Agile Diffusers Inference (ADI) is a C++ project. Its purpose is to leverage the acceleration capabilities of ONNXRuntime and the high compatibility of the .onnx model format to provide a convenient solution for the engineering deployment of Stable Diffusion.
-
Open Source: ONNXRuntime is an open-source project, allowing users to freely use and modify it to suit different application scenarios.
-
Scalability: It supports custom operators and optimizations, allowing for extensions and optimizations based on specific needs.
-
High Performance: ONNXRuntime is highly optimized to provide fast inference speeds, suitable for real-time applications.
-
Strong Compatibility: It supports model conversion from multiple deep learning frameworks (such as PyTorch, TensorFlow), making integration and deployment convenient.
-
Cross-Platform Support: ONNXRuntime supports multiple hardware platforms, including CPU, GPU, TPU, etc., enabling efficient execution on various devices.
-
Community and Enterprise Support: Developed and maintained by Microsoft, it has an active community and enterprise support, providing continuous updates and maintenance.
- 1. build [ort-sd-clitools] for local using
by simply executing script auto_build.sh:
# if you do not pass the BUILD_TYPE parameter, the script will use the default Debug build type.
# and, if you not enable certain ORTProvider by [options]], script will choose default ORTProvider by platform
bash ./auto_build.sh
# Example-MacOS:
bash ./auto_build.sh --platform macos --build-type debug
# Example-Windows:
bash ./auto_build.sh --platform windows --build-type debug
# Example-Linux(Ubuntu):
bash ./auto_build.sh --platform linux --build-type debug
# Example-Android:
bash ./auto_build.sh --platform android \
--build-type debug \
--android-ndk /Volumes/AL-Data-W04/WorkingEnv/Android/sdk/ndk/26.1.10909125 \
--android-ver 27
# Example(with Extra Options) as below, build release with CUDA=ON TensorRT=ON, and custom compiler configs
bash ./auto_build.sh [params] \
--cmake /opt/homebrew/Cellar/cmake/3.29.5/bin/cmake \
--ninja /usr/local/bin/ninja \
--arch-abi x86_64 \
--jobs 8 \
--options "-DORT_ENABLE_CUDA=ON -DORT_ENABLE_TENSOR_RT=ON"currently, this project provide below [Options]:
option(ORT_COMPILED_ONLINE "ort-sd: using online onnxruntime(ort), otherwise local build" ${SD_ORT_ONLINE_AVAIL})
option(ORT_COMPILED_HEAVY "ort-sd: using HEAVY compile, ${Red}only for debug, default OFF${ColourReset}" OFF)
option(ORT_BUILD_COMMAND_LINE "ort-sd: build command line tools" ${SD_STANDALONE})
option(ORT_BUILD_COMBINE_BASE "ort-sd: build combine code together to build a single output lib" OFF)
option(ORT_BUILD_SHARED_ADI "ort-sd: build ADI project shared libs" OFF)
option(ORT_BUILD_SHARED_ORT "ort-sd: build ORT in shared libs" OFF)
option(ORT_ENABLE_TENSOR_RT "ort-sd: using TensorRT provider to accelerate inference" ${DEFAULT_TRT_STATE})
option(ORT_ENABLE_CUDA "ort-sd: using CUDA provider to accelerate inference" ${DEFAULT_CUDA_STATE})
option(ORT_ENABLE_COREML "ort-sd: using CoreML provider to accelerate inference" ${DEFAULT_COREML_STATE})
option(ORT_ENABLE_NNAPI "ort-sd: using NNAPI provider to accelerate inference" ${DEFAULT_NNAPI_STATE})
enable if you have to (ONLY FOR YOU TRULY NEEDS, UNRECOMMENDED).
