Now in experimental release, suggestions welcome.
Youjiang Xu, Yahong Han, Richang Hong, Qi Tian. "Sequential Video VLAD: Training the Aggregation Locally and Temporally." IEEE TIP, 2018, DOI:10.1109/TIP.2018.2846664. [Paper]
@inproceedings{Xu2018Sequential,
author = {Youjiang Xu and Yahong Han and Richang Hong and Qi Tian},
title = {Sequential Video VLAD: Training the Aggregation Locally and Temporally},
booktitle = {IEEE TIP},
year = {2018},
}
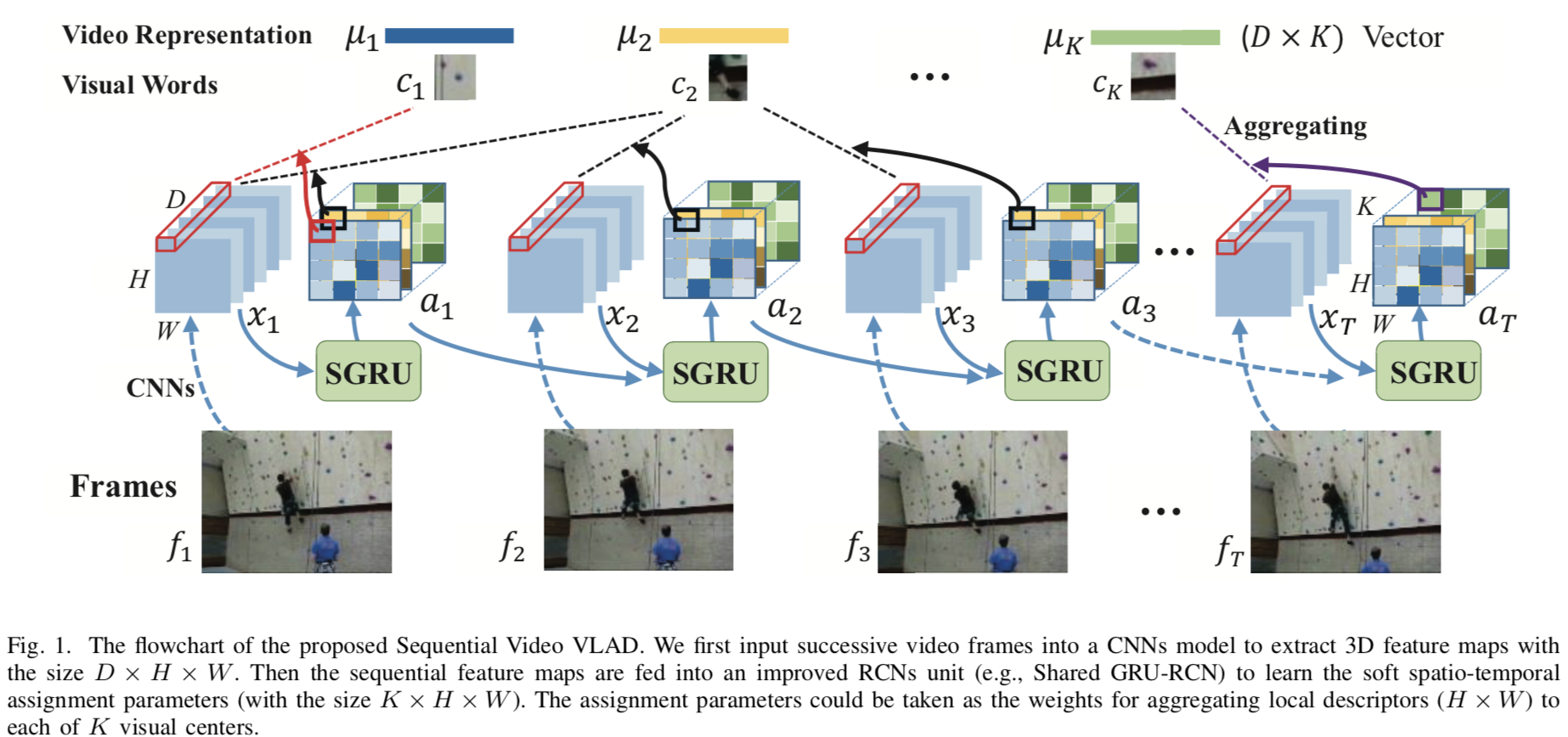
This is an implementation of Sequential VLAD (SeqVLAD) in PyTorch.
Note: always use git clone --recursive https://github.com/youjiangxu/seqvlad-pytorch to clone this project.
Otherwise you will not be able to use the inception series CNN archs.
The split files in ./data/hmdb51_splits/ are provided by ActionVLAD. They renamed the filename to avoid issues with special characters in the filenames. More details can be seen here
To train a new model, we can use the main.py script.
