The goal of this repository is to enable real time super resolution for upsampling low resolution videos. Currently, the design follows the SR-GAN architecture. But instead of residual blocks, inverted residual blocks are employed for parameter efficiency and fast operation. This idea is somewhat inspired by Real time image enhancement GANs.
The training setup looks like the following diagram:
The following runtimes/fps are obtained by averaging runtimes over 800 frames. Measured on a GTX 1080.
| Input Image Size | Output Size | Time (s) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128x128 | 512x512 | 0.019 | 52 |
| 256x256 | 1024x1024 | 0.034 | 30 |
| 384x384 | 1536x1536 | 0.068 | 15 |
We see it's possible to upsample to 720p at around 30fps.
This was tested on Python 3.7. To install the required packages, use the provided requirements.txt file like so:
pip install -r requirements.txtA pretrained generator model on the DIV2k dataset is provided in the 'models' directory. It uses 6 inverted residual blocks, with 32 filters in every layer of the generator.
Upsampling is done via phase shifts in the low resolution space for speed.
To try out the provided pretrained model on your own images, run the following:
python infer.py --image_dir 'path/to/your/image/directory' --output_dir 'path/to/save/super/resolution/images'To train, simply execute the following command in your terminal:
python main.py --image_dir 'path/to/image/directory' --hr_size 384 --lr 1e-4 --save_iter 200 --epochs 10 --batch_size 14Model checkpoints and training summaries are saved in tensorboard. To monitor training progress, open up tensorboard by pointing it to the 'logs' directory that will created when you start training.
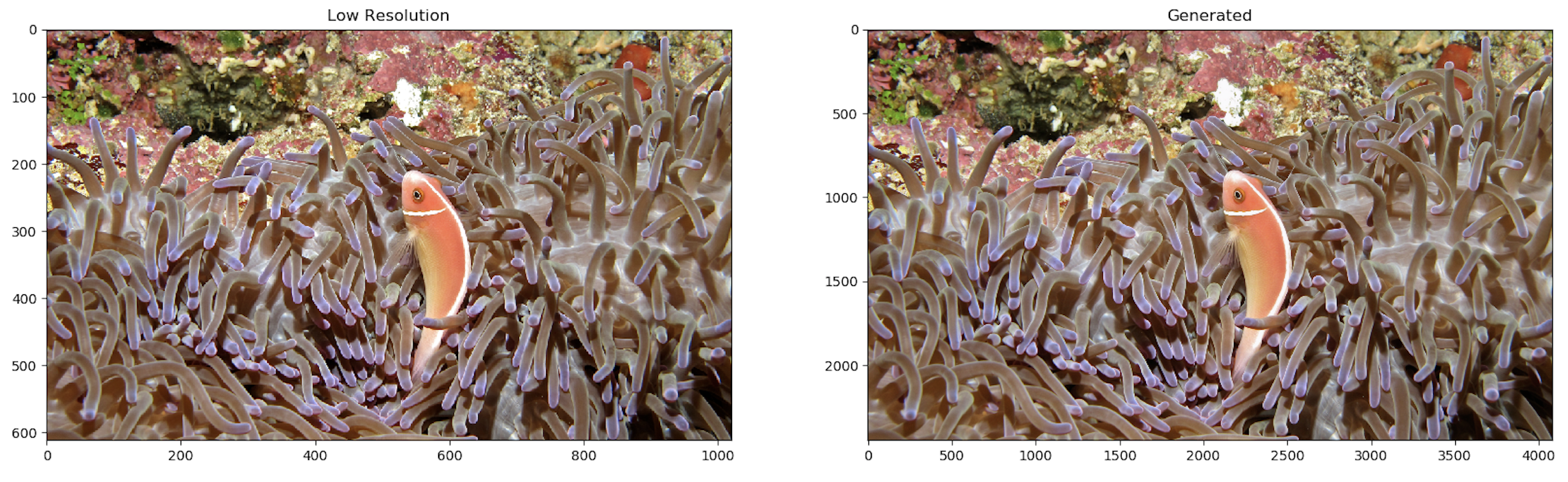
Following are some results from the provided trained model. Left shows the low res image, after 4x bicubic upsampling. Middle is the output of the model. Right is the actual high resolution image.
384x384 to 1536x1536 Upsampling
 256x256 to 1024x1024 Upsampling
256x256 to 1024x1024 Upsampling
 128x128 to 512x512 Upsampling
128x128 to 512x512 Upsampling

Upsampling HQ images 4x as a check to see the image is not destroyed (since the network is trained on low quality, it should also upsample high quality images while preserving their quality).
The provided model was trained on 384x384 inputs, but to run it on inputs of arbitrary size, you'll have to change the input shape like so:
from tensorflow import keras
# Load the model
model = keras.models.load_model('models/generator.h5')
# Define arbitrary spatial dims, and 3 channels.
inputs = keras.Input((None, None, 3))
# Trace out the graph using the input:
outputs = model(inputs)
# Override the model:
model = keras.models.Model(inputs, outputs)
# Now you are free to predict on images of any size.If you have ideas on improving model performance, adding metrics, or any other changes, please make a pull request or open an issue. I'd be happy to accept any contributions.