We introduce ScaleQuest, a scalable, cost-effective, and novel data synthesis method that utilizes small-size open-source models to generate questions from scratch without the need for seed data with complex augmentation constraints.
We release two question generator models and four problem-solving models.
| Model | Type | MATH | Olympiad Bench | 🤗 HuggingFace Download Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScaleQuest-DeepSeekMath-7B-QGen | question generator | - | - | link |
| ScaleQuest-Qwen2-Math-7B-QGen | question generator | - | - | link |
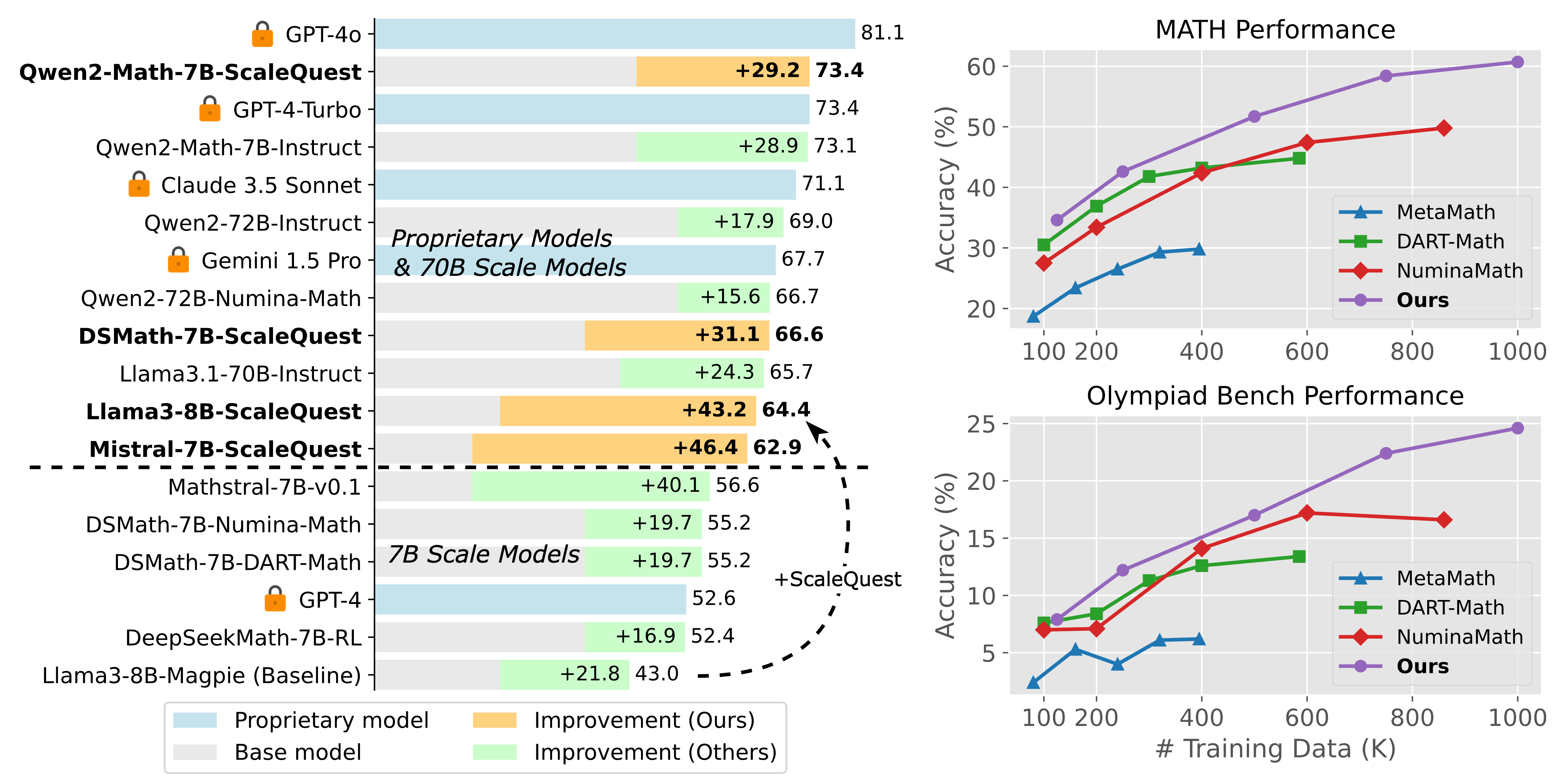
| Mistral-7B-ScaleQuest | problem solver | 62.9 | 26.8 | link |
| Llama3-8B-ScaleQuest | problem solver | 64.4 | 25.3 | link |
| DeepSeekMath-7B-ScaleQuest | problem solver | 66.6 | 29.9 | link |
| Qwen2-Math-7B-ScaleQuest | problem solver | 73.4 | 38.5 | link |
This repository contains our complete data synthesis method, including:
You should install the dependencies:
conda create -n scalequest python=3.11
conda activate scalequest
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolationBelow is an question generator exmaple using ScaleQuest-Qwen2-Math-7B-QGen
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
model_name = "dyyyyyyyy/ScaleQuest-Qwen2-Math-7B-QGen"
pre_query_template = "<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\n"
stop_tokens = ["<|im_start|>", "<|im_end|>", "<|endoftext|>"]
llm = LLM(
model=model_name,
tokenizer=model_name,
tensor_parallel_size=1,
max_model_len=4096,
enable_prefix_caching=True,
trust_remote_code=True,
swap_space=16,
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95,
)
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
n=4,
max_tokens=1024,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.99,
stop=stop_tokens,
)
outputs = llm.generate(pre_query_template, sampling_params)
# Print the outputs.
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
for idx, generated_output in enumerate(output.outputs):
generated_text = generated_output.text
print(f"Sample {idx + 1}:")
print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}")
print(f"Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
print("-" * 50)Below is an problem solver example using Qwen2-Math-7B-ScaleQuest
