This Repo contains Code and trained Models for the Paper Mastering Zero-Shot Interactions in Cooperative and Competitive Simultaneous Games

Interpretation of Albatross by Midjourney
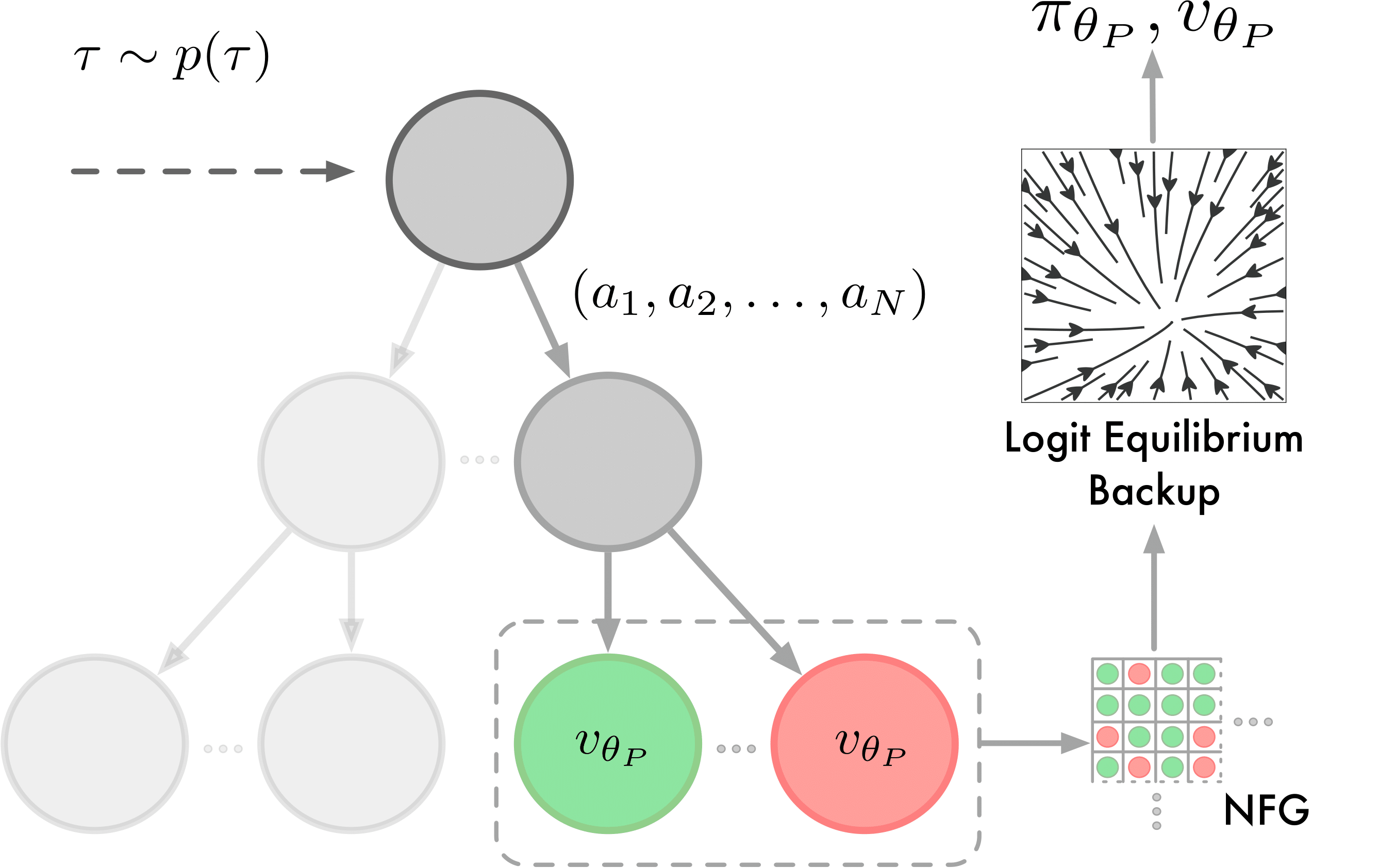
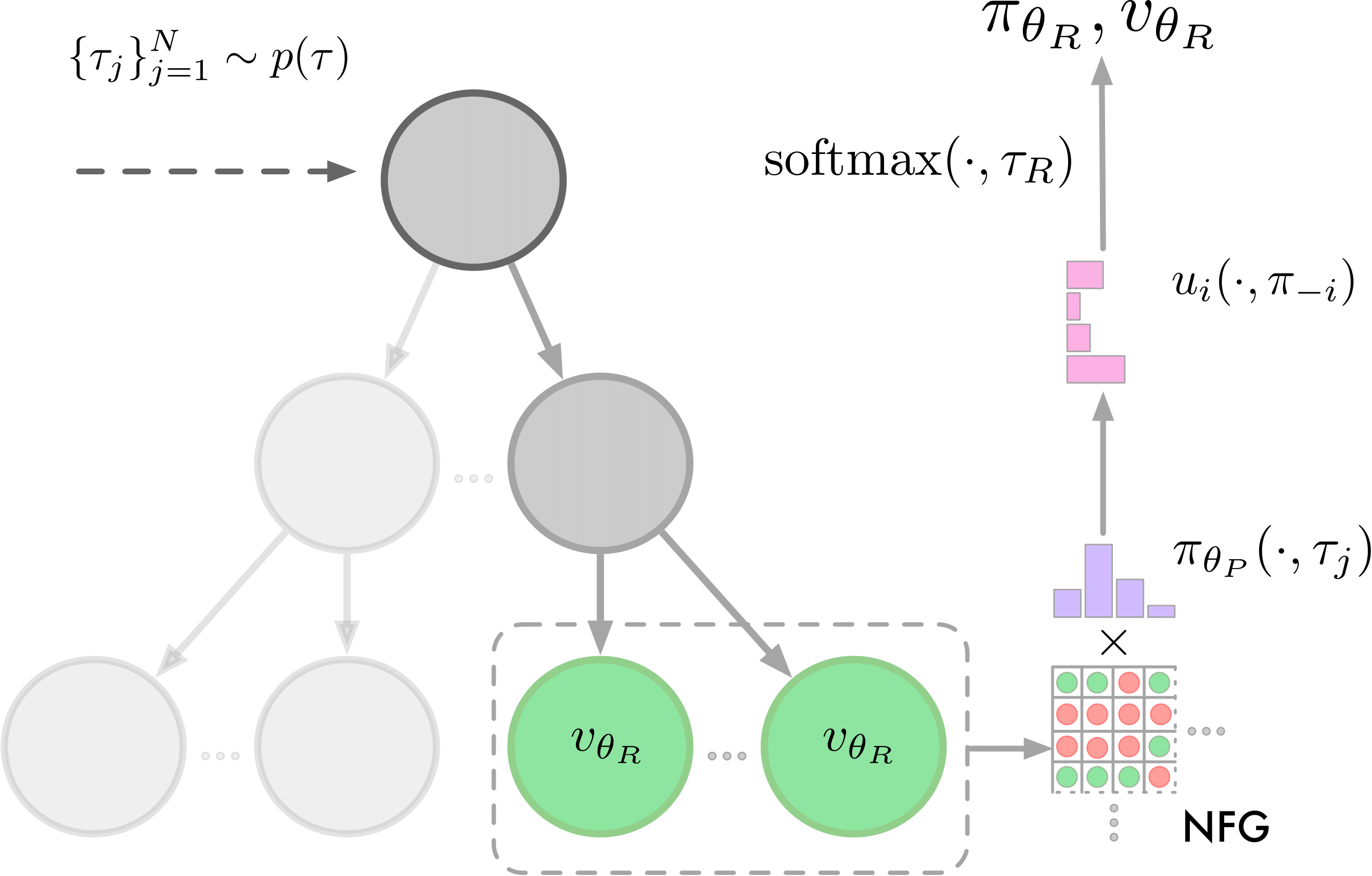
Training architecture of the proxy and response models of Albatross. Both models are trained via planning-augmented self-play using fixed-depth search and are conditioned on one (proxy model) or multiple (response model) temperatures tau that are drawn from a distribution p(tau). The response model uses the trained proxy model to compute the Smooth Best Response Logit Equilibrium (SBRLE).
