Please see this repository for the up-to-date method: https://github.com/qibinshi/TeleseismicDenoiser
A machine learning tool to separate earthquake and ambient noise signals for the seismic data in time domain.
Step 1: Download the event catalog based on distance range to a given station
Step 2:
2a - Download continuous seismic data
2b - Get the STEAD earthquake waveform data with SNR > 40dB and stack with STEAD noise signals
2c - Shuffle the phase of continuous data from a given station to get the local ambient noise signals, then stack with the STEAD earthquake waveform.
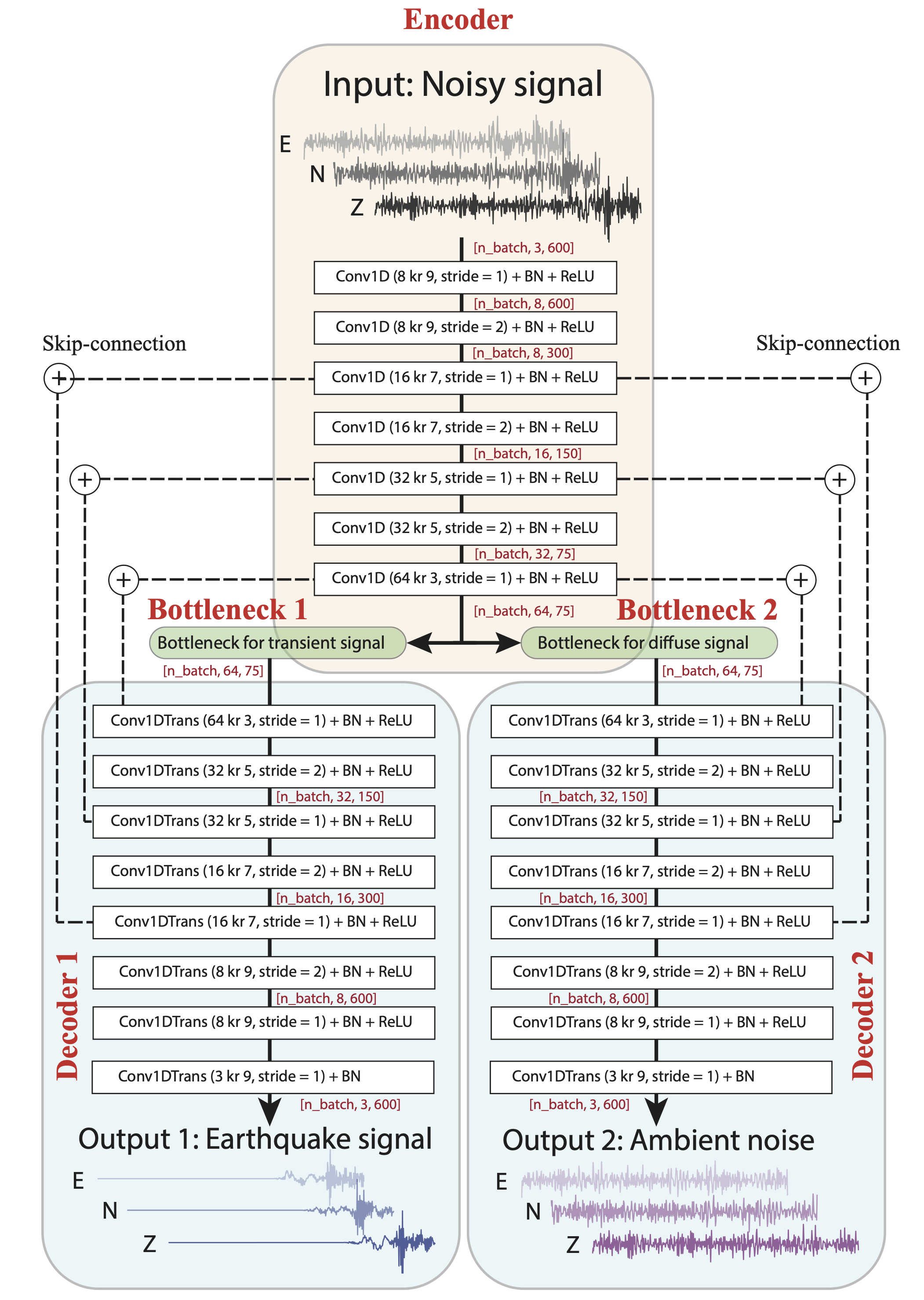
2d - Combine the waveforms datasets from 2b and 2c to get the final datasets that will be used to train the WaveDecompNet.
Step 3: Training the WaveDecompNet using the prepared datasets with specified bottleneck. Because of the internal randomness of ML algorithm, the searching paths for optimal parameters may be slightly different when repeating the execution. Multiple run of the model training may help (just change the first i_run for-loop) but there are little different in the final results. (Trained models that are showned in the paper can be found in the folder /trained_models
-
step3_training_1D.py gives the results shown in the paper.
-
step3_training_1D_hyperparam_tuning.py is used to tune the training parameters
Step 4: Test the trained model with the test datasets, and output the comparisons of waveforms in time domain and frequency domain.
Step 5: Load models with different bottlenecks and compare how well they can reconstruct the waveforms by calculating explained variance (EV) score.
Step 6: Apply the trained model directly to the continuous seismic data to separate the earthquake and ambient noise signals.
Step 7:
7a - Applying the STA/LTA to the decomposed earthquake signals
7b - Applying the signal station cross-correlation to the decomposed ambient noise signals.