AutoGenU for Jupyter
Introduction
This project provides the continuation/GMRES method (C/GMRES method) based solvers for nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) and an automatic code generator for NMPC, called AutoGenU.
The following C/GMRES based solvers are provided:
ContinuationGMRES: The original C/GMRES method (single shooting).MultipleShootingCGMRES: The multiple shooting based C/GMRES method with condensing of the state and the Lagragne multipliers with respect to the state equation.MSCGMRESWithInputSaturation: The multiple shooting based C/GMRES method with condensing of the state, the Lagragne multipliers with respect to the state equation, and variables with respect to the constraints on the saturation function on the control input.
Requirement
- C++11 (MinGW or MSYS and PATH to either are required for Windows users)
- CMake
- Python 3.6 or later, Jupyter Lab or Jupyter Notebook, SymPy (to generate
nmpc_model.hpp,nmpc_model.cpp,main.cpp, andCMakeLists.txtbyAutoGenU.ipynb) - Python 3.6 or later, NumPy, Matplotlib, seaborn (to plot simulation data on
AutoGenU.ipynb) - ffmpeg (to generate animations in
pendubot.ipynb,cartpole.ipynb,hexacopter.ipynb, andmobilerobot.ipynb)
Usage
AutoGenU
AutoGenU.ipynb generates following source files under your setting state equation, constraints, cost function, and parameters:
nmpc_model.hppnmpc_model.cppmain.cppCMakeLists.txt
You can also build source files for numerical simulation, execute numerical simulation, and plot or save simulation result on AutoGenU.ipynb.
C/GMRES based solvers of NMPC
The C/GMRES based solvers in src/solver directory can be used independently of AutoGenU.ipynb. You are then required the following files:
nmpc_model.hpp: write parameters in your modelnmpc_model.cpp: write equations of your modelmain.cpp: write parameters of solvers
In addition to these files, you have to write CMakeLists.txt to build source files.
Demos
Demos are presented in pendubot.ipynb, cartpole.ipynb, hexacopter.ipynb, and mobilerobot.ipynb. You can obtain the following simulation results jusy by runnig these .ipynb files. The details of the each models and formulations are described in each .ipynb files.
Pendubot
Inverting a pendubot using MSCGMRESWithInputSaturation solver.
Cartpole
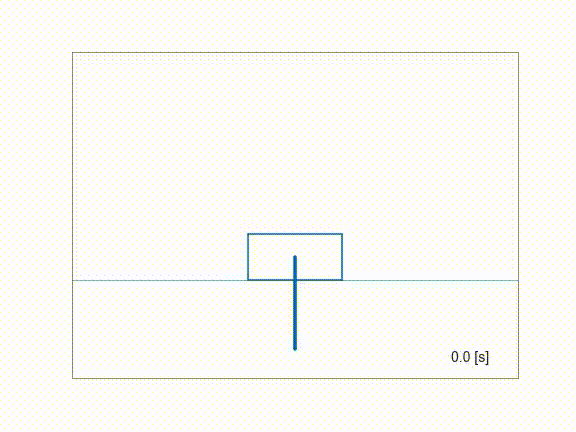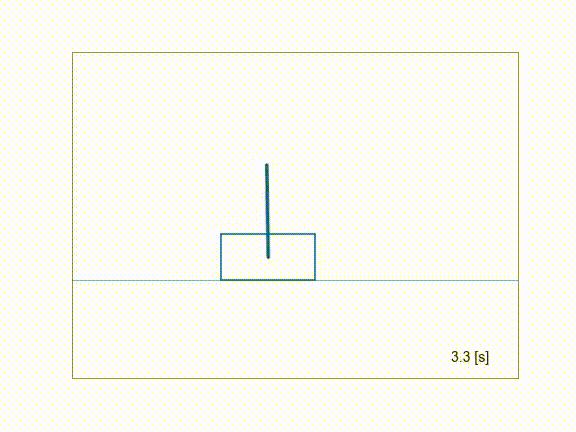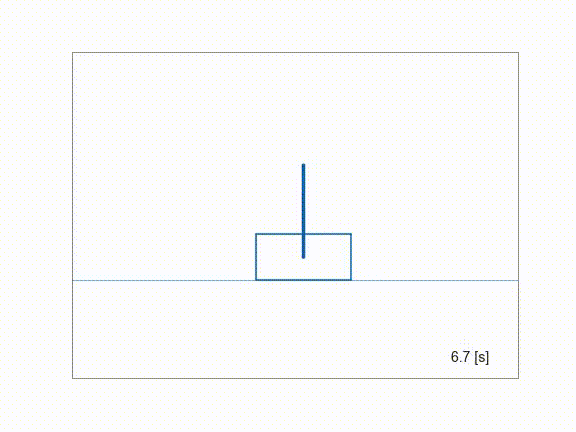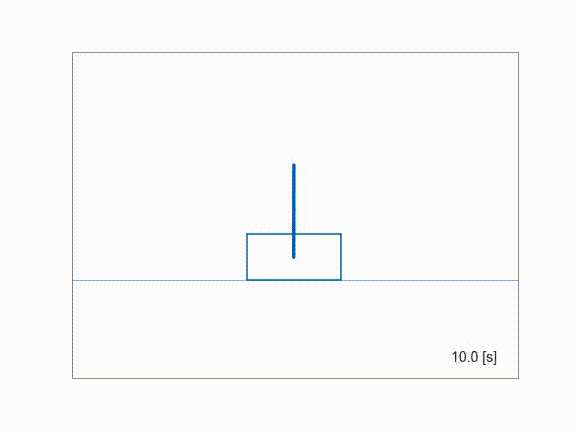
Inverting a cartpole using ContinuationGMRES solver.