- 2. Now, you can use the command-line tools generated by CMake to execute the relevant functionalities of this project
doing 1-step img2img inference, like:
# cd to ./[cmake_output]/bin/ ,like:
cd ./cmake-build-debug/bin/
# and here is an example of using this tool:
# sd-turbo, img2img, positive, inference_steps=1, guide=1.0, euler_a(for 1-step purpose)
./ort-sd-clitools -p "A cat in the water at sunset" -m img2img -i ../../sd/io-test/input-test.png -o ../../sd/io-test/output.png -w 512 -h 512 -c 3 --seed 15.0 --dims 1024 --clip ../../sd/sd-base-model/onnx-sd-turbo/text_encoder/model.onnx --unet ../../sd/sd-base-model/onnx-sd-turbo/unet/model.onnx --vae-encoder ../../sd/sd-base-model/onnx-sd-turbo/vae_encoder/model.onnx --vae-decoder ../../sd/sd-base-model/onnx-sd-turbo/vae_decoder/model.onnx --dict ../../sd/sd-dictionary/vocab.txt --beta-start 0.00085 --beta-end 0.012 --beta scaled_linear --alpha cos --scheduler euler_a --predictor epsilon --tokenizer bpe --train-steps 1000 --token-idx-num 49408 --token-length 77 --token-border 1.0 --gain 1.1 --decoding 0.18215 --guidance 1.0 --steps 1 -v- Below show What actually happened in [Example: 1-step img2img inference] in Latent Space (Skip All Models):
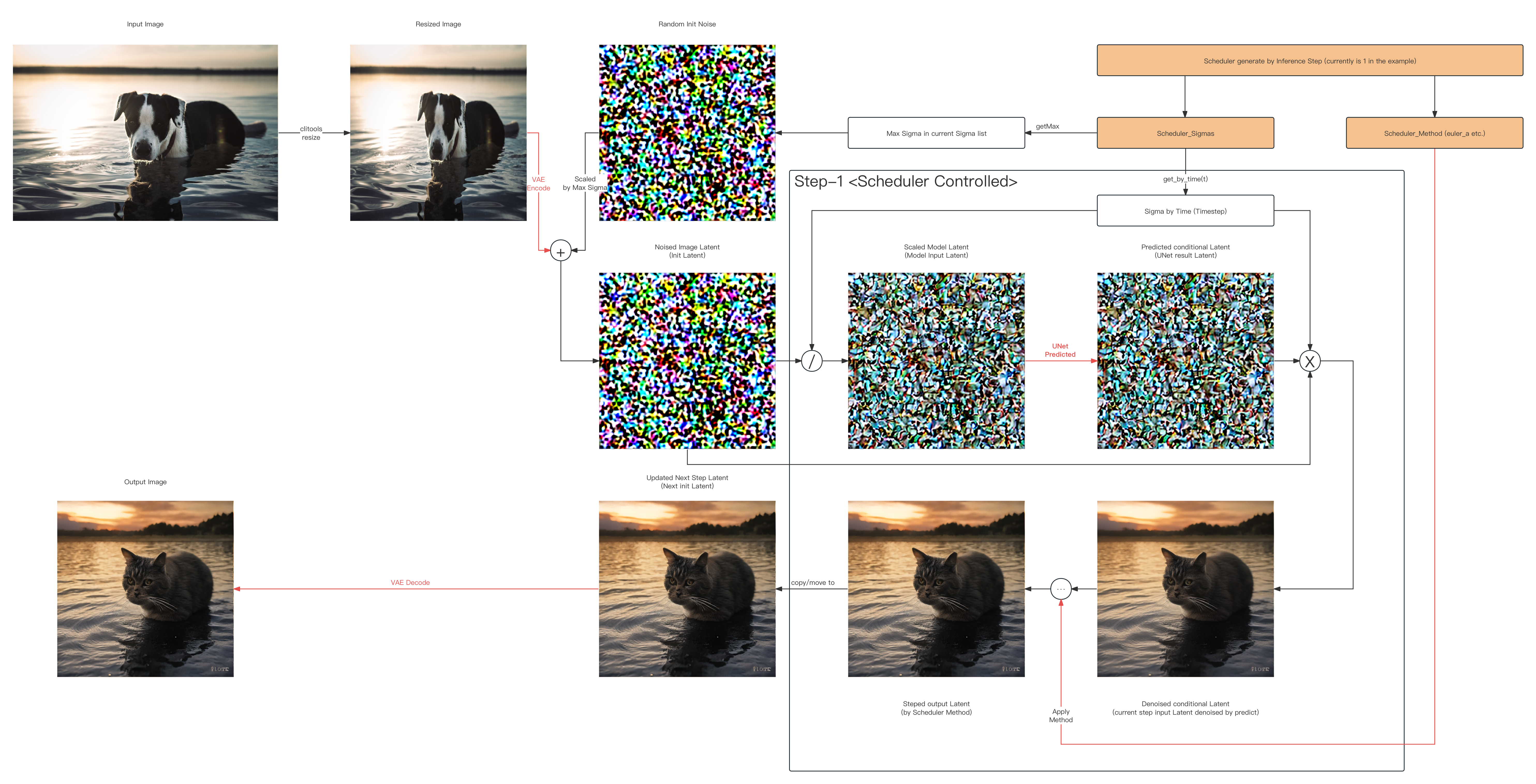
And now, you can have a try~ (0w0 )
-
Manually Prepare Inference Engine, see at: Engine's README.md
-
Manually Prepare ONNX-Format Converter & SD-Models, see at: SD_ORT's README.md
Basic Pipeline Functionalities (Major)
-
[SD_v1] Stable-Diffusion (v1.0 ~ v1.5, turbo) (after 2024/06/04 tested)
- v1.0 (HuggingFace): Initial version ✅
- v1.1 (HuggingFace): Improved image quality and generation speed ✅
- v1.2 (HuggingFace): Further optimized generation effects ✅
- v1.3 (HuggingFace): Added more training data ✅
- v1.4 (HuggingFace): Enhanced image generation diversity ✅
- v1.5 (HuggingFace): Final optimized version ✅
