This application has 3 sub-programs:
sreis used to find potential 'Hive' performance issues caused by small files and excessive partitions.u3is used to review 'Hive 1/2' environments for Hive3 upgrade planning.perfis used to check the throughput of a JDBC connection.
| Sub-Program | Database | Version | Tested | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
u3 |
MySql | 5.6 | Limited | Recommend upgrading 5.7. This is the lower MySql supported env for HDP |
| 5.7 | Yes | |||
| 8.0 | No | Not supported by HDP | ||
| MariaDb | 10.1 | No, but should work as 10.2 does | ||
| 10.2 | Yes | |||
| Postgresql | 9.6 | No, but should work | ||
| 10 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | ||
| 11 | No, but should work at 10 does | |||
| Oracle | 12 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | |
sre |
MySql | 5.6 | Limited | Recommend upgrading 5.7. This is the lower MySql supported env for HDP |
| 5.7 | Partly | Some sre reports use CTE in the SQL, which isn't supported in this version. Those report will error, the other will run fine. |
||
| 8.0 | No | Not supported by HDP | ||
| MariaDb | 10.1 | No, but should work as 10.2 does | ||
| 10.2 | Yes | |||
| Postgresql | 9.6 | No, but should work | ||
| 10 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges | ||
| 11 | No, but should work at 10 does | |||
| Oracle | 12 | Yes | Field Tested, May still be a few rough edges |
Ensure you have the database appropriate driver in the ${HOME}/.hive-sre/aux_libs directory.
I've tried to match supported DB's for HDP 2.6.5 and 3.1.x as much as I could.
Running hive-sre-cli on the command line is an alias to the hadoopcli application here.
It is an interactive HDFS Client Command Line tool.
Included in this application suite is a ping performance tool that you can use to measure cluster host letancy. It is a MapReduce application that uses a list of hosts and will ping those hosts from the MR Map Task and record the results to HDFS.
The MR program take a few options:
usage: hadoop jar <jar-file> com.cloudera.utils.mapreduce.MRPingTool -d <output-dir> -hl <hdfs_host_list_file> [-c <count>] [-m <num_of_mappers>]
-c,--count <arg> Ping Count (The number of iterations we'll run
ping). Each ping request makes 5 pings.
So if this value is 3, we'll do 3 sets of 5 pings
(15 total). Default 5
-d,--directory <arg> Output Directory [REQUIRED]
-h,--help Help
-hl,--host-list <arg> The host list file on HDFS. A text file with a
FQHN (full qualified host name) per
line.[REQUIRED]
-m,--mappers <arg> Number of Mappers. To get coverage, should be
more than the compute node count. But no
guarantee of even distribution, so best to over
subscribe. Default 2
CentOS 7.6 (ping)
The ping output is parsed by the application and other OS/versions may yield different output, which we've not (yet) setup parsing for.
- You've downloaded the Hive setup/ingest/eval scripts
- This has been tested again CentOS 7.
- The user running the MR job has rights in each compute node to run
ping. - That
pingis allowed on the network and not blocked between hosts. - The MR Job is run with the right user credentials and from an Edgenode configured for the target cluster.
- We need the hadoop MR libs to submit the job.
- The user running the job has ACL's that allow them to write to the EXTERNAL db location you create with
ping_ddl.sql. - Build a 'host list' file with ALL the FQHN (fully qualified hostnames) in the cluster that you want to test.
- This is a text file with a single host FQHN per line. Similar to /etc/hosts.
- Place the file (we'll use the name
host_list.txt) in your HDFS home directory.
- We are using the standard EXTERNAL and MANAGED Warehouse locations on HDFS
- PING_DB = ping_perf
- BATCH_ID = 2022-10-22_01
- Run DDL Scripts in Beeline
2.
beeline -f ping_ddl.sql --hivevar PING_DB=ping_perf - Run MR Job, using the expected Partition Directory of the
rawtable as the output. The-mparameter controls the number of 'mappers' created. The intent is to get a map task on every compute node in the cluster. To do that, with perfect distribution (unlikely), you need at least as many mappers as there are compute nodes. We recommend 2-3x that incase some nodes get doubled up. There's no way to ensure every host runs a task, hence the over subscription here. Use the eval report to determine where the gaps where (if any) and run again. 4.hadoop jar /usr/local/hive-sre/lib/hive-sre-shaded.jar com.cloudera.utils.mapreduce.MRPingTool -m 40 -c 3 -hl host_list.txt -d /warehouse/tablespace/external/hive/ping_perf.db/raw/batch_id=2022-10-21_01 - Run the Ingest script in
beeline6.beeline -f ping_ingest.sql --hivevar PING_DB=ping_perf --hivevar BATCH_ID=2022-10-21_01 - Run the eval scripts in
beeline --hivevar PING_DB=ping_perf --hivevar BATCH_ID=2022-10-21_01
USE THE PRE-BUILT BINARY!!! You won't have the necessary dependencies to build this from scratch without downloading and building the 'Hadoop Cli'.
Don't Build, Download the LATEST binary here!!!
On the edgenode:
- Remove previous install directory
rm -rf hive-sre-install - Expand the tarball
tar zxvf hive-sre-dist.tar.gz.This produces a child
hive-sre-installdirectory. - Two options for installation:
- As the root user (or
sudo), runhive-sre-install/setup.sh. This will install thehive-srepackages in/usr/local/hive-sreand create symlinks for the executables in/usr/local/bin. At this point,hive-sreshould be available to all user and in the default path. - As the local user, run
hive-sre-install/setup.sh. This will install thehive-srepackages in$HOME/.hive-sreand create symlink in$HOME/bin. Ensure$HOME/binis in the users path and runhive-sre.