We can utilize the following bash script to train the SeqVLAD with RGB inputs on the split 1 of HMDB51 :
split=1
timesteps=25
num_centers=64
lr=0.02
dropout=0.8
first_step=80
second_step=150
total_epoch=210
two_steps=120
optim=SGD
prefix=hmdb51_rgb_split${split}
python ./main.py hmdb51 RGB ./data/hmdb51_splits/train_split${split}.txt ./data/hmdb51_splits/test_split${split}.txt \
--arch BNInception \
--timesteps ${timesteps} --num_centers ${num_centers} --redu_dim 512 \
--gd 20 --lr ${lr} --lr_steps ${first_step} ${second_step} --epochs ${total_epoch} \
-b 64 -j 8 --dropout ${dropout} \
--snapshot_pref ./models/rgb/${prefix} \
--sources <path to source rgb frames of hmdb51> \
--two_steps ${two_steps} \
--activation softmax \
--optim ${optim}When training with Flow inputs, it can be:
split=1
timesteps=25
num_centers=64
lr=0.01
dropout=0.7
first_step=90
second_step=180
third_step=210
total_epoch=240
two_steps=120
optim=SGD
prefix=hmdb51_flow_split${split}
python /mnt/lustre/xuyoujiang/action/seqvlad-pytorch/main.py hmdb51 Flow ./data/hmdb51_splits/train_split${split}.txt ./data/hmdb51_splits/test_split${split}.txt \
--arch BNInception \
--timesteps ${timesteps} --num_centers 64 --redu_dim 512 \
--gd 20 --lr ${lr} --lr_steps ${first_step} ${second_step} --epochs ${total_epoch} \
-b 64 -j 8 --dropout ${dropout} \
--snapshot_pref ./models/flow/${prefix} \
--sources <path to source optical frame of hmdb51> \
--resume <path to tsn flow pretrained model> \
--resume_type tsn --two_steps ${two_steps} \
--activation softmax \
--flow_pref flow_ \
--optim ${optim}For the Flow stream, we utilized the tsn pretrained model to initialize our model. Thus, we release the pretrained tsn models to reproduct our method easily. The pretrained models are released as follows: (the models are reimplemented by us, but not the official models.)
| Model | Modality | Split | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMDB51 | RGB | 1 | hmdb51_bninception_split1_rgb_model_best.pth |
| HMDB51 | RGB | 2 | hmdb51_bninception_split2_rgb_model_best.pth |
| HMDB51 | RGB | 3 | hmdb51_bninception_split3_rgb_model_best.pth |
| HMDB51 | Flow | 1 | hmdb51_bninception_split1_flow_model_best.pth |
| HMDB51 | Flow | 2 | hmdb51_bninception_split2_flow_model_best.pth |
| HMDB51 | Flow | 3 | hmdb51_bninception_split3_flow_model_best.pth |
After training, there will checkpoints saved by pytorch, for example hmdb51_rgb_split1_checkpoint.pth.
Use the following command to test its performance in the standard TSN testing protocol:
python test_models.py hmdb51 RGB ./data/hmdb51_splits/test_split${split}.txt \
hmdb51_rgb_split1_checkpoint.pth \
--arch BNInception \
--save_scores seqvlad_split1_rgb_scores \
--num_centers 64 \
--timesteps 25 \
--redu_dim 512 \
--sources <path to source rgb frames of hmdb51> \
--activation softmax \
--test_segments 1Or for flow models:
python test_models.py hmdb51 Flow ./data/hmdb51_splits/test_split${split}.txt \
hmdb51_flow_split1_checkpoint.pth \
--arch BNInception \
--save_scores seqvlad_split1_flow_scores \
--num_centers 64 \
--timesteps 25 \
--redu_dim 512 \
--sources <path to source optical frames of hmdb51> \
--activation softmax \
--test_segments 1 \
--flow_pref flow_If you're only looking for our final last-layer features that can be combined with your method, we provide those for the following dataset:
./logits/hmdb51/For example, you can use the following command to merge two modality results (e.g., RGB+Flow) and obtain the final accuracy on HMDB51 split1.
python ./merge_hmdb.py --rgb ./logits/hmdb51/hmdb51_rgb_split1.npz --flow ./logits/hmdb51/hmdb51_flow_split1.npzThe performance (accuracy) of the seqvlad on HMDB51 is as follows:
| Split | RGB | Flow | RGB+Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 55.23 | 65.36 | 72.88 |
| 2 | 54.31 | 74.77 | 70.39 |
| 3 | 53.66 | 65.49 | 71.18 |
| Average | 54.4 | 65.20 | 71.48 |
Note: We first build our SeqVLAD on the repository of old-seqvlad-pytorch, which is folked from tsn-pytorch. And in order to reproduct our method easily, we release the source code in this repository SeqVLAD-Pytorch.
- 2018-05-11 upload the pretrained tsn model, add logits.