Hexacopter
Trajectory tracking of a hexacopter using MultipleShootingCGMRES solver.
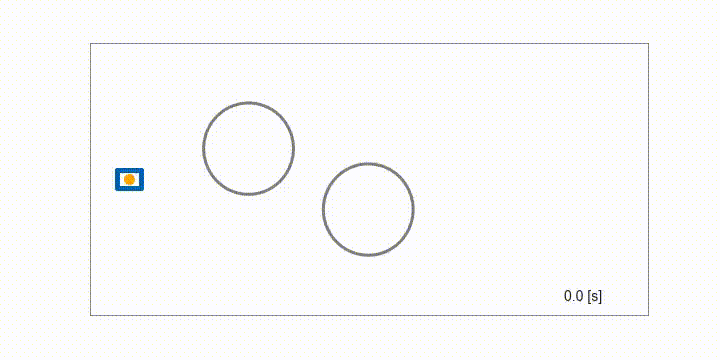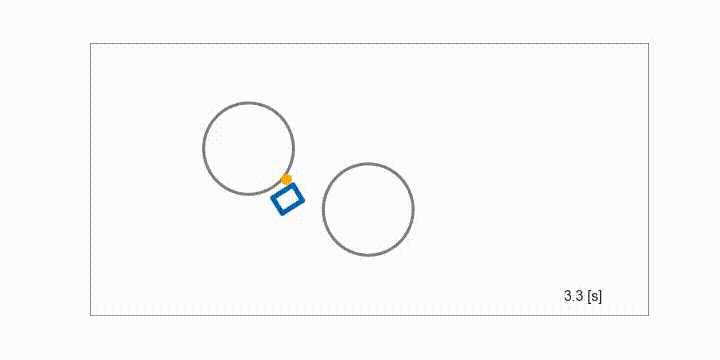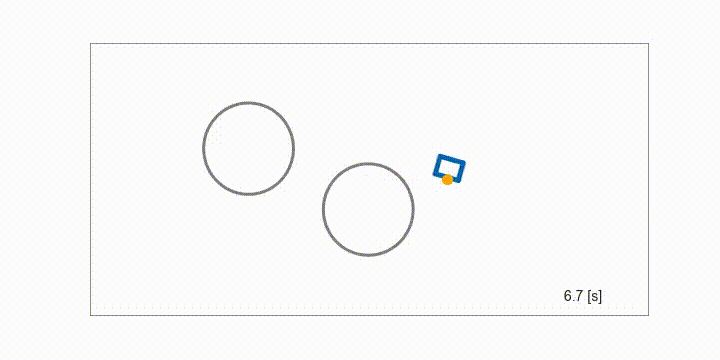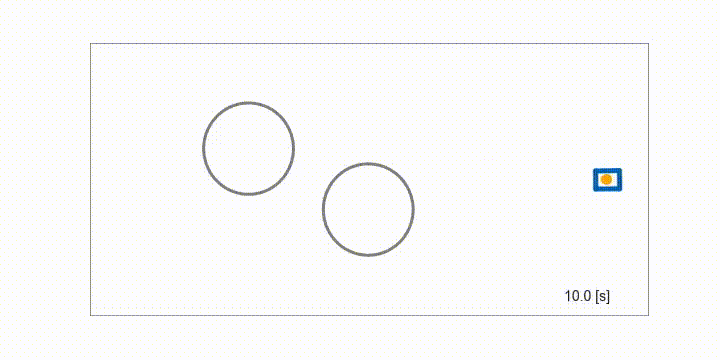
Mobile robot
Obstacle avoidance of a mobile robot using MultipleShootingCGMRES solver with the semi-smooth Fischer-Burmeister method for inequality constraints.
License
MIT
References
- T. Ohtsuka A continuation/GMRES method for fast computation of nonlinear receding horizon control, Automatica, Vol. 40, No. 4, pp. 563-574 (2004)
- C. T. Kelly, Iterative methods for linear and nonlinear equations, Frontiers in Apllied Mathematics, SIAM (1995)
- Y. Shimizu, T. Ohtsuka, M. Diehl, A real‐time algorithm for nonlinear receding horizon control using multiple shooting and continuation/Krylov method, International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, Vol. 19, No. 8, pp. 919-936 (2008)



