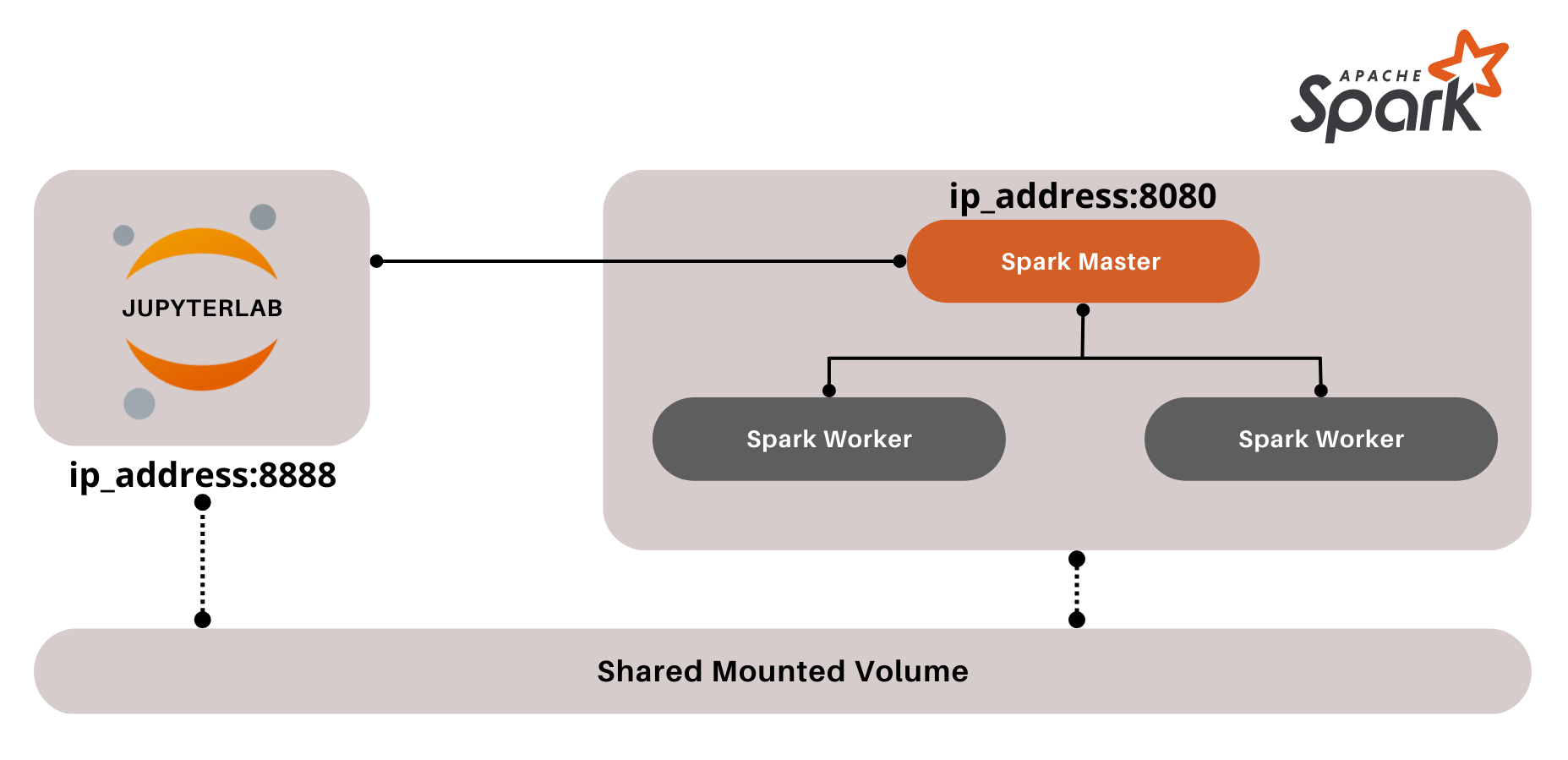
The four components which make up the cluster are the JupyterLab IDE, the Spark master node, and two Spark worker nodes.
The user is able to access the master node using the GUI provided by Jupyter notebooks, and is able to submit Spark commands. The master node then takes the input, distributes the workload to the workers nodes, and sends the results back to the IDE.
All the components are connected through a network, and data is shared between them through a shared mounted volume.