This repository contains Git-submodules, which need to be initialized after cloning.
git clone https://github.com/ymahlau/albatross.git
cd albatross
git submodule init
git submodule update --init --recursive
Firstly, it is necessary to compile the c++ modules as most algorithms and game dynamics are implemented in that language. For this purpose, you need a g++ compiler on your system (for C++ version 11).
# Windows
cd src/cpp/alglib
cmd < compile.bat
cd ..
cmd < compile.bat
# Linux
cd src/cpp/alglib
sh compile.sh
cd ..
sh compile.sh
This may take a while
mamba env create -f environment.yml
mamba env update -f environment.yml
mamba activate battlesnake-rl
pip uninstall pytorch
mamba install pytorch-cuda==11.7 cudatoolkit pytorch==2.0.1 torchvision -c pytorch -c nvidia
mamba activate battlesnake-rl
- overcooked_ai_py: Overcooked Environment from (Carrol et al.). Used for comparison with our internal C++ Implementation of Overcooked
- scripts: Python Scripts for generating training configs, tournament evaluations and plots of the results
- imp_env: Unused, RL-Environment for infrastructure management (https://github.com/moratodpg/imp_marl)
- test: Extensive Unittests. Mirrors the folder structure of src
- trained_models/bc_state_dicts: trained pytorch models / behavior cloning agents
- src:
- agent: Interface and implementation of agents playing a game
- analysis: GUI for displaying neural network predictions in the game of Battlesnake
- cpp: C++ Library for Battlesnake/Overcooked game and various game theoretic algorithms
- depth: Code for parallel evaluation of different tree search depths
- equilibria: Python interface for game theoretic algorithms. Internally calls the C++ code.
- game: Game interface
- battlesnake: BattleSnake game
- normal_form: Normal form games and random initialization
- overcooked: Game of Overcooked implemented in C++
- overcooked_slow: Original implementation of Overcooked in Python, same game dynamics
- misc: Various code snippets for multiprocessing, plotting or training
- modelling: Maximum likelihood estimation interface, internally calls C++ library
- network: Neural Network Architectures, notably ResNet, MobileNetV3 and MobileOne
