This project implements neural network for semantic segmentation in Tensorflow .
The main file of the project is convolutional_autoencoder.py, which contains code for dataset processing (class Dataset), model definition (class Model) and also code for training.
To abstract layers in the model, we created layer.py class interface. This class has currently two implementations: conv2d.py and max_pool_2d.py.
To infer on the trained model, have a look at infer.py file.
Finally, there are several folders:
- data* contain preprocessed dataset (Please note that current model implementation is supposed to work with at least 128x128 images.)
- imgaug contains code for data augmentation (https://github.com/aleju/imgaug)
- noteboks contains some interesting image segmentation ipython notebooks
There are many neural network architectures for semantic image segmentation (to have some basic overview, you can read project_summary.pdf), but most of them use convolutional encoder-decoder architecture.

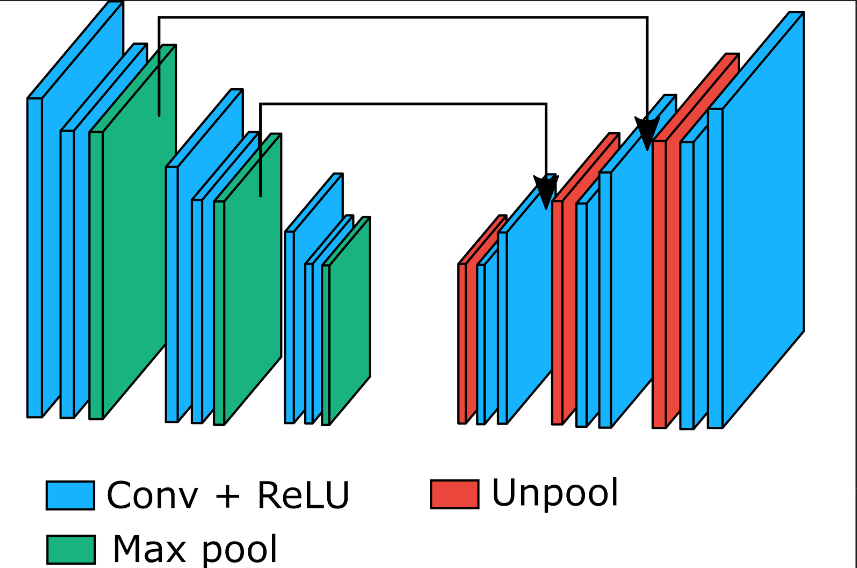
Encoder in these networks has in many cases structure similar to some image classification neural network (e.g. vgg-16). Layers in the decoder are then ussualy inverse to layers used in the encoder (e.g. for convolution that makes its input smaller, we use deconvolution; for max_pool we use some form of "demax_pool").
Inspired by previous success of convolutional encoder-decoder architectures, we decided to implement it as well. In the encoder part, we use three similar "modules", each consisting of convolution layer with stride 2 followed by convolutution layer with stride 1 and no-overlapping max_pool with kernel 2. The decoder section then for each layer in the encoder contains its "counter-part" (network output dimension == input dimension):
- for no-shrinking convolution layer use the same layer
- for shrinking convolution layer use transposed deconvolution with same arguments
- for max pool layer use nearest neighbour upsampling (tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor)
We also found that adding skip-links from encoder to decoder makes the model perform better (~1%).
*Convolutional encoder-decoder architecture used in this project*This project uses publicly available dataset of faces: http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/part_labels. The repository contains three versions of this dataset differing in the image resolution (28x28, 128x128, 250x250).
The original dataset consists of three target categories (face, hair, background). To make the segmentation easier, we decided to create two subsets of original targets: one containing merged hair and background classes("targets_face_only") and other containing merged hair and face classes("targets").
We experimented with several architectures (some of them are mentioned in project_summary.pdf). Even though original images are RGB, we decided to use them in grayscale. The best performance we managed to achieve on 128x128 images was 97.36% in means of per-pixel accuracy.
*Sample results of the best model segmentation. The first row contains input faces, second ground truth image segmentation, third model output and the fourth row shows thresholded model output*- Python 3.5
- Tensorflow > 1.0
- Opencv 3.x
-
Tensorflow:
- FCN implementation: https://github.com/MarvinTeichmann/tensorflow-fcn
- SegNet implementation: https://github.com/tkuanlun350/Tensorflow-SegNet
- Some interesting segmentation notebooks: https://github.com/warmspringwinds/tensorflow_notes
-
Papers:
- Fully convolutional networks (Nov 14) : https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~jonlong/long_shelhamer_fcn.pdf
- SegNet: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.00561.pdf
- DeconvNet (May 15): https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.04366v1.pdf
- DeepLab-LargeFOV (Dec 14): https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.7062v4.pdf