Data-driven defect prediction has become increasingly important in software engineering process. Since it is not uncommon that data from a software project is insufficient for training a reliable defect prediction model, transfer learning that borrows data/knowledge from other projects to facilitate the model building at the current project, namely Cross-Project Defect Prediction (CPDP), is naturally plausible. Most CPDP techniques involve two major steps, i.e., transfer learning and classification, each of which has at least one parameter to be tuned to achieve their optimal performance. This practice fits well with the purpose of automated parameters optimization. However, there is a lack of thorough understanding about what are the impacts of automated parameters optimization on various CPDP techniques.
Bearing this consideration in mind, this paper presents the first empirical study that looks into such impacts on 62 CPDP techniques, 13 of which are chosen from the existing CPDP literature while the other 49 ones have not been explored before. We build defect prediction models over 20 real-world software projects that are of different scales and characteristics.
Our major findings are:
Automated parameter optimization substantially improves the defect prediction performance of 77% CPDP techniques with a manageable computational cost. Thus more efforts on this aspect are required in future CPDP studies.
Transfer learning is of ultimate importance in CPDP. Given a tight computational budget, it is more cost-effective to focus on optimizing the parameter configuration of transfer learning algorithms
The research on CPDP is far from mature where it is ‘not difficult’ to find a better alternative by making a combination of existing transfer learning and classification techniques.
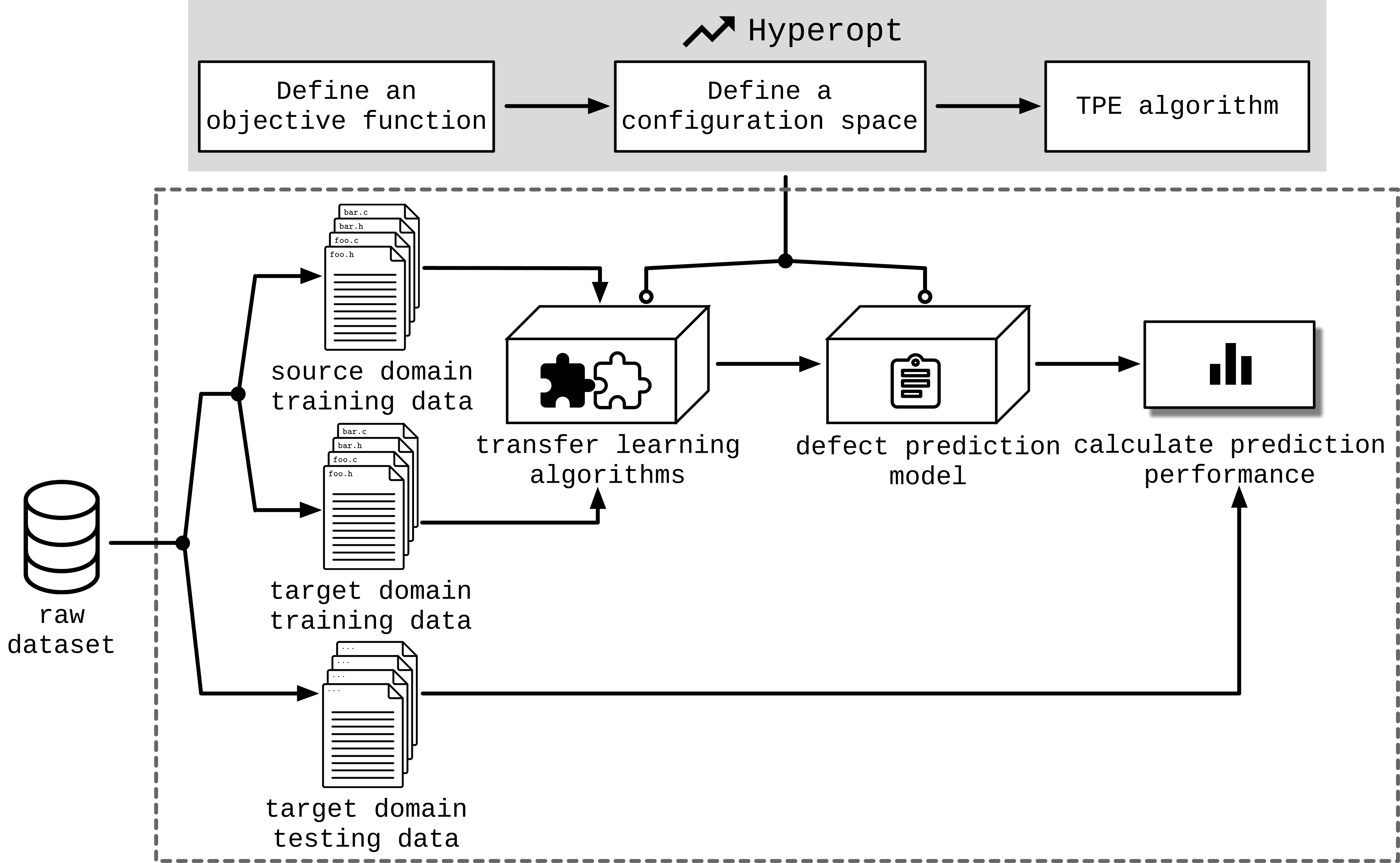
Hyperopt is a Python library that provides algorithms and software infrastructure to optimise hyperparameters of machine learning algorithms. In this project, we use Hyperopt as the optimiser (its basic optimisation driver is hyperopt.fmin) to optimise the parameter configurations of the CPDP techniques. The architecture of our automated parameter optimisation on CPDP model by using Hyperopt is as follows.
- AEEEM
- JURECZKO (12 selected projects)
- ReLink
Python version should be 3.6- Install thrid-party packages (In
Anacaondaenvironment)pip install hyperoptpip install scikit-learn==0.20.4pip install iteration_utilitiesconda install tqdmpip install imbalanced-learn==0.4pip install func_timeout
Please follow
INSTALL.mdbefore starting to run the code.
- Run
code\optADPT.pyto evaluate the impact of parameter optimization on the transfer learning in CPDP. - Run
code\optCLF.pyto evaluate the impact of parameter optimization on the classifier in CPDP. - Run
code\optALL.pyto evaluate the impact of parameter optimization on both transfer learning and classifier in CPDP simultaneously. - Run
code\optSEQ.pyto evaluate the impact of parameter optimization in a sequential manner, i.e., optimising the parameters of transfer learning before those of the classifier.
This code is flexible to any further development.
- If you want to investigate more transfer learning algorithms, please amend
code\Algorithms\domainAdaptation.py. - If you want to investigate more classifiers, please amend
code\Algorithms\Classifier.py - If you want to adapt the calling format, please amend
code\Alogrithms\Framework.py.
If you meet any problems, please feel free to contact us.
- Ke Li (k.li@exeter.ac.uk)
- Zilin Xiang (zilin.xiang@hotmail.com)