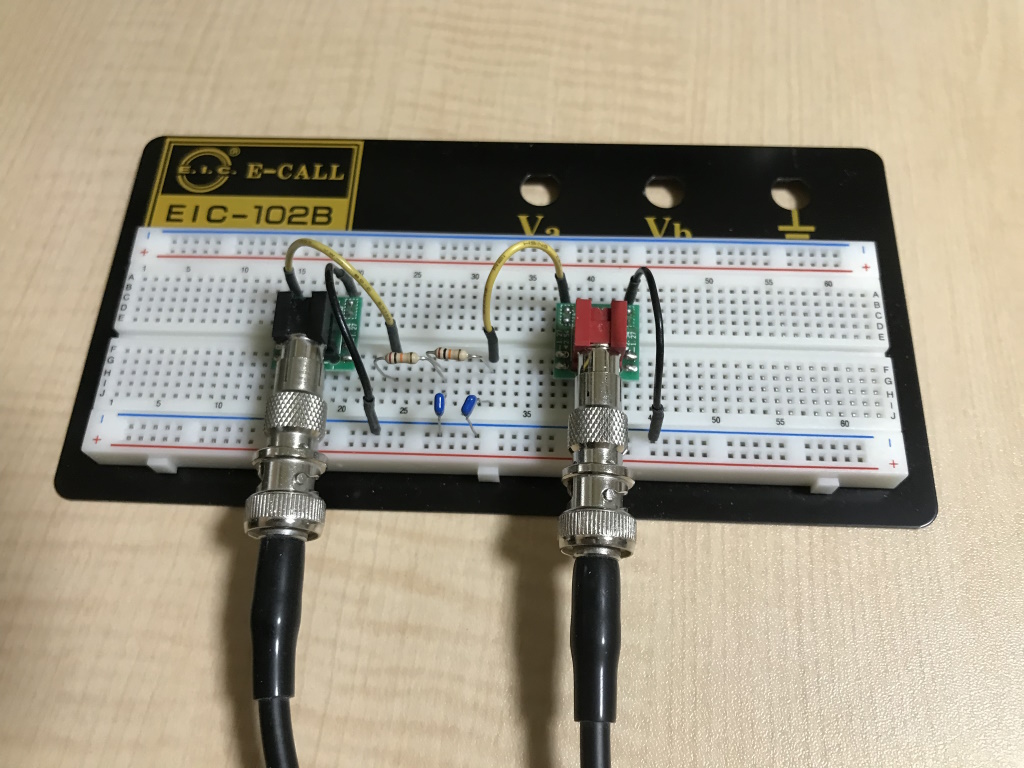
PCのオーディオインターフェースを利用してオーディオシステムの周波数特性を解析するためのシンプルなツールです。振幅と位相の応答を得るために、2種類の測定方法を用意しています。
This is a simple tool for analyzing the frequency response of audio systems using the PC's audio interface. Two measurement methods are available to obtain amplitude and phase responses.
- IR methods
- using pure impulses
- using Linear Swept-Sine (OATSP)
- using Log Swept-Sine (Pink TSP)
- using MLS
- Stepped Sweep method
Implemented with JUCE.
- JUCE framework 7.0.4: download, repository
- Projucer: download, or build from source
- C++ build tools: Visual Studio, Xcode, etc.
- ASIO SDK (optional, Windows only): https://www.steinberg.net/developers/
- Open the .jucer file with the Projucer.
- Correct the JUCE module path and properties, add exporters and save.
- Build the generated C++ projects.
CC0 1.0 Universal
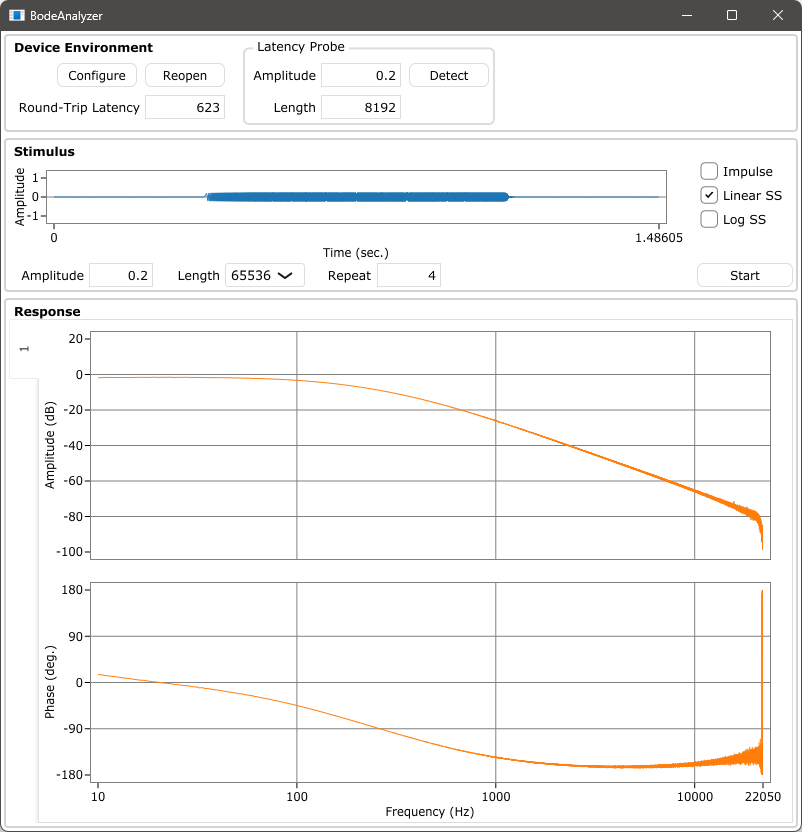
時間の遅れは位相の遅れとして測定されるので、システムの往復レイテンシを正確に把握することは重要です。この機能では、探査信号と応答信号の相互相関関数を求めることによってターゲットシステムを経由した往復レイテンシを特定します。探査信号として非周期的な乱数列を使用します。
Since time delay is measured as a phase delay, it is important to determine the precise round-trip latency of the system. This function identifies the round-trip latency through the target system by determining the cross-correlation function between the probe signal and the response signal. An acyclic random number sequence is used as the probe signal.
