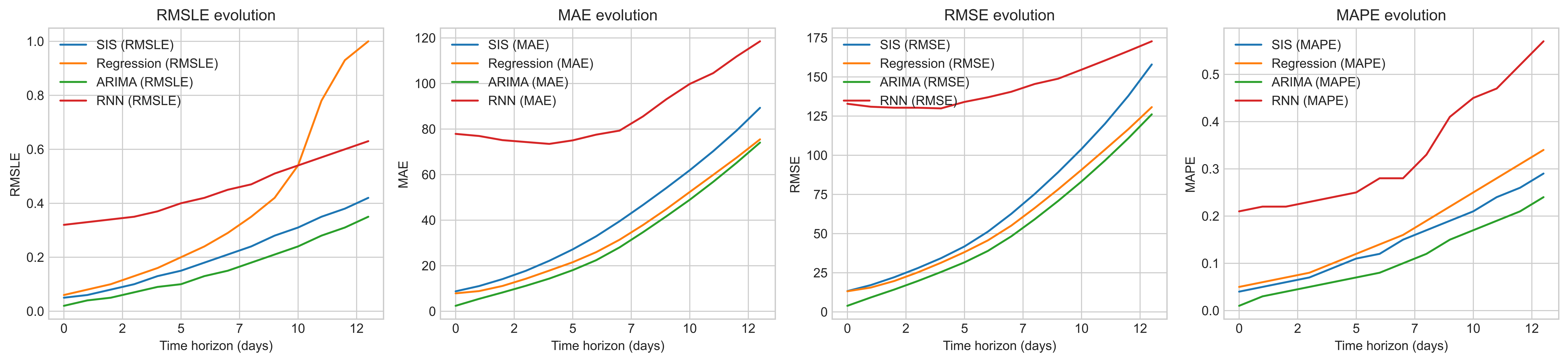
Comparative study of the main techniques used for COVID modeling where the information available is infected curve. The objective is to identify those univariate techniques that produce the best results, analyzing whether the more complex models are really able to provide better predictions.
Since COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, the urgency to obtain accurate predictive methods to help institutions make decisions on measures to apply and the uncertainty surrounding the virus has facilitated the publication and application of different techniques. The motivation of this study is to compare them, in particular compartmental epidemiological models, linear regression models, ARIMA family models and recurrent neural networks.