- As the root user (or
DO NOT RUN hive-sre from the installation directory.
If you install both options, your environment PATH will determine which one is run. Make note of this because an upgrade may not be reachable.
This will create and install the hive-sre and hive-sre-cli applications to your path.
Try it out on a host with default configs (if kerberized, get a ticket first):
hive-sre-cli
OR
hive-sre
See the config docs for details.
To ease the launch of the application below, configure these core environment variables.
hive-sre u3|sre -all|-hdp2|-hdp3|-cdh`
NOTE It is NOT necessary to use the -cfg option if your config is $HOME/.hive-sre/cfg/default.
Use the -pkey <password-key> and -p <password-to-encrypt options of hive-sre
hive-sre u3 -pkey cloudera -p have-a-nice-day
Will generate:
...
Encrypted password: HD1eNF8NMFahA2smLM9c4g==
Copy this encrypted password and place it in your configuration file for the connection password. Repeat for the other passwords, if it's different, and paste it in the configuration as well.
Using the same -pkey <password-key> you used to generate the encrypted password, we'll run hive-sre
hive-sre u3 -all|-hdp2|-hdp3|-cdh -pkey cloudera ...
When the -pkey option is specified WITHOUT the -p option (used previously), hive-sre will understand to decrypt the configuration passwords before connecting to the resources. If you receive jdbc connection exceptions, recheck the -pkey and encrypted password from before.
NOTE: The encrypted password process is shared by u3, sre, and perf. It's not necessary to use different configs or password keys.
If you're not sure the password is correct, copy the 'encrypted' password from the config file and run:
hive-sre u3 -pkey <password-key> -dp <encrypted_password>
For example:
# Encrypt
dstreev@e01 ~ $ hive-sre u3 -pkey cloudera -p have-a-nice-day
APP_DIR: /usr/local/hive-sre/bin
Running Host instance
Application JAVA_OPTS=-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/home/dstreev/bin/certs/gateway-client-trust.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit
PRG_ARGS= "u3" "-pkey" "cloudera" "-p" "have-a-nice-day"
openjdk version "1.8.0_272"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_272-b10)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.272-b10, mixed mode)
Launching: u3
Using Config: /home/dstreev/.hive-sre/cfg/default.yaml
1:Encrypted Password: HD1eNF8NMFahA2smLM9c4g==
# Decrypt
dstreev@e01 ~ $ hive-sre u3 -pkey cloudera -dp HD1eNF8NMFahA2smLM9c4g==
APP_DIR: /usr/local/hive-sre/bin
Running Host instance
Application JAVA_OPTS=-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/home/dstreev/bin/certs/gateway-client-trust.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=changeit
PRG_ARGS= "u3" "-pkey" "cloudera" "-dp" "HD1eNF8NMFahA2smLM9c4g=="
openjdk version "1.8.0_272"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_272-b10)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.272-b10, mixed mode)
Launching: u3
Using Config: /home/dstreev/.hive-sre/cfg/default.yaml
2:Decrypted Password: have-a-nice-day
The output is a set of files with actions and error (when encountered). The files maybe txt files or markdown. You may want to use a markdown viewer for easier viewing of those reports. The markdown viewer needs to support github markdown tables .
Only active processes will show up in the UI. The UI will refresh every second and display the current details below.
There are several 'processes' that are defined in u3. Each process will run 1 or more 'sub-processes'. The counters lists in the UI are specific to the 'process' and 'sub-processes' in that section.
The number of concurrent processes is controlled by the parallelism variable in the configuration yaml defined above.
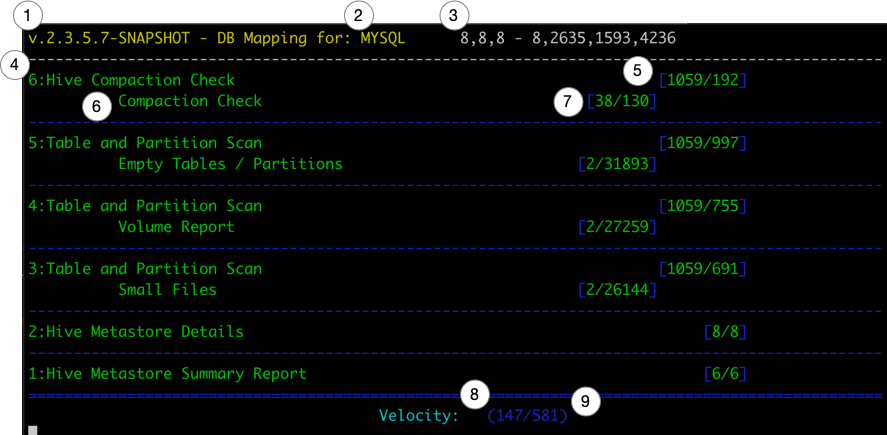
hive-sreversion information- Metastore RDBMS Type
- Thread Status
a,b,c - d,e,f,j- (a) Core Pool Size
- (b) Largest Pool Size
- (c) Max Pool Size
- (d) Active Thread Count
- (e) Completed Thread Tasks
- (f) Remaining Thread Queue
- (j) Total Task Count
- Procedure Name
- Procedure Counts
[Total/Completed]Totalis the full count of all tasks for that processCompletedis the number of tasks this procedure has completed.
- Procedure Check - Child of Procedure
- Procedure Check Counts -
errors/successes - Velocity - Total Time in Seconds process has been running.
- Velocity - The average number of Tasks completed per second since job started.
- Note that not all Tasks are equal. Task times vary based on the content of the cluster and area being inspected. And can largely be effected by Namenode performance.
- Sorting results for loc_scan..
sort -k 1 --field-separator="|" loc_scan_missing_dirs.md > loc_scan_missing_dirs_sorted.txt