- search: Interface for different Search algorithms. Notable implementations are MCTS, Fixed Depth Search, Iterative Deepening and SM-OOS. All variants have standard interface for selection, expansion, backup and extraction functions.
- supervised: Code for supervised training. Includes optimization, loss computation and annealing.
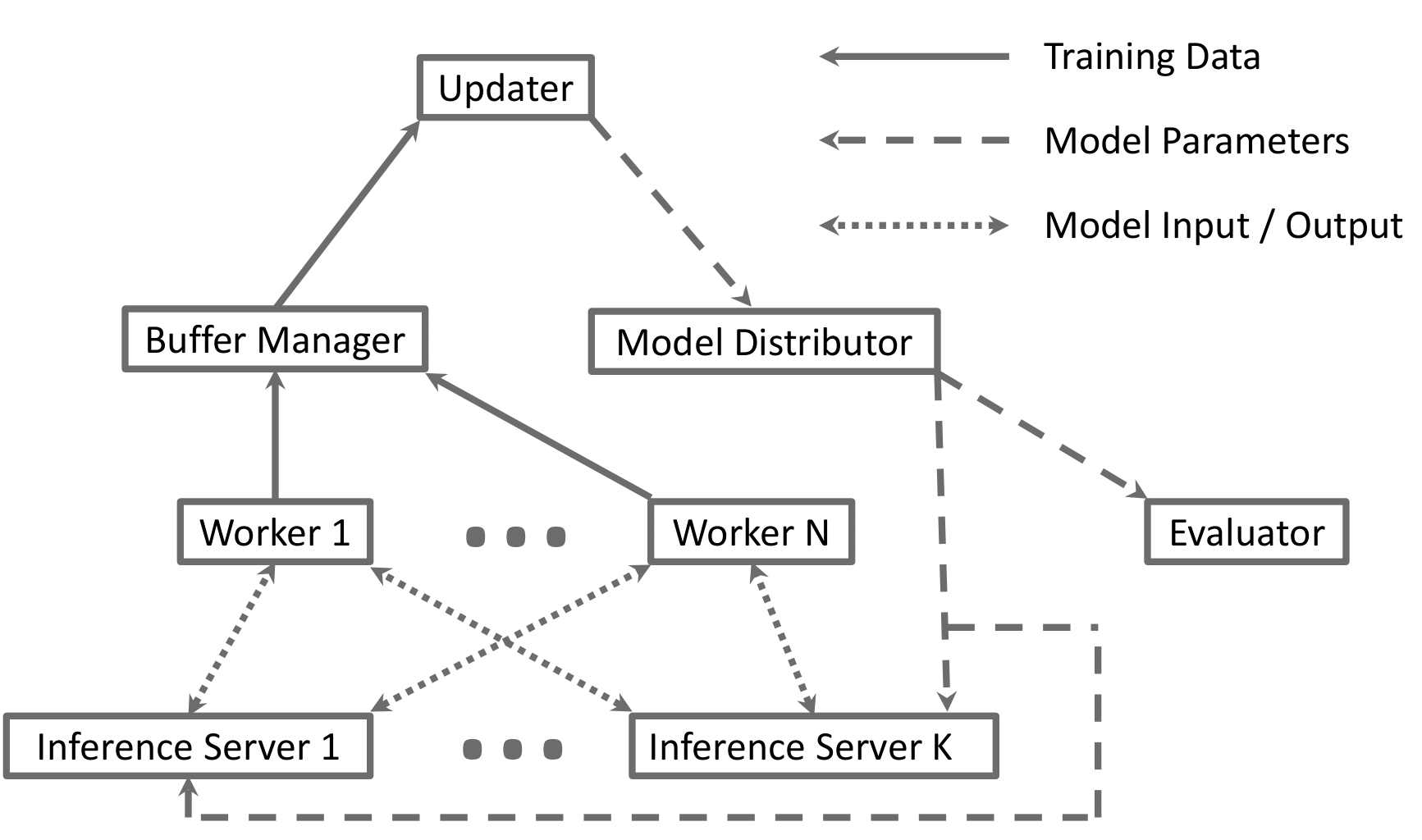
- trainer: Parallelized training framework for reinforcement learning. See description above.
All of the trained Albatross and AlphaZero models can be found in the "trained_models" folder. For overcooked, we use the following naming abbreviations:
- aa: Asymmetric Advantage
- cc: Counter Circuit
- fc: Forced Coordination
- co: Coordination Ring
- cr: Cramped Room
The battlesnake models are abbreviated by the scheme "{Number of Players}{(non)-deterministic}{grid_size}". You can create an Agent with a trained Albatross-Model in the following manner:
net_path = Path(__file__).parent / 'trained_models' / 'battlesnake'
seed = 0
resp_path = net_path / f'4nd7_resp_{seed}.pt'
proxy_path = net_path / f'4nd7_proxy_{seed}.pt'
net = get_network_from_file(resp_path)
alb_network_agent_cfg = NetworkAgentConfig(
net_cfg=net.cfg,
temperature_input=True,
single_temperature=False,
)
alb_online_agent_cfg = AlbatrossAgentConfig(
num_player=4,
agent_cfg=alb_network_agent_cfg,
device_str='cpu',
response_net_path=str(resp_path),
proxy_net_path=str(proxy_path),
noise_std=None,
num_samples=1,
init_temp=5,
)
alb_online_agent = AlbatrossAgent(alb_online_agent_cfg)
Games are also created by specifying a game config and the creating the game. Most game modes have a predefined game config (see src/game/battlesnake/bootcamp), but feel free to create new game modes as desired:
game_cfg = survive_on_7x7_4_player()
game = get_game_from_config(game_cfg)
Baseline-Search agents can be used for evaluation and are constructed as:
base_agent_cfg = AreaControlSearchAgentConfig()
base_agent_cfg.search_cfg.eval_func_cfg = SymmetricAreaControlEvalConfig()
base_agent = get_agent_from_config(base_agent_cfg)
In the "scripts"-folder, you can find many examples on how to use the Albatross-Agents. Additionally, there are examples on how to train Albatross, if you want to use it in different games. This might require writing a wrapper for the new game, which adheres to the Game interface in this repository (see src/game/game.py)