This tutorial will loosely follow spaCy's official tutorial.
- Introduction to spaCy
- Installation
- Tokenization
- Stop words
- Lemmatization
- Sentence Segmentation
- Part-of-speech (POS) tagger
- Named entity recognizer (NER)
- Syntactic dependency parser
- Intermediate spaCy
- Word vectors
- Working with big dataset
- Pipelines
- Advanced spaCy
- Using GPU
- Model training
- Transfer learning from BERT (text classifier)
- Annotation with Prodigy
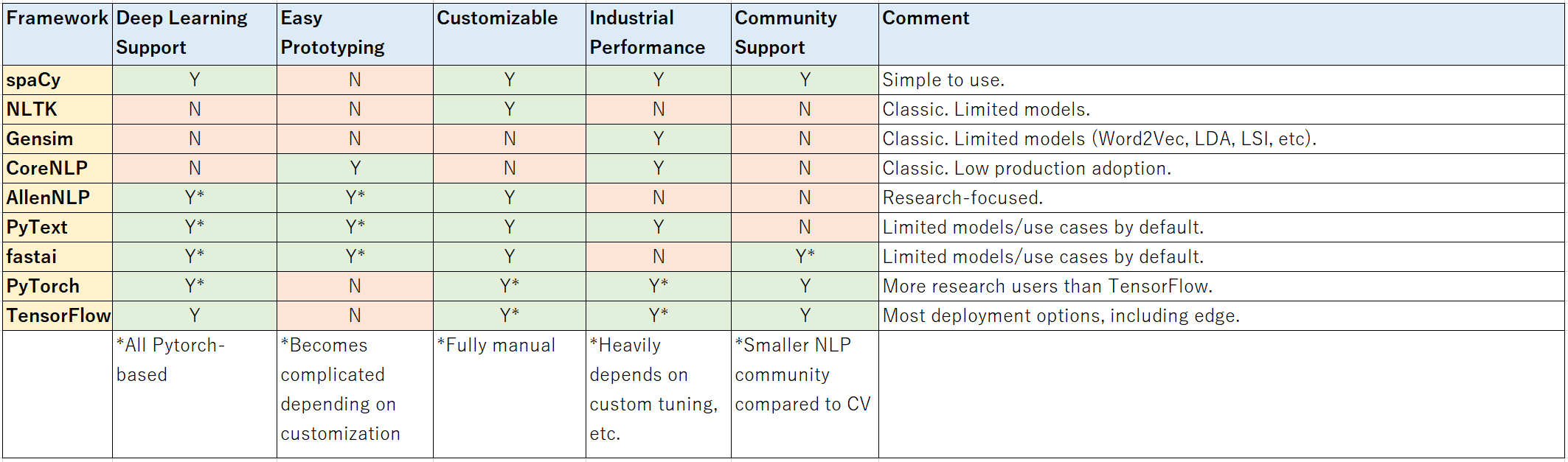
*** Based on my experience. Partially taken from PyText paper
- End-to-end NLP analysis and machine learning
- Preprocessing for downstream analysis and machine learning
- Baseline for more complex custom models
- The following tasks (The ones in bold are recommended tasks):
Automatic speech recognition- Constituency parsing (partially supported)
- Coreference resolution (partially supported)
- Active learning annotation (thru Prodigy)
- Chunking (only noun phrase)
Crossmodal- Data masking (possible with spaCy's models and Matcher)
- Dependency parsing
Dialogue- Entity linking
Grammatical error correction- Information extraction (possible with spaCy's models and Matcher)
- Intent Detection
and Slot Filling - Language modeling (ULMFiT-like language model is experimental)
- Lemmatization
Lexical normalizationMachine translationMissing elementsMulti-task learningMulti-modal- Named entity recognition
- Natural language inference (partially supported)
- Part-of-speech tagging
- Question answering (partially supported)
Relationship extraction- Rule-based Matcher (you don't need a model for this :) )
- Semantic textual similarity
Semantic role labeling- Sentiment analysis
- Sentence segmentation
