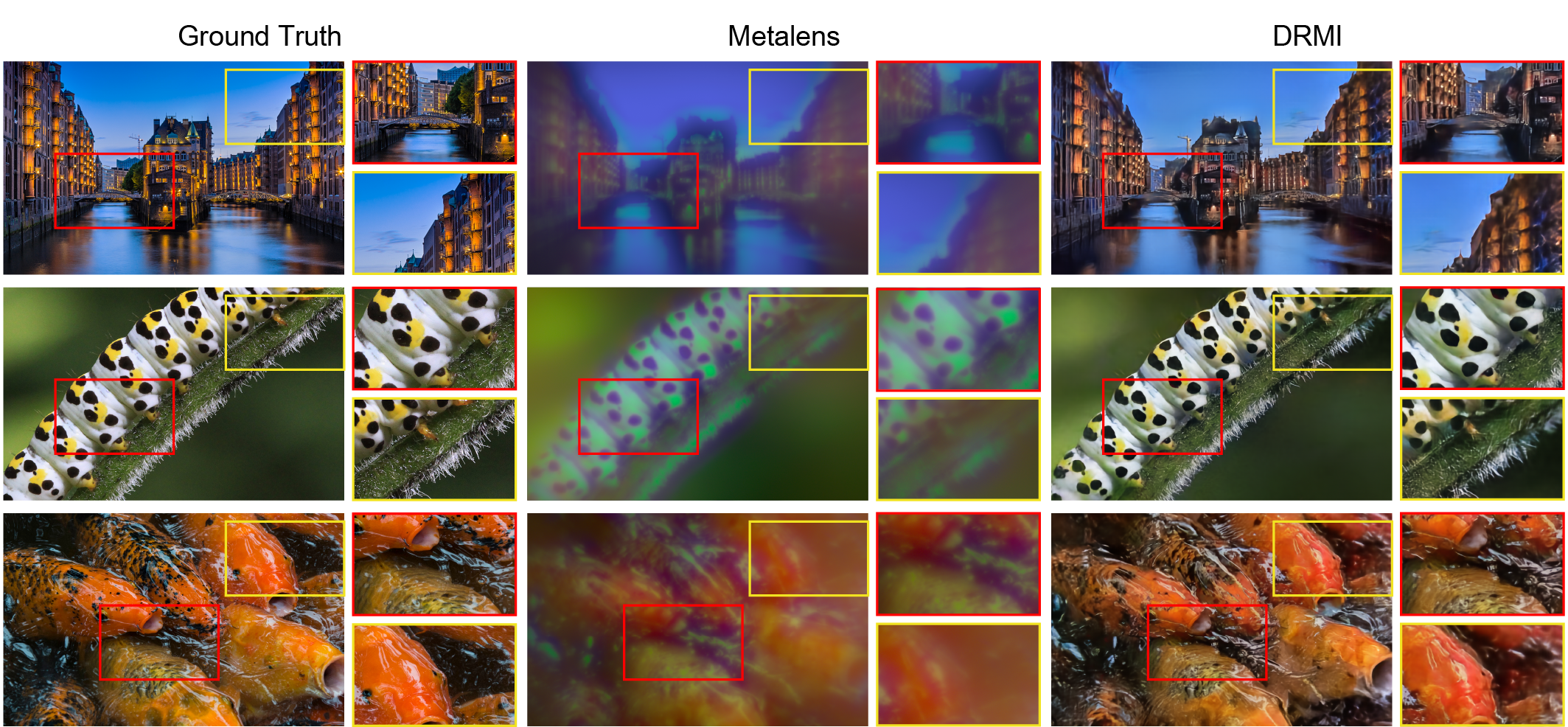
In this study, we propose the DNN-based image Reconstruction framework customized for Metalens Imaging system (DRMI) to overcome all these physical constraints by learning defects of the largest mass-produced metalenses (a 10-mm diameter).
| Model | Image Quality Metric (mean/std) | Frequency Measurement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | LPIPS | MAE | Cosine Similarity | |
| Metalens | 14.722/1.328 | 0.464/0.160 | 0.788/0.112 | 3.2805 | 0.922 |
| MIRNetV2 | 18.517/1.893 | 0.586/0.135 | 0.553/0.098 | 2.2403 | 0.967 |
| SFNet | 18.231/1.727 | 0.597/0.129 | 0.520/0.095 | 2.1941 | 0.965 |
| HINet(Local) | 21.400/2.333 | 0.674/0.117 | 0.449/0.097 | 1.8508 | 0.982 |
| NAFNet | 21.731/2.382 | 0.676/0.116 | 0.436/0.097 | 1.8165 | 0.983 |
| DRMI | 22.109/2.423 | 0.691/0.109 | 0.428/0.096 | 1.7585 | 0.984 |
- Download our repository
git clone https://github.com/yhy258/EIDL_DRMI.git
cd EIDL_DRMI- Create conda environment
conda create -n DRMI python=3.8
conda activate DRMI- Install requirements.txt
- Linux
- PyTorch >= 1.8.1
pip install -r requirements.txtOur metalens dataset used in the paper can be accessed on Figshare.
The train-test data should be placed in data/DRMI_dataset/{train or test} directory. :
EIDL_DRMI (repository)
└───data
└───DRMI_dataset
├───train
│ ├───ground_truth.lmdb
│ └───meta.lmdb
└───test
├───ground_truth.lmdb
└───meta.lmdb
The pretrained DRMI weights used in the paper can be accessed on Google Drive.
The checkpoint should be placed in save_model/{model_type} directory. : (model_type = DRMI)
EIDL_DRMI (repository)
└───save_model
└───DRMI
└───coord_fourier_adv_model_7500.pt
After preparing the dataset in data/DRMI_dataset directory, use
python3 DRMI_train.py
To change the settings for training, modify config.py or DRMI_train.py. As you train, the model's checkpoints are saved to the save_root/model_type you specified in config.py. The name of the checkpoint is determined by the training settings.
python3 DRMI_evaluation.py
Upon evaluation, performance metrics for the restoration result are printed, and the restored image data is saved to the image_save_path/model_type location previously set by the user, along with the ground truth image data used.
@article{seo2023deep,
title={Deep-learning-driven end-to-end metalens imaging},
author={Seo, Joonhyuk and Jo, Jaegang and Kim, Joohoon and Kang, Joonho and Kang, Chanik and Moon, Seongwon and Lee, Eunji and Hong, Jehyeong and Rho, Junsuk and Chung, Haejun},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.02669},
year={2023}
}