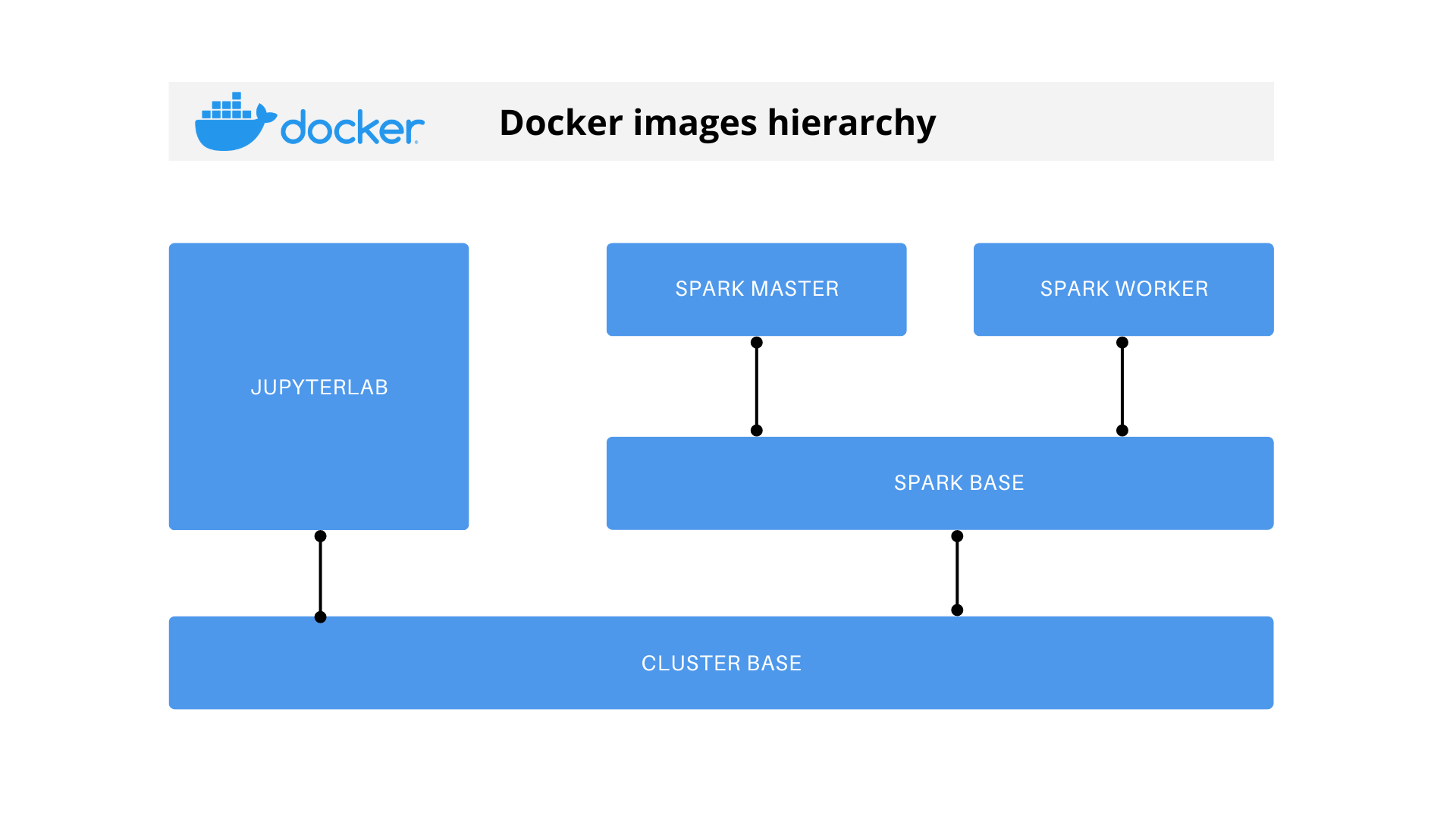
We need to create, build and compose the Docker images for JupyterLab and Spark nodes to make the cluster. We will use the following Docker image hierarchy:
We can get images from Docker Hub: https://hub.docker.com/repositories/yahyanjd
Or we can build it from the docker files in the Dockerfiles directory
You can use the following command to build the images using Docker:
make build-dockerOr you can use Podman to build the images with this command:
make build-podmanTo launch the cluster, use one of the following commands:
make run-podman
make run-dockerAnd to stop it, use one of the following commands:
make stop-podman
make stop-docker