- Stop words
- Tokenization (character, word, sub-word-level)
Summarization- Text classification
Topic modeling- Word Embedding (standard Word2Vec/GloVe, sense2vec, and contextualized)
- WordNet (partially supported)
このチュートリアルはspaCyの公式チュートリアルとMegagon Labsのスライド、オージス総研の記事を参考にしています。
- spaCy初級
- spaCyとGiNZAのインストール
- トークン化
- ストップワード
- 見出し語化
- 文単位分割
- 品詞(POS)タグ付け
- 固有表現抽出(NER)
- 依存構文解析のラベル付け
- spaCy中級
- 単語ベクトル
- 大規模データ処理
- パイプライン処理
- spaCy上級
- GPUの使用
- モデル学習
- 日本語BERTの転移学習(文書分類)
- Prodigyでのラベル付け
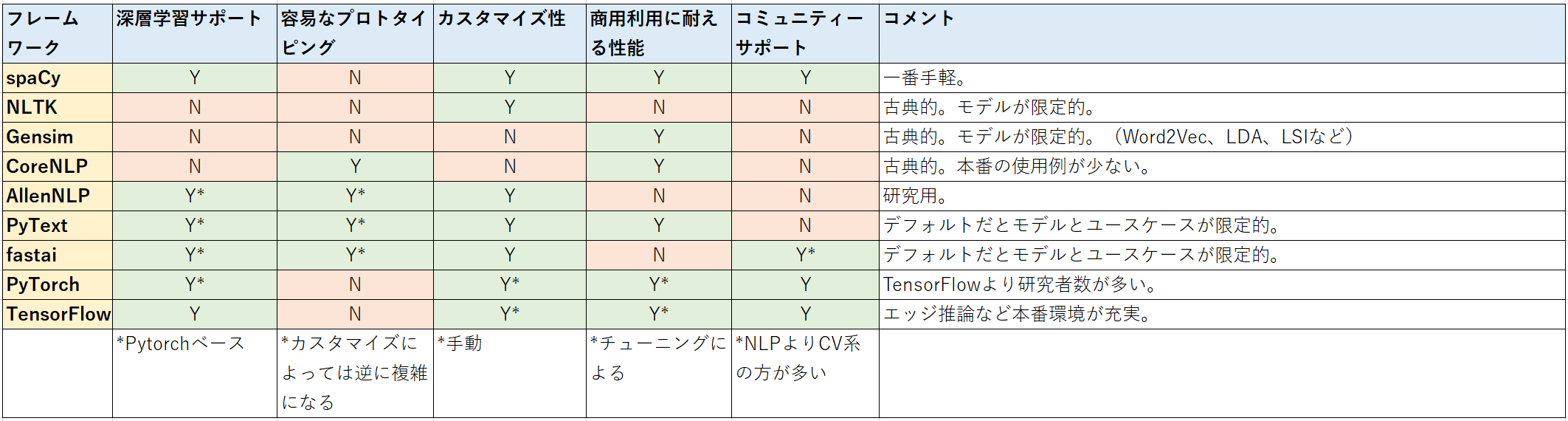
*** 個人的な経験に基づく。PyTextの論文を一部抜粋
- 自然言語の分析から機械学習まで全て
- 下流タスク(分析や機械学習)の前処理
- より複雑なカスタムモデル用のベースライン
- 以下のタスク(太字が推奨タスク):
Automatic speech recognition- Constituency parsing (一部サポート)
- Coreference resolution (一部サポート)
- Active learning annotation (Prodigyで)
- Chunking (名詞句のみ)
Crossmodal- Data masking (spaCyのモデルとMatcherで可能)
- Dependency parsing(依存構文解析のラベル付け)
Dialogue- Entity linking
Grammatical error correction- Information extraction (spaCyのモデルとMatcherで可能)
- Intent Detection
and Slot Filling - Language modeling (ULMFiTのようなLMは試験的)
- Lemmatization(見出し語化)
Lexical normalizationMachine translationMissing elementsMulti-task learningMulti-modal- Named entity recognition(固有表現抽出)
- Natural language inference (一部サポート)
- Part-of-speech tagging(品詞タグ付け)
- Question answering (一部サポート)
Relationship extraction- Rule-based Matcher(ルールベースのマッチング) (モデル不要)
- Semantic textual similarity
Semantic role labeling- Sentiment analysis
- Sentence segmentation
- Stop words(ストップワード)
- Tokenization(トークン化) (character, word, sub-word-level)
Summarization- Text classification(文章分類)
Topic modeling- Word Embedding (通常のWord2VecやGloVe、sense2vec、文脈を考慮した単語ベクトルなど)
- WordNet (一部サポート)