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "dyyyyyyyy/Qwen2-Math-7B-ScaleQuest"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
question = "Find the value of $x$ that satisfies the equation $4x+5 = 6x+7$."
sys_prompt = "<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n"
query_prompt = "<|im_start|>user" + "\n"
# {query}
prompt_after_query = "\n" + "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}.<|im_end|>" + "\n"
resp_prompt = "<|im_start|>assistant" + "\n"
prompt_before_resp = ""
# {resp}
delim = "<|im_end|>" + "\n"
prefix_prompt = f"{query_prompt}{question}{prompt_after_query}{resp_prompt}{prompt_before_resp}".rstrip(" ")
full_prompt = sys_prompt + delim.join([prefix_prompt])
# print(full_prompt)
inputs = tokenizer(full_prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=512, do_sample=False)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][len(inputs.input_ids[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True))- Training a question generator through question fine-tuning (code in the
src/train_question_generator/qft_trainfolder). - Constructing preference data (code in the
src/train_question_generator/question_optimfolder) and performing question preference optimization (code in thesrc/train_question_generator/qpo_trainfolder).
You can run QFT and QPO by the following command:
cd src/train_question_generator && bash scripts/run_dsmath_qft.sh
cd src/train_question_generator && bash scripts/run_qwen2math_qft.sh- Using the trained question generator to synthesize questions (code in the
src/data_generationfolder). - Applying a filtering process to the generated questions (code in the
src/data_generation/question_filteringfolder).
cd src/data_generation && bash scripts/run.sh- Generating responses (code in the
src/data_generationfolder) - applying a reward filtering strategy (code in the
src/data_generation/reward_filteringfolder).
cd src/data_generation && bash scripts/run.shWe use DART-Math framework for instruction tuning and evaluation.
@article{ding2024unleashing,
title={Unleashing Reasoning Capability of LLMs via Scalable Question Synthesis from Scratch},
author={Ding, Yuyang and Shi, Xinyu and Liang, Xiaobo and Li, Juntao and Zhu, Qiaoming and Zhang, Min},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.18693},
year={2024}
}