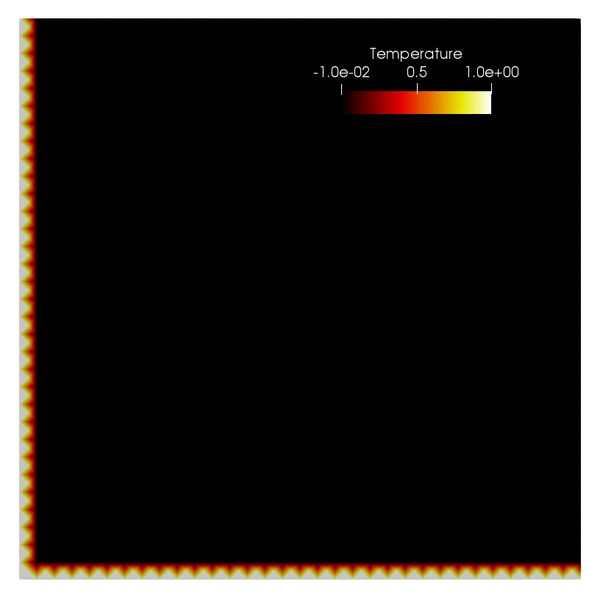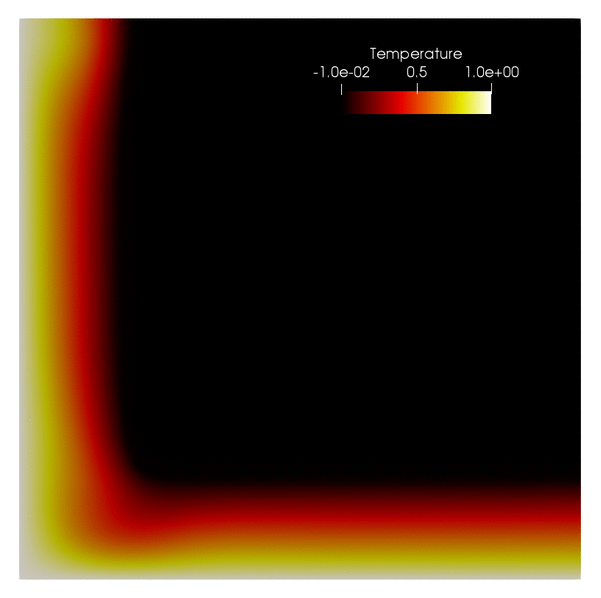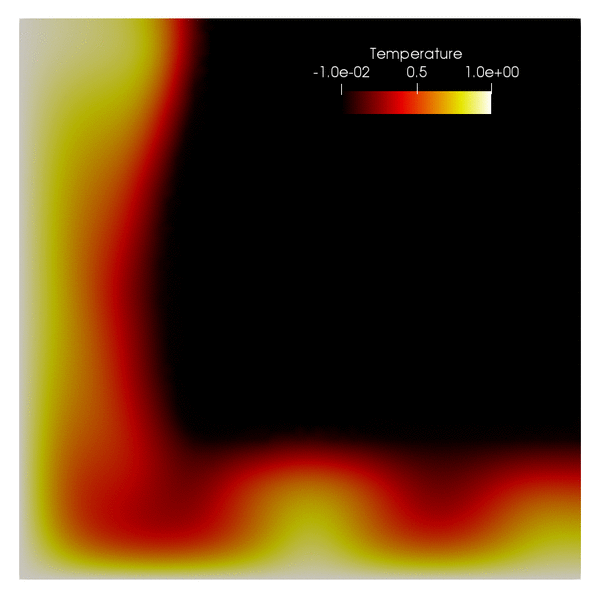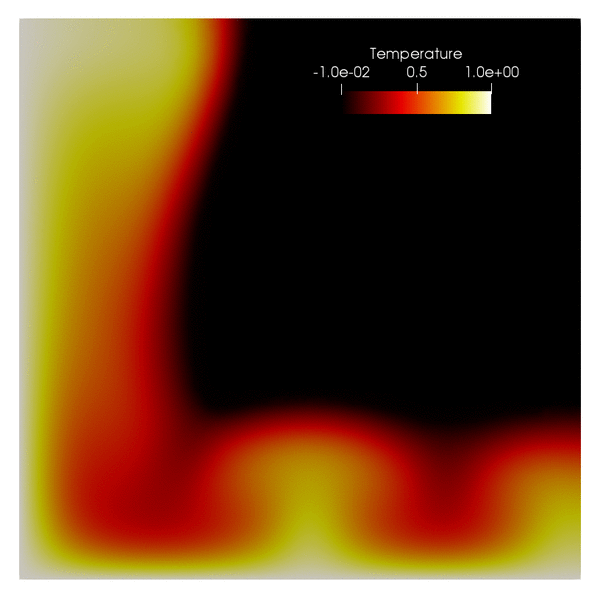
phaseflow-fenics
Phaseflow simulates the convection-coupled melting and solidification of phase-change materials (PCM's). We adopt an enthalpy-based, single-domain semi-phase-field, finite element method, with monolithic system coupling and global Newton linearization. The governing equations are composed of
- Incompressible flow driven by buoyancy: unsteady Navier-Stokes mass and momentum with Boussinesq approximation
- Convection-diffusion of the enthalpy field, with an enthalpy source term accounting for the latent heat of the phase-change material
Features include
- An extensible Python class for time-dependent simulations
- Checkpointing/restarting using HDF5
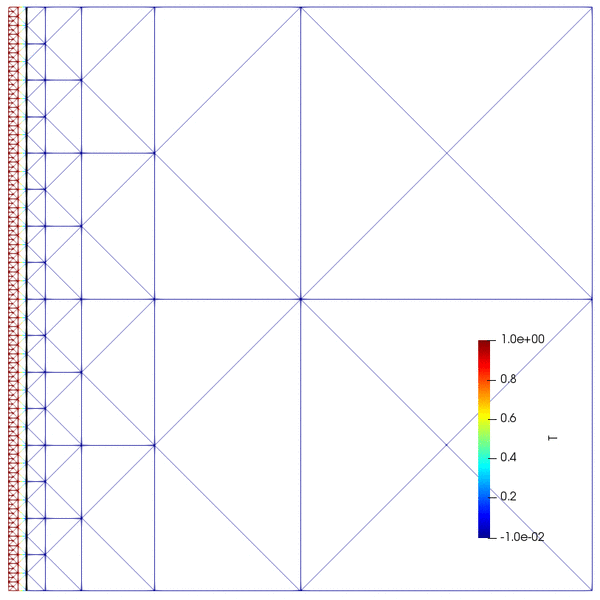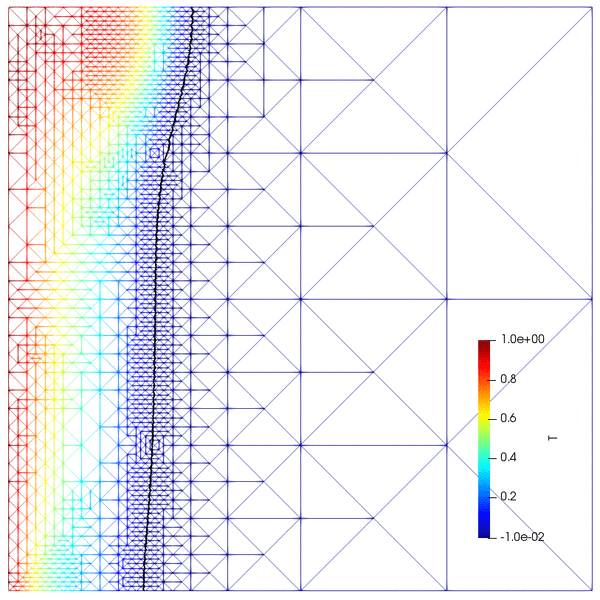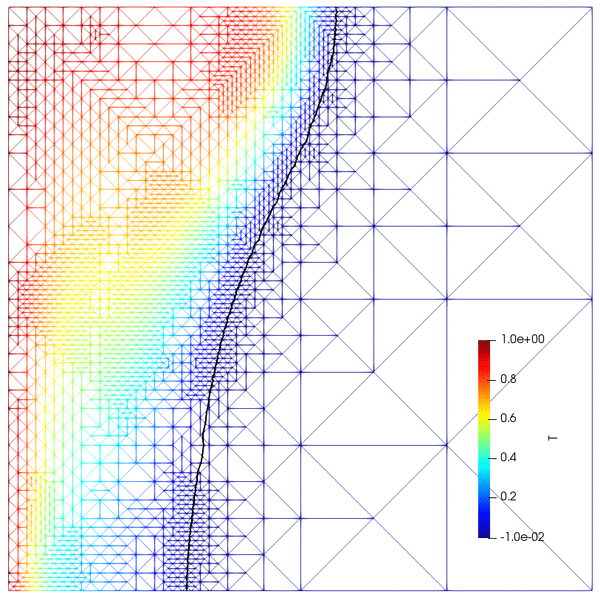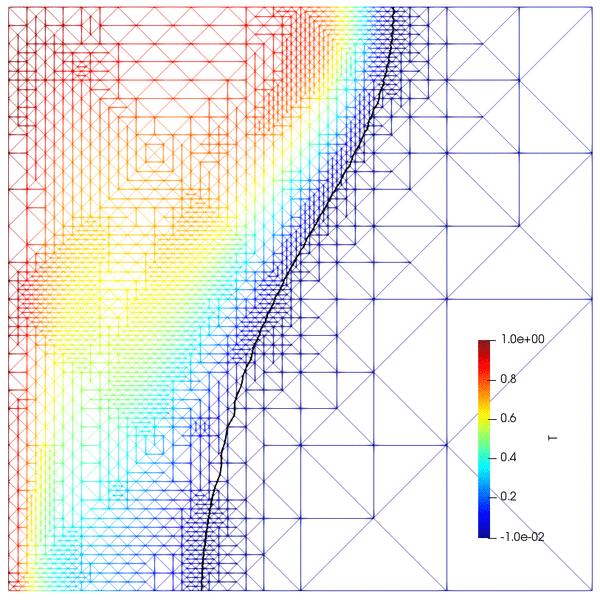
- Goal-oriented adaptive mesh refinement (AMR)