fig. Latency Probe processing flow diagram
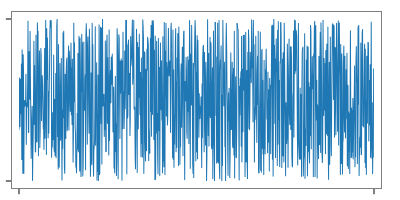 fig. random number sequence as plobe signal (a)
fig. random number sequence as plobe signal (a)
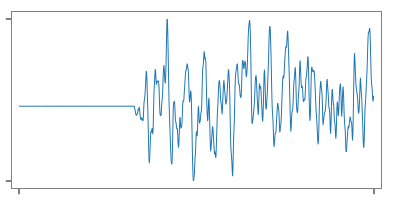 fig. delayed and deformed response signal (b)
fig. delayed and deformed response signal (b)
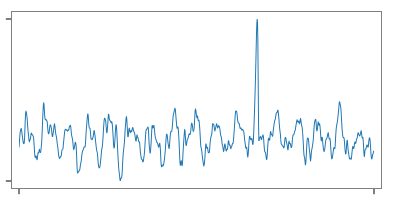 fig. obtained correlation function (c)
fig. obtained correlation function (c)
この手法では、Swept-Sineと呼ばれる刺激信号を使用してターゲットシステムのインパルス応答を求め、それを変換することで周波数応答を得ます。Swept-SineはTSP (time stretched pulse)としても知られています。
This method uses a stimulus signal called the Swept-Sine to obtain the impulse response of the target system, and then transforms it to obtain the frequency response. Swept-Sine is also known as TSP (time stretched pulse).
fig. Swept-Sine Method processing flow diagram
definitions:
Linear Swept-Sine (OATSP):
Log Swept-Sine (Pink TSP):
where
Inverse Function:
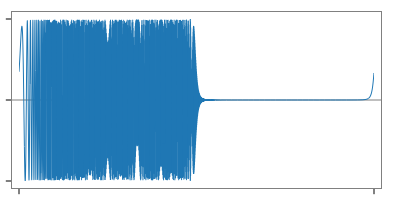 fig. linear tsp signal generated according to the formula
fig. linear tsp signal generated according to the formula
 fig. linear tsp signal with rotation applied
fig. linear tsp signal with rotation applied
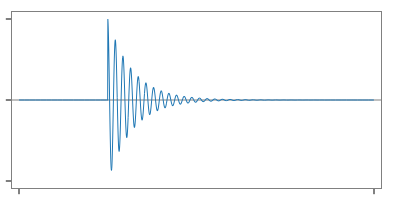 fig. obtained impulse response
fig. obtained impulse response
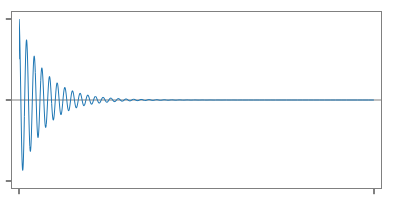 fig. impulse response with rotation applied
fig. impulse response with rotation applied
この手法では、MLS (maximum length sequence, M系列)を刺激信号に使用してターゲットシステムのインパルス応答を求め、それを変換することで周波数応答を得ます。
This method uses the MLS (maximum length sequence, m-sequence) as the stimulus signal to obtain the impulse response of the target system, and then transforms it to obtain the frequency response.
fig. MLS Method processing flow diagram
この手法では、一ステップごとに刺激信号の周波数を変化させ、同期検波によって対応する振幅と位相の応答を逐次測定します。古典的な周波数応答の測定方法です。
測定速度向上のため、LPFのセトリングタイムを最小化しています。また、ナイキスト周波数近傍の特性を改善するため、オーバーサンプリングを施しています。
In this method, the frequency of the stimulus signal is varied at each step, and the corresponding amplitude and phase responses are measured sequentially by synchronous detection. It is a classical frequency response measurement method.
The settling time of the LPF is minimized to improve the measurement speed. And, Oversampling is applied to improve the characteristics near the Nyquist frequency.
fig. Stepped Sweep Method processing flow diagram
現在のところ更なる開発の予定は無いが、あると良さそうな改良点を追記する。
Although there are no plans for further development at this time, I add some improvements that would be nice to have.
- Calibration
測定結果は使用したオーディオインターフェースの特性の影響を受ける。これを補正するためにはループバック特性を測定し、その逆関数をキャリブレーション特性とする。
Measurement results are affected by the characteristics of the audio interface used. To compensate it, measure the loopback response and use the inverse function of it as calibration characteristics.
- Variable plotting range and scale settings
- Export as PDF
etc etc