Android Boilerplate
Sample Android app that we use at ribot as a reference for new Android projects. It demonstrates the architecture, tools and guidelines that we use when developing for the Android platform (https://github.com/ribot/android-guidelines)
Libraries and tools included:
- Support libraries
- RecyclerViews and CardViews
- RxJava and RxAndroid
- Retrofit 2
- Dagger 2
- SqlBrite
- Butterknife
- Timber
- Picasso
- Otto event bus
- Functional tests with Espresso
- Robolectric
- Mockito
- Checkstyle, PMD and Findbugs for code analysis
Requirements
- Android SDK.
- Android 6.0 (API 23) .
- Latest Android SDK Tools and build tools.
Architecture
This project follows ribot's Android architecture guidelines that are based on MVP (Model View Presenter). Read more about them here.
How to implement a new screen following MVP
Imagine you have to implement a sign in screen.
- Create a new package under
uicalledsignin - Create an new Activity called
ActivitySignIn. You could also use a Fragment. - Define the view interface that your Activity is going to implement. Create a new interface called
SignInMvpViewthat extendsMvpView. Add the methods that you think will be necessary, e.g.showSignInSuccessful() - Create a
SignInPresenterclass that extendsBasePresenter<SignInMvpView> - Implement the methods in
SignInPresenterthat your Activity requires to perform the necessary actions, e.g.signIn(String email). Once the sign in action finishes you should callgetMvpView().showSignInSuccessful(). - Create a
SignInPresenterTestand write unit tests forsignIn(email). Remember to mock theSignInMvpViewand also theDataManager. - Make your
ActivitySignInimplementSignInMvpViewand implement the required methods likeshowSignInSuccessful() - In your activity, inject a new instance of
SignInPresenterand callpresenter.attachView(this)fromonCreateandpresenter.detachView()fromonDestroy(). Also, set up a click listener in your button that callspresenter.signIn(email).
Code Quality
This project integrates a combination of unit tests, functional test and code analysis tools.
Tests
To run unit tests on your machine:
./gradlew test
To run functional tests on connected devices:
./gradlew connectedAndroidTest
Note: For Android Studio to use syntax highlighting for Automated tests and Unit tests you must switch the Build Variant to the desired mode.
Code Analysis tools
The following code analysis tools are set up on this project:
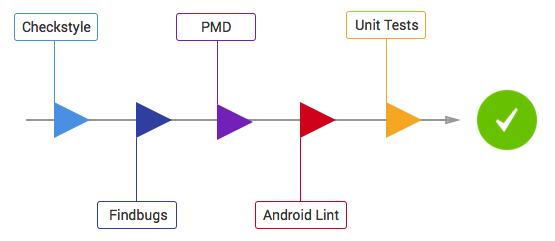
- PMD: It finds common programming flaws like unused variables, empty catch blocks, unnecessary object creation, and so forth. See this project's PMD ruleset.
./gradlew pmd
- Findbugs: This tool uses static analysis to find bugs in Java code. Unlike PMD, it uses compiled Java bytecode instead of source code.
./gradlew findbugs
- Checkstyle: It ensures that the code style follows our Android code guidelines. See our checkstyle config file.
./gradlew checkstyle
The check task
To ensure that your code is valid and stable use check:
./gradlew check
This will run all the code analysis tools and unit tests in the following order:
Distribution
The project can be distributed using either Crashlytics or the Google Play Store.
Play Store
We use the Gradle Play Publisher plugin. Once set up correctly, you will be able to push new builds to the Alpha, Beta or production channels like this
./gradlew publishApkRelease
Read plugin documentation for more info.
Crashlytics
You can also use Fabric's Crashlytics for distributing beta releases. Remember to add your fabric
account details to app/src/fabric.properties.
To upload a release build to Crashlytics run:
./gradlew assembleRelease crashlyticsUploadDistributionRelease
New project setup
To quickly start a new project from this boilerplate follow the next steps:
- Download this repository as a zip.
- Change the package name.
- Rename packages in main, androidTest and test using Android Studio.
- In
app/build.gradlefile,packageNameandtestInstrumentationRunner. - In
src/main/AndroidManifest.xmlandsrc/debug/AndroidManifest.xml.
- Create a new git repository, see GitHub tutorial.
- Replace the example code with your app code following the same architecture.
- In
app/build.gradleadd the signing config to enable release versions. - Add Fabric API key and secret to fabric.properties and uncomment Fabric plugin set up in
app/build.gradle - Update
proguard-rules.proto keep models (see TODO in file) and add extra rules to file if needed. - Update README with information relevant to the new project.
- Update LICENSE to match the requirements of the new project.
License
Copyright 2015 Ribot Ltd.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.