- Coarsening of time-dependent meshes via re-meshing and projection
Phaseflow spatially discretizes the PDE's with the finite element method, and to this end uses the Python/C++ finite element library FEniCS. Many other features are provided by FEniCS, including the nonlinear (Newton) solver, goal-oriented adaptive mesh refinement, and solution output to HDF5, among others.
We present the mathematical model, the numerical methods, the Phaseflow implementation and its verification in an accepted proceedings paper, Monolithic simulation of convection-coupled phase-change - verification and reproducibility. Per the MIT license, you are free to use this code as you wish; but please do cite our paper if this is reasonable.
Author: Alexander G. Zimmerman alexander.zimmerman@aices.rwth-aachen.de
Benchmark results
- Lid-driven cavity
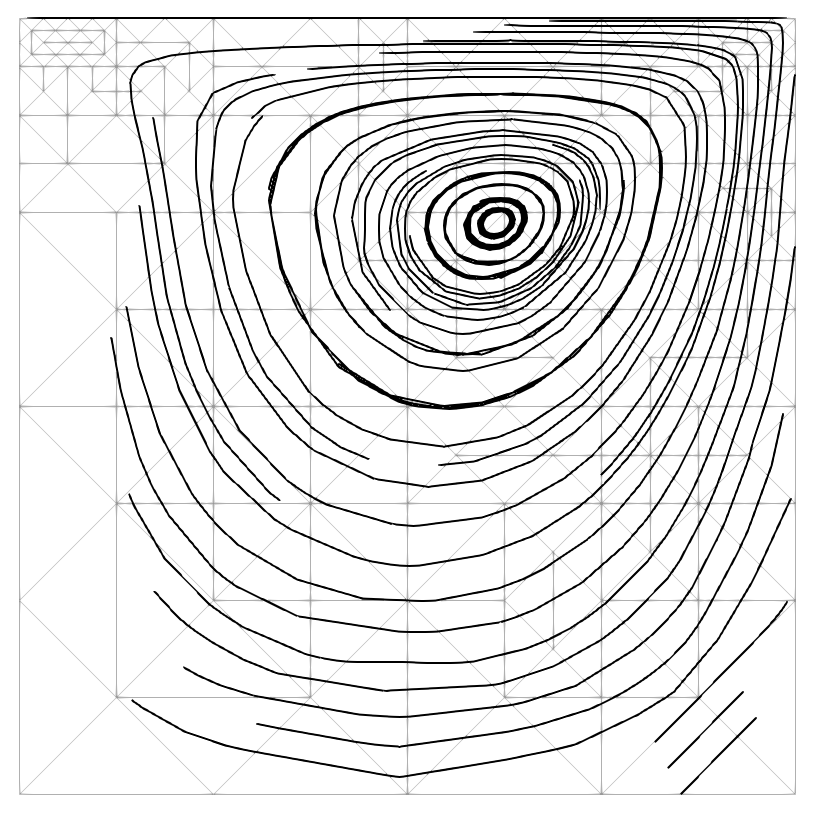
- Heat-driven cavity
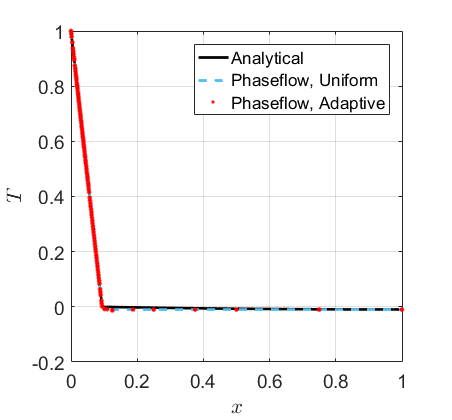
- Stefan problem
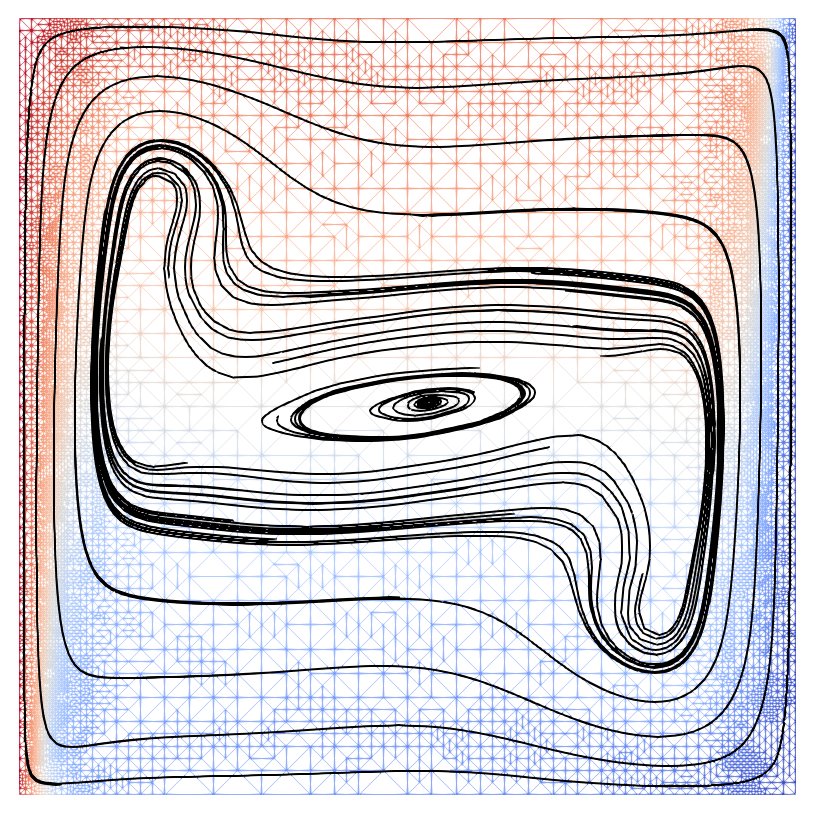