- turbo (HuggingFace): Community-driven optimized version, faster and efficiency ✅
-
[SD_v2] Stable-Diffusion (v2.0, v2.1)
- v2.0 (HuggingFace): Significant improvements in image quality and generation efficiency
- v2.1 (HuggingFace): Further optimized model stability and generation effects
-
[SD_v3] Stable-Diffusion (v3.0)
- v3.0 (HuggingFace): Anticipated next-generation version with more improvements and new features
-
[SDXL] Stable-Diffusion-XL
- SDXL (HuggingFace): Experimental version for larger-scale models and higher-resolution image
- SDXL-turbo (HuggingFace): Community-driven optimized version, faster and efficiency
-
[SVD] Stable-Video-Diffusion
- SVD (HuggingFace): Version specifically for video generation and editing
Scheduler Abilities
-
Strategy
- Discrete/Method Default (discrete) (after 2024/05/22)
- Karras (karras)
-
Sampling Methods
- Euler (euler) (after 2024/06/04 ✅tested)
- Euler Ancestral (euler_a) (after 2024/05/24 ✅tested)
- Laplacian Pyramid Sampling (lms) (after 2024/07/09 ✅tested)
- Latent Consistency Models (lcm) (after 2024/07/04 ✅tested)
- Heun's Predictor-Corrector (heun) (after 2024/07/08 ✅tested)
- Unified Predictor-Corrector (uni_pc)
- Pseudo Numerical Diffusion Model Scheduler (pndm)
- Improved Pseudo Numerical Diffusion Model Scheduler (ipndm)
- Diffusion Exponential Integrator Sampler Multistep (deis_m)
- Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (ddim) (after 2024/07/12 ✅tested)
- Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (ddpm) (after 2024/07/09 ✅tested)
- Diffusion Probabilistic Models Solver in Stochastic Differential Equations (dpm_sde)
- Diffusion Probabilistic Models Solver in Multistep (dpm_m)
- Diffusion Probabilistic Models Solver in Singlestep (dpm_s)
Tokenizer Type
- Byte-Pair Encoding (bpe) (after 2024/07/03 ✅tested)
- Word Piece Encoding (wp) (after 2024/05/27 ✅tested)
- Sentence Piece Encoding (sp) [if necessary]