- Convection-coupled melting of an octadecane PCM
For users:
Run Phaseflow on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
Install FEniCS.
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:fenics-packages/fenics
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends fenics
Clone Phaseflow's git repository.
git clone https://github.com/geo-fluid-dynamics/phaseflow-fenics.git
Run some of the tests.
python3 -m pytest -v -s -k "lid_driven_cavity" phaseflow-fenics
Pro tip: Windows 10 now has the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Go to the Microsoft Store and Search "Ubuntu". As of this writing, this gives you a native installation of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, and this works wonderfully well with FEniCS and Phaseflow.
Run Phaseflow in Docker (e.g. on Windows, Mac, many Linux distributions)
The FEniCS project provides a Docker image with FEniCS and its dependencies already installed. See their "FEniCS in Docker" manual.
Get the free community edition of Docker.
Pull the Docker image and run the container, sharing a folder between the host and container.
docker run -ti -v $(pwd):/home/fenics/shared --name fenics quay.io/fenicsproject/stable:latest
Install missing dependencies.
pip3 install --user h5py
Clone Phaseflow's git repository.
git clone https://github.com/geo-fluid-dynamics/phaseflow-fenics.git
Run some of the tests.
python3 -m pytest -v -s -k "lid_driven_cavity" phaseflow-fenics
Visualizing results
While FEniCS has some nice standard visualization options inline using Python, Phaseflow (using built-in methods in FEniCS) typically writes solutions to the XDMF format, which stores the data using HDF5 and adds an XML interface so that the data can be properly parsed by common open-source visualization tools (e.g. ParaView or VisIt).
For developers:
Project structure
This project mostly follows the structure suggested by The Hitchhiker's Guide to Python.
Guidelines
Mostly we try to follow PEP proposed guidelines, e.g. The Zen of Python (PEP 20), and do not ever from fenics import * (PEP 8).